Get With The
Guidelines® - Resuscitation PMT® Coding Instructions
Last Updated January 2024
Print Coding Instructions
Table
of Contents
Admission
& Discharge
CPA Event
ARC Event
MET Event
PCAC
Optional Fields
Scoring Definitions
IHCA Site Characteristics
Highlighted Text =
Updated since last version of document
Note about sampling:
Sampling
is not permitted as part of the data entry process. Sites may
choose whether or not to enter CPA events, ARC events, MET events or a
combination of the three, however, within each module, 100% data
capture is required.
Note about optional data elements:
Optional data points appear in the Get With The
Guidelines-Resuscitation Patient Management Tool (PMT) as dark grey
shaded areas. These areas of the PMT contain data abstraction elements
that may be left blank, yet the record may be closed and identified as
complete without an error message. If these data elements contain
information that your facility is not interested in evaluating, you may
elect to not complete them in order to decrease your data abstraction
burden. It is important that you remain consistent in your
decision over time so as to assure the highest degree of data accuracy.
It is recommended that the decision, whether or not to abstract
optional data points, should be made after some thought and consensus
by facility quality improvement staff and should remain in effect for
no less than 3 months at a time.
Date/Time Precisions: Date and
Time fields have an
additional "Precision" drop-down right above the MM/DD/YYYY HH:MI
blanks. The Precision is used to indicate how much of the Date and Time
data is known and can be abstracted.
- The default level is "MM/DD/YYYY HH:MI". This is used if
the entire Date and Time information is available. Time should be
entered in 24hr/Military format.

- If
the time is not documented, first select the check box to the right of
the date/time field called "Time Not Documented". The date/time field
will then select a Precision of "MM/DD/YYYY" for you (only if you check
off "Time Not Documented" first).

Admission
& Discharge
Select MET only check box if entering a patient who only
had one or more MET events. If the MET event resulted in an
ARC /
CPA event or if an ARC or CPA event occurred at another time during the
admission, the MET check box should be unchecked and the remaining
Admission and Discharge information should be entered.
1.1
Admit
System Entry Date/Time
Enter the date and time the patient entered the system, based
on subject type (below). If the time is not available, select “Time
Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Notes for Abstraction:
- Hospital Inpatient – Date/time the
patient was admitted to
the hospital, including direct admissions and admissions through the ED
(used when first event occurs as hospital inpatient).
- Emergency Department- Date/time the patient was admitted/registered into the Emergency Department
- Ambulatory/Outpatient – Date/time
the patient registered in the Ambulatory/Outpatient area.
- Rehab Facility Inpatient* (separate
admission) – Date/time of the event.
- Skilled Nursing Facility Inpatient*
(separate admission) – Date/time of the event.
- Mental Health Facility Inpatient*
(separate admission) – Date/time of the event.
- Visitor or Employee (includes
healthcare personnel and other non-patients) – Date/time of the event.
- Newborn (patients born during this
admission) – Date/time of birth.
- Out
of Hospital Cardiac Arrest (PCAC)– Date/time the
need for chest compression and/or defibrillation was first recognized.
- Transfer
Patients (includes patients that are transferred to your facility from
another acute care hospital for continued management of a cardiac
arrest event) – Date/time the need for chest compression and/or
defibrillation was first recognized for the cardiac arrest event for
which they were transferred to your facility.
*Note:
Some
hospitals have Rehab, Skilled Nursing and/or Mental Health areas or
adjacent facilities to which patients are admitted (separate from
hospital admission) where the code team responds.
Date of Birth
Enter the patient’s date of birth. If unknown, select “Unknown/Not
Documented.”
Date/Time of Birth
Enter the patient’s date and time of birth. If DOB unknown or
not documented, select “DOB Unknown/Not Documented", if
time is unknown select "Time Not Documented." Note: In the online form, time is only available for response if the patient is "born this admission (or transferred from birth hospital)."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Age at System Entry
Enter the age of the patient at the time of system entry and
indicate “minute(s)”, “hours(s)”, “day(s)”, “week(s)”,
“month(s)”, or “year(s)”. If “Date
of Birth” and “System Entry Date” have
been provided, the age will be automatically derived.
Estimated
Select if age is estimated by hospital staff. If age is not
documented and CANNOT be estimated, select “Age Unknown/Not
Documented.”
Born this admission or transferred from birth
hospital?
Was patient born during this admission or transferred from
the hospital where birth occurred.
Note:
This question is asked when patient is ≤ 1 year
of age at system entry.
Patient Gender Identity
The gender identity, self-identified by the patient. This may or may not match sex assigned at birth.
- Male
- Female
- Female-to-Male (FTM)/Transgender Male/Trans Man
- Male-to-Female (MTF)/Transgender Female/Trans Woman
- Genderqueer, neither exclusively male nor female
- Additional gender category or other: _________________
- Did not disclose
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Female-to-Male (FTM)/Transgender Male/Trans Man" if the patient was assigned the female sex at birth but currently identifies on the male spectrum. (Also known as a transgender man).
- Select "Male-to-Female (MTF)/Transgender Female/Trans Woman" if the patient was assigned the male sex at birth but identifies on the female spectrum. (Also known as a transgender woman).
- Select "Genderqueer, neither exclusively male nor female" if the patient's sex identity and/or gender expression falls outside the binary categories of male or female. Patient may define their sex as falling somewhere in between male and female, or they may define it as wholly different from these terms.
- Select "Additional gender category or other. ________" if the patient self-identifies with any other gender that is not listed above, then specify in the blank section provided.
Suggested
Data Sources:
- Admission Notes
- Referral notes
Patient-Identified Sexual Orientation
The self-reported sexual orientation of the patient. Also defined as the gender(s) to which a person is physically attracted.
- Straight or heterosexual
- Lesbian or gay
- Queer, pansexual, and/or questioning
- Something else; please specify: _________________
- Don't know
- Declined to answer
Notes for Abstraction:
- Straight or heterosexual - Select this option if the patient reports an orientation of sexual attraction to members of the opposite sex.
- Lesbian or gay - Select this option if the patient reports an orientation of sexual attraction to members of the same sex.
- Queer, pansexual, and/or questioning - Select this option if the patient reports any of the given options:
- Pansexual - Refers to a person who is sexually and/or romantically attracted to persons of any gender identity and/or biological sex. Pansexual people may also refer to themselves as gender-blind.
- Queer - Refers to a person whose attractions and/or romantic relationships are not heterosexual or whose gender identities are not the same as those assigned at birth.
- Questioning - This describes someone who is questioning their sexual orientation or gender identity.
Suggested
Data Sources:
Admission Notes
Referral notes
Race
Select
the patient’s self-assessed race/ethnicity, or if not available, the
physician or institution’s assessment. Assumptions should not be made
based on physical characteristics. This data allows for analysis of
race-related patterns of care. If patient is multi-racial, select each
race they designate. Select all that apply from the list provided. Select all that apply from the list
provided. If the patient is Asian or Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander,
select the specific sub-category (or sub-categories) of race if known.
Selection of a race sub-category is optional.
Options
include:
- American
Indian/Alaska Native - A person having origins in any of the
original peoples of North and South American (including Central
America) and who maintains tribal affiliation or community attachment
(e.g., any recognized tribal entity in North and South America
(including Central America), Native American).
- Asian
- A person having origins in any of the original peoples of
the Far East, southeast Asia, or the Indian subcontinent,
including for example, India, China, Philippines, Japan, Korea,
Vietnam, or Other including, but not limited to Cambodia, Malaysia,
Hmong, and Thailand. If Asian, select the specific
sub-category (or sub-categories). Select all that apply from the list
provided.
- Asian
Indian
- Chinese
- Filipino
- Japanese
- Korean
- Vietnamese
- Other
Asian: The patient identified as some other Asian
sub-category not provided in the options above or did not identify a
sub-category.
- Black
or African American - A person having origins in any of the
black racial groups of Africa. Terms such as “Haitian” or “Negro” can
be used in addition to “Black or African American”.
- Native
Hawaiian/Pacific Islander - A person having origins in any
of the other original peoples of Hawaii, Guam or Mariana Islands,
Samoa, or other Pacific Islands. If Native Hawaiian/Pacific
Islander, select the specific sub-category (or sub-categories). Select
all that apply from the list provided.
- Native
Hawaiian
- Guamanian
or Chamorro
- Samoan
- Other
Pacific Islander: The patient identified as some other Native
Hawaiian/Pacific Islander subcategory not provided in the options above
or did not identify a subcategory.
- White
– Patients race is White or a person having origins in in any
of the original peoples of Europe, Middle East or North Africa (e.g.,
Caucasian, Iranian, White)
- UTD
(Unable to determine) – Unable to determine the
patient’s race or not stated (e.g., not documented, conflicting
documentation or patient unwilling to provide).
Notes for Abstraction:
- The
data element, Hispanic Ethnicity, is required in addition to this data
element.
- Although the terms "Hispanic" and "Latino" are actually descriptions of the patient’s ethnicity, it is not uncommon to find them referenced as race. If the patient’s race is documented only as Hispanic/Latino, select "White". If the race is documented as mixed Hispanic/Latino with another race, use whatever race is given (e.g., Black-Hispanic - select "Black"). Other terms for Hispanic/Latino include Chicano, Cuban, H(for Hispanic), Latin American, Latina, Mexican, Mexican-American, Puerto Rican, South or Central American, and Spanish.
- If the Asian or Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander patient does not identify a subcategory, leave the sub-category blank.
Hispanic Ethnicity
Documentation
that the patient is of Hispanic ethnicity or Latino.
In addition to the Yes and No/UTD response options,
there is the ability to select specific sub-choices of Mexican/Mexican
American/Chicano, Puerto Rican, Cuban, or Another
Hispanic/Latino/Spanish Origin.
- Yes:
Patient is of Hispanic ethnicity or Latino.
- No/UTD:
Patient is not of Hispanic ethnicity or Latino or unable to determine
from medical record documentation.
The
data element, Race, is required in addition to
this Hispanic Ethnicity data element.
Suggested
Data Sources:
- Emergency
department record
- Face
sheet
- History
and physical
- Nursing
admission assessment
- Progress
notes
Inclusion
Guidelines for Abstraction: A person of Cuban, Mexican,
Puerto Rican, South or Central American, or other Spanish culture or
origin, regardless of race is to be considered of Hispanic or
Latino ethnicity. The term "Spanish origin" can be used in
addition to "Hispanic or Latino."
Examples:
- Black-Hispanic
- Chicano
- H
- Hispanic
- Latin
American
- Latino/Latina
- Mexican-American
- Spanish
- White-Hispanic
Exclusion
Guidelines for Abstraction:
None
OPTIONAL:
If yes,
If
the patient is of Hispanic ethnicity or Latino, select the specific
sub-category (or sub-categories) identified by the
patient.
- Mexican,
Mexican American, Chicano/a
- Puerto
Rican
- Cuban
- Another
Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish Origin: The patient identified as some
other Hispanic, Latino or Spanish origin not provided in the options
above.
Notes for
Abstraction: If the patient did not identify a
subcategory, leave this field blank
Canada Coding Instructions
DEMOGRAPHICS
Sex
Sex
Definition: The patient's biological and physiological status on arrival at the site.
Variable Name: sex
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- Collect the documented patient's sex at admission or the first documentation after arrival.
- Consider the sex to be unable to be determined and select "Unknown" if:
- The patient refuses to provide their sex.
- Documentation is contradictory.
- Documentation indicates the patient is a Transsexual.
- Documentation indicates the patient is a Hermaphrodite.
- Documentation indicates the patient is Non-binary
Suggested Data Sources:
- Registration Form
- Admission Notes
- Referral Notes
Gender
Definition: The gender identity, self-identified by the patient. This may or may not match sex assigned at birth.
Variable Name: patgenid
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Male
- Female
- Gender diverse
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Gender diverse" if the patient's sex identity and/or gender expression falls outside the binary categories of male or female. Patient may define their sex as falling somewhere in between male and female, or they may define it as wholly different from these terms.
Suggested Data Sources:
- Admission Data
- Care Plans
- Transfer Notes
- History and Physical
- Emergency Department Records
Date of Birth
Definition: The month, day, and year the patient was born.
Variable Name: dob
Format: Date (MM/DD/YYYY)
Allowable Values:
- MM = Month (01-12)
- DD = Day (01-31)
- YYYY = Year (1880 - Current Year)
Notes for Abstraction:
- Since this data element is critical in determining the population for all measures, the abstractor should NOT assume that the claim information for the birthdate is correct. If the abstractor determines through chart review that the date is incorrect, she/he should correct and override the downloaded value. If the abstractor is unable to determine the correct birthdate through chart review, she/he should default to the date of birth on the claim information.
Suggested Data Sources:
- Registration Form
- Admission Notes
- Referral Notes
Patient Postal Code
Definition: The zip/postal code of the patient's residence. For United States Zip Codes, the hyphen is implied.
Variable Name: capostalcode
Format: Text
Allowable Values:
- Numerical Value
- Alpha-Numeric Combination dependent on patients' residence
Notes for Abstraction:
- If the patient is determined to not have a permanent residence, then the patient is considered homeless and Homeless should be checked.
- If the patient resides in another country, the zip or postal code from that country should be entered as a string of alpha-numeric characters (e.g. The zip code for a patient who lives in Bras d'Or, Canada should have their zip code entered as, "B1Y3X9" with no spaces.
Suggested Data Sources:
- Registration Form
- Admission Notes
Province or Territory
Definition: The province or territory that patient resides.
Variable Name: -
Format: Single select
Allowable Values:
- Alberta
- British Columbia
- Manitoba
- New Brunswick
- Newfoundland and Labrador
- Nova Scotia
- Ontario
- Prince Edward Island
- Quebec
- Saskatchewan
- Northwest Territories
- Nunavut
- Yukon
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select one of the provinces or territories where the patient claims to have full-time residency.
Suggested Data Sources:
- Registration Form
- Admission Notes
Race and Ethnicity
Race
Definition: The patient's self-assessed race/ethnicity, or if not available, the physician or institution's assessment of the patient's race. Assumptions should not be made based on physical characteristics. This data allows for analysis of race-related patterns of care. If patient is multi-racial, select each race they designate.
Variable Name: race
Format: Multi-Select
Allowable Values:
- Black
- East/Southeast Asian
- Indigenous
- First Nations
- Métis
- Inuk/Inuit
- Prefer not to answer
- Latino
- Middle Eastern
- South Asian
- White
- Another race category
- Do not know
- Prefer not to answer
Notes for Abstraction:
- If the patient is Indigenous, select the specific sub-category (or sub-categories) of race if known. If a subcategory is not documented, leave the sub-category options blank.
Suggested Data Sources:
- ED Record
- Admission Notes
- Registration form
Birth Weight (patients <30 days old only)
For patients that are less than 30 days old at the time of system entry date, enter the patient's birth weight. Indicate "pounds", "kilograms", or "grams." If the patient's birth weight is not documented, select "Unknown/Not Documented."
Weight same as birth weight
For patients that are less than 30 days old at the time of system entry date, if the weight at admission is the same as the birth weight, check off this box. This will auto-populate the subsequent "Weight" data element.
Weight (required for pediatric and newborn/neonate patients only)
Enter the patient’s weight at the time of the first (or index) event and indicate "pounds",
“kilograms”, or “grams”. If
the patient’s weight is not known, select “Unknown/Not
Documented.”
This
data element is only required for patients less than 18 years of age.
Length (patients <30 days old only)
For patients that are less than 30 days old at the time of system entry date, enter the patient's length. Indicate "inches" or "centimeters." If multiple lengths are documented, enter the first documented length. If length is not documented, select "Unknown/Not Documented."
Head Circumference (patients <30 days old only)
For patients that are less than 30 days old at the time of system entry date, enter the patient's head circumference. Indicate "inches" or "centimeters." If multiple head circumference measurements are documented, enter the first documented head circumference. If head circumference is not documented, select "Unknown/Not Documented."
Admission
CPC
Admission
PCPC
Using the CPC/PCPC Scale (see Scoring
Definitions),
enter the patient’s Cerebral Performance Category (Adults – Age
>
18) or Pediatric Cerebral Performance Category (Pediatrics – Age
<
18). If the CPC/PCPC is not documented AND cannot
be calculated from information in medical record, select the “Unknown/Not
Documented” option. The intent of this data element is to determine the patient’s cognitive function prior to the index event.
Admission scoring is based on the following:
- Hospital Inpatients : Time of
hospital admission.
- ED Patients : Time of ED admission.
- Ambulatory/Outpatient : Time of
ambulatory registration.
- Newborns age greater than 24 hr :
Immediately prior to event.
- Newborns in the delivery room and/or age less
than 24 hr : No score should be entered.
- Rehab facility, SNF, Mental Health inpatients
(separate admission) : Immediately prior to event.
- Visitor/Employee : Immediately prior
to event.
Adult Cerebral Performance Categories/CPC Scale
The Adult CPC scale is defined by the following:
- CPC 1
: Good cerebral performance* – Conscious, alert, able to
work, might have mild neurologic or psychologic deficit.
- CPC 2
: Moderate cerebral disability* – conscious, sufficient
cerebral function for independent activities of daily life. Able to
work in sheltered environment.
- CPC 3
: Severe cerebral disability
– Conscious, dependent on others for daily support because of impaired
brain function. Ranges from ambulatory state to severe dementia or
paralysis.
- CPC 4
: Coma or vegetative state
– Any degree of coma without the presence of all brain death criteria.
Unawareness, even if appears awake (vegetative state) without
interaction with environment; may have spontaneous eye opening and
sleep/awake cycles. Cerebral unresponsiveness.
- CPC 5
: Brain death – Apnea, areflexia, EEG silence, etc.
Pediatric/Neonate Cerebral Performance
Categories/PCPC Scale
The pediatric/neonate PCPC scale is defined by the following:
- PCPC 1
: Normal - Age-appropriate level of functioning; preschool
child developmentally appropriate; school-age child attends regular
classes.
- NEONATE
: Normal - No obvious neurological abnormalities.
- PCPC 2
: Mild cerebral disability
- Able to interact at an age-appropriate level; minor neurological
disease that is controlled and does not interfere with daily
functioning (e.g., seizure disorder that is well controlled with
medication); preschool child may have minor developmental delays, but
more than 75% of all daily living developmental milestones are above
the 10 th percentile; school-age child attends regular school, but
grade is not appropriate for age, or child is failing appropriate grade
because of cognitive difficulties.
- NEONATE
: Mild cerebral disability
- Minor neurological abnormality; neurological disease that is
controlled and does not interfere with daily functioning (e.g., seizure
disorder that is well controlled with medication).
- PCPC 3
: Moderate cerebral disability
- Below age-appropriate functioning; neurological disease that is not
controlled and severely limits activities; most activities of preschool
child’s daily living developmental milestones are below the 10th
percentile; school-age child can perform activities of daily living,
but attends special classes because of cognitive difficulties and/or
has a learning deficit.
- NEONATE
: Moderate cerebral disability
- Neurological disease that is not controlled (e.g., breakthrough
seizures despite medications which affect responsiveness to
environment).
- PCPC 4
: Severe cerebral disability
- Preschool child’s activities or daily living milestones are below the
10th percentile, and child is excessively dependent on others for
provision of activities of daily living; school-age child may be so
impaired as to be unable to attend school; school-age child is
dependent on others for provision of activities of daily living;
abnormal motor movements for both preschool and school-age child may
include non-purposeful, decorticate, or decerebrate responses to pain.
- NEONATE
: Severe cerebral disability
- Obvious severe neurological disorder: Abnormal motor movements may
include non-purposeful, decorticate or decerebrate response to pain.
- PCPC 5
: Coma or vegetative state - Coma; unawareness.
- NEONATE
: Coma or vegetative state - Coma; unawareness.
- PCPC 6
: Brain death
- NEONATE : Brain death
Examples:
- 70 year old patient admitted to your facility with pneumonia. The patient’s medical history states that prior to this admission the patient had no known issues; he was living alone at home and was working 40 hours a week at the same job he has held for the past 30 years. Enter a CPC of 1.
- 18 month old patient with hypoplastic left heart admitted to your facility for repair. Patient suffers a post-op cardiac arrest event. Child Life Specialist documented in the medical record that prior to this admission the patient had minor developmental delays as well as a seizure disorder that was controlled with medication. Enter PCPC of 2.
- 45 year old patient admitted to an outside hospital for an elective surgical procedure presents to your hospital for further management. Prior to this admission, the patient had no known deficits. The patient was awake, alert, and oriented without diminished cognitive function at the outside hospital just prior to experiencing respiratory distress requiring intubation. Patient experiences a cardiac arrest event on day 3 of admission to your facility. Enter CPC of 1 as this is indicative of the patient’s cognitive function prior to suffering respiratory distress at the outside facility.
Vaccinations & Testing
- COVID-19 Vaccination
- COVID-19 Vaccination Date
- COVID-19 Vaccine Manufacturer
- Did the patient receive both doses of vaccine? (if applicable)
- Is there documentaton that this patient was included in a COVID-19 vaccine trial?
- Influenza Vaccination
COVID-19 Vaccination
Collected For: GWTG
Definition: Documentation whether or not the patient received a COVID-19 vaccination.
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- COVID-19 vaccine was given during this hospitalization.
- COVID-19 vaccine was received prior to admission, not during this hospitalization.
- Documentation of patient's refusal of COVID-19 vaccine
- Allergy/ sensitivity to COVID-19 vaccine or if medically contraindicated
- Vaccine not available
- None of the above/ Not documented/ UTD.
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select the response that best fits the patient's vaccination status.
- If a patient received the vaccine as part of a COVID-19 vaccine trial, then select the appropriate option above (during hospitalization or Prior to hospitalization) and document "Yes" for the question below, "Is there documentation that this patient was included in a COVID-19 vaccine trial?".
- If the patient has tested positive for another infectious disease that disqualifies them from receiving a COVID-19 vaccination, the option "Allergy/sensitivity to COVID-19 vaccine or if medically contraindicated" should be selected.
Suggested Data Sources:
- Admission Data
- Discharge Data
Additional Notes / Guidelines for Abstraction: N/A
COVID-19 Vaccination Date
Collected For: GWTG
Definition: Documentation of the date of the COVID-19 vaccination. This refers to the date when the COVID-19 vaccination was administered.
Variable Name: covidvaccdt
Format: Date (MM/DD/YYYY)
Allowable Values:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- MM = Month (01-12)
- DD = Day (01-31)
- YYYY = Year (2012 - Current Year)
- Unknown
Notes for Abstraction:
- Only report the date the vaccine was given if it was administered during this hospitalization.
- Document the Date of the first dose of vaccine administration
- Select "Unknown" if the date is not documented.
Suggested Data Sources:
Additional Notes / Guidelines for Abstraction: N/A
COVID-19 Vaccination Manufacturer
Collected For: GWTG
Definition: Documentation of the manufacturer of the COVID-19 vaccine.
Question For: Who was the manufacturer of the COVID-19 vaccine?
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- AstraZeneca
- Johnson & Johnson's / Janssen
- Moderna
- Novavax
- Pfizer
- Other
- Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
Suggested Data Sources:
Additional Notes / Guidelines for Abstraction: N/A
Did the patient receive both doses of vaccine? (if applicable)
Collected For: GWTG
Definition: Documentation that the patient received both doses of a two-dose COVID-19 vaccine.
Question For: Did the patient receive both doses of vaccine? (if applicable)
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "No" if the patient has received only one dose of a two-dose COVID-19 vaccine.
- Select "Not applicable" if the COVID-19 vaccine the patient received only requires one dose (e.g., Johnson & Johnson's / Janssen).
Suggested Data Sources:
Additional Notes / Guidelines for Abstraction: N/A
Is there documentation that this patient was included in a COVID-19 vaccine trial?
Collected For: GWTG
Definition: Documentation of if the patient was included in a COVID-19 vaccine trial.
Variable Name: covidvaccdoc
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
Suggested Data Sources:
- Admission Data
- Hospitalization Data
Influenza Vaccination
Collected For: GWTG
Definition: Documentation whether or not the patient received an influenza vaccination.
Variable Name: fluvacc
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Influenza vaccine was given during this hospitalization during the current flu season.
- COVID-19 vaccine was received prior to admission during the current flu season, not during this hospitalization.
- Documentation of patient's refusal of influenza vaccine
- Allergy/ sensitivity to influenza vaccine or if medically contraindicated
- Vaccine not available
- None of the above/ Not documented/ UTD.
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select the response that best fits the patient's vaccination status.
- If the patient has tested positive for COVID-19 or another infectious disease that disqualifies them from receiving a flu vaccination, the option "Allergy/sensitivity to COVID-19 vaccine or if medically contraindicated" should be selected.
Suggested Data Sources:
Table of Contents
1.2
Newborns/Neonates
Note:
The following section is required for patients born during this
admission or transferred from delivering hospital.
Did mother receive prenatal care?
- Yes: There is documentation in the medical record that the mother received prenatal care.
- No: There is documentation in the medical record that the mother did not receive prenatal care.
- Not Documented: There is no mention of prenatal care in the medical record.
Maternal conditions (check all that apply):
Enter any documented maternal conditions. Valid entries:
- None
- Alcohol exposure
- Chorioamnionitis
- Cocaine/crack use
- Diabetes
- Eclampsia
- GHTN (Pregnancy Induced Hypertension/Gestational
Hypertension)
- Magnesium exposure
- Major trauma
- Maternal Group B Strep (Positive)
- Maternal infection
- Methamphetamine/ICE use
- Narcotic given to mother within 4 hours of
delivery
- Narcotics addiction and/or on methadone
maintenance
- Pre-eclampsia
- Prior Cesarean
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Other (specify)
Fetal monitoring
Indicate if fetal monitoring was present and, if so, which
type.
- External
- Internal
- Performed, method unknown
- Unknown/Not Documented: There is no documentation of fetal monitoring in the medical record.
- None: There is documentation that no fetal monitoring was present.
Delivery mode
Enter the mode of delivery:
- Vaginal/Spontaneous
- Vaginal/Operative (e.g., vacuum,
forceps)
- VBAC: vaginal birth after caesarean
- Cesarean Section (C-section)/Scheduled
- Cesarean Section (C-section)/Emergent
- Unknown/Not Documented
Delivery presentation
Enter the presentation at delivery:
- Cephalic
- Breech
- Unknown/Not documented
Best estimate of gestational age (weeks)
Enter the best estimate of gestational age in weeks. If not
available, select “Not Documented.”
Apgar
Enter the 1 Minute Apgar score. If no 1 minute Apgar score is documented or there is documentation that one was not assigned, select "Unknown/Not assigned."
Enter the 5 Minute Apgar score. If no 5 minute Apgar score is documented or there is documentation that one was not assigned, select "Unknown/Not assigned."
Enter the 10 Minute Apgar score. If no 10 minute Apgar score is documented or there is documentation that one was not assigned, select "Unknown/Not assigned."
Enter the 15 Minute Apgar score. If no 15 minute Apgar score is documented or there is documentation that one was not assigned, select "Unknown/Not assigned."
Enter the 20 Minute Apgar score. If no 20 minute Apgar score is documented or there is documentation that one was not assigned, select "Unknown/Not assigned."
Cord pH
Enter the cord pH. If not documented, select " Unknown/Not Documented."
Also select the location from where the cord pH was drawn. Choose from "arterial," "venous," or "unknown/not documented."
Special circumstances recognized at birth
Enter any special circumstances recognized at birth. Where applicable, for each circumstance selected, answer whether the diagnosis was made prior to birth (prenatal or antenatal) or after birth (postnatal).
- None: Select "None" if there is no documentation of special circumstances recognized at birth.
- Abdominal Wall Defects, such as:
- gastroschisis
- omphalocele
- ectopia cordis
- limb-body wall complex
- cloacal exstrophy
- urachal cyst
- Congenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation/Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation (CCAM/CPAM)
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia, (CDH) such as:
- Bochdalek hernia
- Morgagni hernia
- Diaphragm eventration
- Central tendon defects of the diaphragm
- Acyanotic Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality
, such as
- Aortic Stenosis
- Coarctation of the Aorta
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
- Septal Defects
- Cyanotic Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality
, such as
- Tetralogy of Fallot (TET)
- Total Anolmalous Pulmonary Venous Connection (TAPVC or
TAPVR)
- Hypoplastic Left Heart
- Transposition of the Great Vessels
- Congenital Malformation/Abnormality (non-cardiac)
, such as
- Truncus Arteriosus
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Tracheal-esophageal fistula
- Known/suspected chromosomal/genetic abnormality – (e.g.,
trisomy 21, 13, 18)
- Cord Prolapse
- Decelerations
- Fetal Hydrops
- Meconium Aspiration
- Multiple Gestations
- Nuchal Cord
- Placenta Abruption
- Placenta Previa
- Shoulder Dystocia
- Other Special Circumstances (specify)
Table of Contents
1.3 Induced Hypothermia
Was induced hypothermia initiated?
- Yes: Induced hypothermia (active cooling) was initiated for cardiac arrest
- No/Not Documented: Induced hypothermia (active cooling) was not initiated in a patient that had a cardiac arrest event or cannot be determined from medical record documentation.
- NA (Not Applicable): Patient did not suffer a cardiac arrest event
Notes for Abstraction:
- Active cooling is intentional, controlled reduction of a patient’s core temperature to a target of 32-34 degrees Celsius and includes the terms therapeutic hypothermia, induced hypothermia, targeted temperature management.
- If active cooling was started but terminated prior to achieving target temperatures select “Yes”.
- If the "MET-only Admission" check box is checked off, N/A will be auto-populated in the online form for this field.
1.4
Discharge
Discharge Status
- Dead
- Alive
- Disposition Pending
Note: Record will close
and transmit to the Get With The Guidelines® - Resuscitation registry if disposition is pending.
However, final Discharge Disposition is required and should be entered
when death or discharge has occurred.
Element: During this admission, was a standardized health related social needs form or assessment completed?
Definition: Indicate if there is any documentation in the medical record that the patient was asked about or reported any potential barriers or circumstances that might make it difficult or impossible to access health care services for follow up after discharge.
Variable Name: socdetassess
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- This may be completed using a standardized screening tool or the information may be collected through patient discussion.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Element: If yes, identify the areas of unmet social needs (select all that apply):
Definition: Select the barrier(s) that were identified preventing or limiting the patient's ability to receive further health care services.
Variable Name: socdetareas
Format: Multi-Select
Allowable Values:
- None
- Education
- Employment
- Financial Strain
- Food
- Living Situation/Housing
- Mental Health
- Personal Safety
- Substance Use
- Transportation Barriers
- Utilities
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "None of the areas of unmet social needs listed were identified" if no barriers were identified, or when the medical record documentation does not indicate a barrier.
- If the patient is under 18 years old, apply the responses from a parent or guardian.
- For all tools used to assess social determinants of health, use the following descriptions that closely aligns with your tool's questions/questionnaires:
- Education: Any description that fits the ICD-10 Code Z-55, including but not limited to the problems/risk factors such as Illiteracy, schooling unavailable, underachievement in a school, less than a high school diploma, no general equivalence degree (GED), educational maladjustment, and discord with teachers and classmates.
- Employment: Any description that fits the ICD-10 Code Z-56 including but not limited to unemployment, threat of job loss, stressful work schedule, discord with boss and workmates, uncongenial work environment, sexual harassment on the job, and military deployment status.
- Financial Strain: Patients with any record of financial strain that makes it hard for them to pay for their basic needs like food, housing, medical care, and heating or utility.
- Food: A patient with any record of food insecurity (in the preceding 12 months) e.g.,
- That their food would run out before they got money to buy more, or
- Being without reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, nutritious food, or
- Having limited or uncertain access to adequate food, or
- The food they bought just did not last and they didn�t have money to get more, or
- Experiencing hunger and having concerns regarding the ability to get the next meal.
Additional definition of "Food Insecurity" by US Dept. of HHS:
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) divides food insecurity into the following 2 categories:
- Low food security: "Reports of reduced quality, variety, or desirability of diet. Little or no indication of reduced food intake."
- Very low food security: "Reports of multiple indications of disrupted eating patterns and reduced food intake."
Food insecurity may be long term or temporary. It may be influenced by a number of factors, including income, employment, race/ethnicity, and disability.
- Living Situation/Housing: A patient with a record indicating any of the following (in the preceding 12 months): that
- They do NOT have a steady place to live (they may be temporarily staying with others, in a hotel, in a shelter, living outside on the street, on a beach, in a car, abandoned building, bus or train station, or in a park).
- For those that have a stable place to live, there could be significant concerns/challenges such as lead paint or pipes, or water leaks, etc.
- Any other description closely aligning with ICD-10 Code Z-59 .
- Mental Health: Patients having difficulty doing errands alone such as visiting a doctor's office or shopping due to a mental or emotional condition.
- Personal Safety: Patient with a record of being physically hurt by anyone close to them including family and/or friends. Additionally, any incidence of family/friend threatening them with harm, insult or talk them down, scream, or curse at them should be considered here.
- Substance Use Disorder: Patients who have in the preceding 12 months:
- Had 5 or more drinks in a day (males) or 4 or more drinks in a day (females) - with one drink being considered as 12 ounces of beer, ounces of wine, or 1.5 ounces of 80-proof spirits.
- Used tobacco products (like cigarettes, cigars, snuff, chew, electronic cigarettes)
- Used prescription drugs for non-medical reasons
- Used illegal drugs
The term Substance Misuse may sometime be used interchangeably to refer to Substance Abuse, or Substance Use Disorder.
- Transportation Barriers: A lack of reliable transportation that has kept them from medical appointments, meetings, work or from getting things needed for daily living (in the preceding 12 months).
- Utilities: A patient that has had any utility company (electric, gas, oil, or water) threaten to shut off services in their homes (in the preceding 12 months)..
Referenced ICD-10 Codes are listed in the table below:
ICD-10 Codes:
ICD-10-CM Code Category |
Problems/Risk Factors Included in Category |
| Z55 - Education and literacy |
Illiteracy, schooling unavailable, underachievement in a school, less than a high school diploma, no general equivalence degree (GED), educational maladjustment, and discord with teachers and classmates. |
| Z56 -Employment/ unemployment |
Unemployment, change of job, threat of job loss, stressful work schedule, discord with boss and workmates, uncongenial work environment, sexual harassment on the job, and military deployment status. |
| Z59 - Problems related to housing and economic circumstances |
Sheltered homelessness, unsheltered homelessness, residing in street, inadequate housing, housing instability, discord with neighbors, lodgers and landlord, problems related to living in residential institutions, inadequate food, lack of adequate food, food insecurity, extreme poverty, low income, and insufficient social insurance and welfare support. |
Supporting Definition: N/A
Element: Was there Active or Suspected COVID-19 diagnosis in the 2 weeks prior to admission or during this hospitalization?
Definition: Indicate if the patient was suspected or confirmed to have COVID-19 diagnosis in the 2 weeks prior or during this event.
Variable Name: coviddiag
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Yes, prior to admission
- Yes, during hospitalization
- No
- Unknown/ND
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Yes, prior to admission" OR "Yes, during hospitalization" if a confirmed or suspected COVID-19 diagnosis is documented by the provider, or when a test result is documented in the patient medical record.
- A confirmed diagnosis includes (but is not limited to) a positive laboratory test.
- A suspected diagnosis involves instances where the patient meets all the criteria necessary to be considered a Patient Under Investigation, with signs, symptoms, exposure, and travel history etc. Include any documentation by the provider stating if the test was "suspected", "possible", "probable" or "inconclusive" infection.
Supporting Definition:
Suggested Data Sources:
Element: Method of Diagnosis
Definition: Indicate how the patient was confirmed or suspected to have a COVID-19 diagnosis as documented by the provider.
Variable Name: diagnostype
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- COVID-19 confirmed by a lab test
- Clinical diagnosis assigned by hospital-specific criteria (suspected)
- Unknown/ND
Notes for Abstraction:
- A confirmed diagnosis includes (but is not limited to) a positive laboratory test.
- A suspected diagnosis involves instances where the patient meets all the criteria necessary to be considered a Patient Under Investigation, with signs, symptoms, exposure, and travel history etc. Include any documentation by the provider stating if the test was "suspected", "possible", "probable" or "inconclusive" infection.
- If the patient is suspected but no lab test has been done, record the diagnosis assigned by the hospital's clinical criteria.
- The option "Clinical diagnosis assigned by hospital-specific criteria" can include patients presenting with any signs/symptoms associated with COVID-19 (such as fever, etc.) but a definitive diagnosis has not been established. This option may also be selected if there is documentation of a Positive IgM antibody test in the medical record.
Supporting Definition:
Suggested Data Sources:
Element: Date/Time of Diagnosis
Definition: Indicates the Date/Time when COVID-19 was first diagnosed or suspected.
Variable Name: diagnosdt
Format: Date
Allowable Values:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- MM = Month (01-12)
- DD = Day (01-31)
- YYYY = Year (2012 - Current Year)
- Time: 24 Hour Clock (Military Time)
- HH = Hour (00-23)
- MM = Minutes (00-59)
Notes for Abstraction:
- If there was confirmed (positive) lab results, enter the date/time of the lab results.
- If there was no lab test done, enter the date/time when the provider noted the patient's diagnosis as "suspected", "possible", "probable" or "inconclusive".
- If the patient is suspected but no lab test has been done, record the diagnosis assigned by the hospital's clinical criteria.
- If the patient was diagnosed at a different facility 2 weeks prior to this admission, record the date/time of that diagnosis if available.
Supporting Definition:
Suggested Data Sources:
Discharge Disposition
What
was the patient’s discharge disposition on the day of discharge?
*Note:
Some hospitals have Rehab, Skilled
Nursing, Mental Health unit or adjacent facility to which patients are
admitted after being discharged from the acute care hospital. This
field refers to discharge destination after being discharged from the
acute care hospital.
Element
definition from Specifications Manual for National Hospital Inpatient
Quality Measures
Definition: The
final place or setting to which the patient was discharged on the day
of discharge.
Allowable Values:
1
Home
2
Hospice - Home
3
Hospice – Health Care Facility
4
Acute Care Facility
5
Other Health Care Facility
6
Expired (Died)
7
Left Against Medical Advice/AMA
8
Not Documented or Unable to Determine (UTD)
Notes for
Abstraction:
- Only use
documentation from the day of or the day before discharge when
abstracting this data element.
Example:
Documentation in the Discharge Planning notes on 04-01-20xx state that
the patient will be discharged back home. On 04-06-20xx the physician
orders and nursing discharge notes on the day of discharge reflect that
the patient was being transferred to skilled care. The documentation
from 04-06-20xx would be used to select value “5”.
- Consider
discharge disposition documentation in the discharge summary or a
post-discharge addendum as day of discharge documentation, regardless
of when it was dictated/written.
- If documentation
is contradictory, use the latest documentation. If there is
documentation that further clarifies the level of care that
documentation should be used to determine the correct value to abstract.
Example:
Nursing
discharge note documentation reflects that the patient is being
discharged to “XYZ” Hospital. The Social Service notes from the day
before discharge further clarify that the patient will be transferred
to the rehab unit of “XYZ” Hospital, select value “5”.
- If the medical
record states only that the patient is being discharged to another
hospital and does not reflect the level of care that the patient will
be receiving, select value “4”.
- To select value
“7” there must be explicit documentation that the patient left against
medical advice.
Examples:
- Progress notes
state that patient requests to be discharged but that discharge was
medically contraindicated at this time. Nursing notes reflect that
patient left against medical advice and AMA papers were signed, select
value “7”.
- Physician order
written to discharge to home. Nursing notes reflect that patient left
before discharge instructions could be given, select value “1”.
Suggested Data
Sources:
• Discharge instruction sheet
• Discharge planning notes
• Discharge summary
• Nursing discharge notes
• Physician orders
• Progress notes
• Social service notes
• Transfer record
Excluded Data
Sources:
• Any documentation prior to the day of or day before discharge
• UB-04
Inclusion
Guidelines for Abstraction:
For
Value 1:
•
Assisted Living Facilities
•
Court/Law Enforcement – includes detention facilities, jails, and prison
•
Home – includes board and care, foster or residential care, group or
personal care homes, and homeless shelters
•
Home with Home Health Service
•
Outpatient Services including outpatient procedures at another
hospital, Outpatient Chemical Dependency Programs and Partial
Hospitalization
For Value 3:
•
Hospice Care - General Inpatient and Respite
•
Hospice Care - Residential and Skilled Facilities
•
Hospice Care - Other Health Care Facilities (excludes home)
For
Value 4:
•
Acute Short Term General and Critical Access Hospitals
•
Cancer and Children’s Hospitals
•
Department of Defense and Veteran’s Administration Hospitals
For
Value 5:
•
Extended or Immediate Care Facility (ECF/ICF)
•
Long Term Acute Care Hospital (LTACH)
•
Nursing Home or Facility including Veteran’s Administration Nursing
Facility
•
Psychiatric Hospital or Psychiatric Unit of a Hospital
•
Rehabilitation Facility including Inpatient Rehabilitation
Facility/Hospital or Rehabilitation Unit of a Hospital
•
Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF), Sub-Acute Care or Swing Bed
•
Transitional Care Unit (TCU)
Exclusion
Guidelines for Abstraction:
None
If
Other Health Care Facility
If Other
Health Care Facility is selected for Discharge Disposition, select the
specific facility to which the patient was discharged.
- Skilled
Nursing Facility (SNF): Patient was discharged or
transferred to a skilled nursing facility (SNF) This would
include patients discharged to:
- skilled
nursing facility (SNF),
- SNF
rehabilitation unit (a unit within the SNF),
- Sub-Acute
Care,
- Transitional
Care Unit (TCU),
- Swing
Bed (patients discharged/ transferred to a SNF level of care within the
hospital’s approved swing bed arrangement), or
- Skilled
nursing facility with hospice referral only (has not accepted hospice
care by a hospice organization).
- Inpatient
Rehabilitation Facility (IRF): Patient was discharged or
transferred to an inpatient rehabilitation facility (IRF) including
rehabilitation distinct part units of a hospital
- Long
Term Care Hospital (LTCH): Patient was discharged or
transferred to a Medicare certified long term care hospital (LTCH or
LTACH) or a nursing facility certified under Medicaid but not certified
under Medicare. LTCH Usage Note: For hospitals that meet the
Medicare criteria for LTCH certification. A Long-term care hospital or
long-term care facilities provide acute inpatient care with an average
length of stay greater than 25 days.
- Intermediate
Care facility (ICF): Patient was discharged or
transferred to an intermediate care facility (ICF). This would include
patients discharged to:
- ECF
(Extended Care Facility),
- ICF
(Intermediate Care Facility),
- Nursing
Home,
- Nursing
facility for non-skilled/custodial/residential level of care,
- Veteran’s
Administration Nursing Facility,
- Nursing
facility with neither Medicare nor Medicaid certification
- Nursing
facility with hospice referral only (has not accepted hospice care by a
hospice organization).
- Other:
The patient was discharged or transferred to a Psychiatric Hospital or
Psychiatric Unit of a Hospital or other healthcare facility not defined
in above options.
Date/Time of hospital discharge or death
For in-hospital death, enter the date and time of death. For
survivors, enter the date and time that the patient was discharged from
the hospital. If the time of death/discharge is not available, select “Time
Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Note:
This field refers to discharge
from the acute care hospital (some hospitals have Rehab, Skilled
Nursing or Mental Health area or adjacent facility to which patients
are admitted after being discharged from the acute care hospital).
Was patient declared Do Not Attempt
Resuscitation (DNAR) at any time during this admission?
Date/Time of DNAR order
If time not available, select “Time Not
Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Was life support withdrawn?
Select either “Yes” or “No/Not
Documented.”
Were
organs recovered?
- Yes:
Select "Yes" if organs were recovered. Includes organs,
tissue, and bone marrow
- No:
Select "No " if organs were not recovered
CPC
at Discharge (if patient lived)
PCPC
at Discharge (if patient lived)
Using the CPC/PCPC Scale (see Scoring
Definitions), enter the patient’s Cerebral Performance
Category (Adults – Age ≥
18) or Pediatric Cerebral Performance Category (Pediatrics – Age
< 18) at the time of hospital discharge. If the CPC/PCPC is not
documented and cannot be calculated from
information in medical record, select “Unknown/Not
Documented.”
Discharge Destination
If patient was discharged alive from the hospital*, select
the
option that best describes the patient’s post-hospital discharge
destination.
- Home – Own home or home of
significant other.
- Other acute care hospital
- Rehabilitation center – A facility
whose purpose is to return the patient to the most functional state
possible.
- Skilled nursing facility – A
facility that offers long-term care to patients whose functions may
return very slowly, very slightly, or not at all.
- Other supervised residential facility –
Foster care, progressive care facility, progressive care home, boarding
homes.
- Hospice (includes home hospice)
- Mental health facility (psychiatric, substance
abuse)
- Other Example : H omeless/street
person; jail; prison; detention center )
- Unknown/Not Documented
*Note: Some
hospitals have Rehab,
Skilled Nursing, Mental Health unit or adjacent facility to which
patients are admitted after being discharged from the acute care
hospital. This field refers to discharge destination after being
discharged from the acute care hospital.
CPC/PCPC at Discharge (if patient lived)
Using the CPC/PCPC Scale (see Scoring
Definitions),
enter the patient’s Cerebral Performance Category (Adults – Age
>
18) or Pediatric Cerebral Performance Category (Pediatrics – Age
<
18) at the time of hospital discharge. If the CPC/PCPC is not
documented and cannot be calculated from
information in medical record, select “Unknown/Not
Documented.”
Adult Cerebral Performance Categories/CPC Scale
The Adult CPC scale is defined by the following:
- CPC 1
: Good cerebral performance* – Conscious, alert, able to
work, might have mild neurologic or psychologic deficit.
- CPC 2
: Moderate cerebral disability* – conscious, sufficient
cerebral function for independent activities of daily life. Able to
work in sheltered environment.
- CPC 3
: Severe cerebral disability
– Conscious, dependent on others for daily support because of impaired
brain function. Ranges from ambulatory state to severe dementia or
paralysis.
- CPC 4
: Coma or vegetative state
– Any degree of coma without the presence of all brain death criteria.
Unawareness, even if appears awake (vegetative state) without
interaction with environment; may have spontaneous eye opening and
sleep/awake cycles. Cerebral unresponsiveness.
- CPC 5
: Brain death – Apnea, areflexia, EEG silence, etc.
Pediatric/Neonate Cerebral Performance
Categories/PCPC Scale
The pediatric/neonate PCPC scale is defined by the following:
- PCPC 1
: Normal - Age-appropriate level of functioning; preschool
child developmentally appropriate; school-age child attends regular
classes.
- NEONATE
: Normal - No obvious neurological abnormalities.
- PCPC 2
: Mild cerebral disability
- Able to interact at an age-appropriate level; minor neurological
disease that is controlled and does not interfere with daily
functioning (e.g., seizure disorder that is well controlled with
medication); preschool child may have minor developmental delays, but
more than 75% of all daily living developmental milestones are above
the 10 th percentile; school-age child attends regular school, but
grade is not appropriate for age, or child is failing appropriate grade
because of cognitive difficulties.
- NEONATE
: Mild cerebral disability
- Minor neurological abnormality; neurological disease that is
controlled and does not interfere with daily functioning (e.g., seizure
disorder that is well controlled with medication).
- PCPC 3
: Moderate cerebral disability
- Below age-appropriate functioning; neurological disease that is not
controlled and severely limits activities; most activities of preschool
child’s daily living developmental milestones are below the 10th
percentile; school-age child can perform activities of daily living,
but attends special classes because of cognitive difficulties and/or
has a learning deficit.
- NEONATE
: Moderate cerebral disability
- Neurological disease that is not controlled (e.g., breakthrough
seizures despite medications which affect responsiveness to
environment).
- PCPC 4
: Severe cerebral disability
- Preschool child’s activities or daily living milestones are below the
10th percentile, and child is excessively dependent on others for
provision of activities of daily living; school-age child may be so
impaired as to be unable to attend school; school-age child is
dependent on others for provision of activities of daily living;
abnormal motor movements for both preschool and school-age child may
include non-purposeful, decorticate, or decerebrate responses to pain.
- NEONATE
: Severe cerebral disability
- Obvious severe neurological disorder: Abnormal motor movements may
include non-purposeful, decorticate or decerebrate response to pain.
- PCPC 5
: Coma or vegetative state - Coma; unawareness.
- NEONATE
: Coma or vegetative state - Coma; unawareness.
- PCPC 6
: Brain death
- NEONATE : Brain death
Comments
Use this memo field to document admission-related notes.
Note:
Do not enter any personal health information/protected health information (PHI) in the comments section.
Table of Contents
Cardiopulmonary
Arrest (CPA) Event
CPA Inclusion Criteria
All
patients*, visitors, employees, and
staff within the facility campus (inpatient areas and ambulatory areas
adjacent to the hospital and surrounding areas) who meet the following
criteria.
1. Experience a cardiopulmonary resuscitation
event, defined as either pulselessness or a pulse with inadequate
perfusion requiring:
a. Chest compressions and/or
b. Defibrillation of ventricular fibrillation or
pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
AND
2. The event elicits EITHER a hospital-wide (e.g., for
general
inpatient area) or unit-based (ICU, ED, OR, PACU, delivery room, etc.)
emergency response by acute care facility personnel.2
* No minimum hospital stay is
required.
- Patients with pulse, but
hypoperfusion
requiring chest compression, are included. (Example: child with
bradycardia, pulse and poor perfusion who receives chest compression
during resuscitation).
- All events
requiring chest compression and/or defibrillation in ICUs, PACU, OR and
Delivery Room should be captured and entered into Registry—even if it
requires requesting that hospitals make certain that resuscitation
records are completed for these events.
- Pre-hospital events are not considered
‘ended’ until the patient has sustained >20 minutes ROC.
CPA Exclusion Criteria
The following resuscitation events are excluded:
- Events beginning outside the facility campus, including
during transport to and from the facility.
- CPA stabilized prior to ED arrival
- CPA resuscitation ongoing and continued in ED after
arrival
- CPA resuscitation restarted in ED after arrival, but
prior to achieving >20 minutes sustained ROC 3.
- Events beginning within the facility campus with response
by facility
first-responders, but ongoing resuscitation transferred to EMS
personnel (e.g., fire, paramedic, ambulance).
- Events not requiring chest compression and/or
defibrillation.
- Events with a pulse requiring synchronized or
unsynchronized
cardioversion, not requiring chest compressions or defibrillation of VF
or pulseless VT.
- Successful ICD defibrillation of
ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia not
requiring chest compressions and/or external defibrillation.
- Chemical Code – Modified DNAR status allowing only drugs
without either
chest compression or defibrillation initiated during the event.
- Events occurring after brain death has been established.
Example: A patient with
pre-hospital CPA is
stabilized with ROC at 1200, 5 minutes prior to ED arrival at 1205. At
1212 7 minutes after ED arrival, patient requires additional CPA
resuscitation interventions (chest compression and/or defibrillation),.
ROC was not sustained > 20 min, This would be considered a
single,
ongoing pre-hospital event and would be excluded
Example: A patient with
pre-hospital CPA is
stabilized with ROC at 1000, arrives in ED 10 min later at 1010 , and
requires no additional CPA resuscitation interventions in ED, with ROC
sustained > 20 min at 1021 . This pre-hospital event has ended
and
would be excluded. If patient again requires chest compression and/or
defibrillation in the ED at 1030, 9 min after ROC sustained for
>20
minutes, that event is included as an ED event.
CPA End of Event Definition
A resuscitation event ends when:
There is restoration of circulation (ROC) that is sustained
for
> 20 minutes with no further need for chest compression,
including
with pacemaker or cardiopulmonary bypass/extracorporeal CPR.
Example: A patient with CPA is
stabilized with ROC
at 0900. At 0912 patient requires additional CPA resuscitation
interventions (chest compression and/or defibrillation). ROC was not
sustained > 20 min, This would be considered a single, ongoing
event.
Example: A patient with CPA is
stabilized with ROC
at 1300 and requires no additional CPA resuscitation interventions with
ROC sustained > 20 min at 1321. This first event has ended. If
patient again requires chest compression and/or defibrillation at 1336,
15 min after ROC had been sustained for >20 minutes, that event
is
included as another event.
OR
The resuscitation event is terminated and the patient is
declared
dead (unresponsive to advanced life support (ALS), medical futility,
advance directive, restrictions by family).
Any event that occurs after ROC > 20 minutes is a new
event.
Newly born Delivery CPA Event Only: This is an event form (created October 2013) to specifically capture data on the resuscitation provided to newly born infants who undergo CPA during transition from intrauterine to extrauterine life. This form is to be used on the newly born infant, and is intended to apply specifically to CPA events in infants at the time of birth. If a newly born infant has a CPA event at the time of birth and a subsequent CPA event later during that same admission, the event at the time of birth should be entered on the Newly born Delivery CPA Event Only form and the subsequent event should be entered on the CPA Event form.
All coding instructions that are specific to the Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form alone will be noted in blue font with the words (Newly born Delivery CPA Event Only). As there are shared data elements between this patient population and the general CPA population, abstractors will need to reference both the Newly born Delivery CPA Event Only coding instructions as well as the general CPA coding instructions (where applicable).
Table of Contents
OPTIONAL: Local Event ID
This field provided for those facilities using pre-numbered
event
records or another internal event numbering system who wish to include
that reference in their Get With The Guidelines® - Resuscitation
record. Do not enter any personal health information/protected health information (PHI) into this field.
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) Neonatal delivery event?
- Yes
- No/Not Documented (does not meet inclusion criteria)
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Yes" for a newly born infant that requires resuscitation with chest compressions. Newly born refers to the "at birth" time frame.
- Select "No/Not Documented" if the newly born infant does not require resuscitation with chest compressions.
- If a newly born infant is resuscitated with defibrillation, select "Yes."
Did patient receive chest compressions and/or
defibrillation during this event?
- Yes
- No/Not Documented (does NOT meet inclusion
criteria)
Date/Time the need for chest compressions (or
defibrillation when initial rhythm was VF or Pulseless VT) was first
recognized.
Enter the earliest date and time that the need for chest compressions (or defibrillation when initial rhythm was VF or Pulseless VT) was first recognized by
telemetry or direct observation.
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Note:
If the time is not documented, select the MM/DD/YYY option in the online dropdown and check off "Time Not Documented."
Table of Contents
2.1
Pre-Event Data
OPTIONAL: Was patient discharged from an
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) within 24 hours prior to this CPA Event?
Notes for Abstraction:
- The intent of this data element is to determine whether the patient was discharged from an ICU within 24 hours of the current CPA event.
- For patients with multiple ICU stays within a single admission, abstract "Yes" only if the patient was discharged from an ICU within 24 hours prior to the CPA event for which this CPA event form is being completed.
- If a patient was discharged from an ICU during this admission, but greater than 24 hours prior to this CPA event, answer "No."
OPTIONAL: If yes, enter the date the patient
was admitted to non-ICU unit after ICU discharge PRIOR to this CPA
event.
Note
: ICU includes all Critical Care areas (e.g., ICU, CCU, NICU, PICU,
etc.)
OPTIONAL: Was patient discharged from a
Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) within 24 hours prior to this CPA
event?
OPTIONAL: Was patient in the ED within 24 prior
to this CPA event?
Notes for Abstraction:
- The intent of this data element is to determine whether the patient was discharged from the ED within 24 hours of the current CPA event.
- For patients that have their CPA event while in the ED, answer "No."
- If a patient was discharged from the ED during this admission, but greater than 24 hours prior to this CPA event, answer "No."
OPTIONAL: Did patient receive
conscious/procedural sedation
(including general anesthesia) within 24 hours prior to this CPA event?
OPTIONAL:
Enter all vital signs (up to 4 sets) taken
in the 4 hours prior to the CPA event (Date, Time, Heart Rate, Blood
Pressure, Respiratory Rate, SpO 2
, Temperature).
- If
there are more than 4 sets of vital signs taken in the 4 hours prior to
the CPA event, take the 4 complete sets that were taken closest to
the event.
- If
in the 4 hours prior to the CPA event you have a combination of
complete (Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, Respiratory Rate, SpO2, and
Temperature) and incomplete vital signs
(missing one or more of the data elements) you may enter incomplete
vital signs.
- Note
: If no vital signs were taken in the 4 hours prior to the CPA event,
enter the last documented set of vital signs with date and time prior
to the CPA event. If no vital signs are available, select “None
Documented”
- Note
: If
systolic blood pressure was obtained via Doppler or pulse, leave the
diastolic blood pressure field blank and override the data quality edit
check.
Table of Contents
2.2
Pre-existing Conditions - Section changed
to REQUIRED in October 2012
Did patient have an out-of-hospital arrest leading to this admission?
- Yes: Patient had an out-of-hospital arrest that lead to this episode of hospitalization.
- No/Not Documented: Patient did not have an out-of-hospital arrest that lead to this episode of hospitalization or cannot be determined from medical record documentation.
Notes for Abstraction:
- For patients that had an out-of hospital arrest that lead to presentation at an outside hospital, and who are then transferred to your facility for further management, select “Yes.”
Pre-existing conditions at time of
the event (check all that apply)
Select only conditions that existed prior to the event. For those conditions where there is a time interval indicated, only respond affirmatively if the diagnosis is made prior to the CPA event for which you are completing the event form. There is
no
limit on the number of conditions that you can select, so you should
select all of the conditions that apply.
Note:
The following list is specific
to certain conditions of particular interest to Get With The
Guidelines® - Resuscitation and is not meant to be an exhaustive list
of all possible pre-existing conditions. Additionally, where a time
interval is indicated, it is NOT limited
to the current admission.
Example: If EMS identifies Hypotension at 1:00 at a patient’s home,
arrives at the ED at 1:30 and the patient arrests at 2:00,
“Hypotension” should be selected from the list below (within 4 hours).
- None – Select this option only if
there are no documented pre-existing conditions found in
the list below.
- Acute CNS non-stroke event – Select
if there was evidence of decreased mental status, delirium, or coma not
due to acute stroke within 4 hours up to time of the event.
- Acute stroke
– Select if there is a documented diagnosis during this hospitalization of stroke, ischemic stroke, or hemorrhagic stroke. Do not select "acute stroke" here if the patient has a documented past medical history of stroke prior to this admission. This response is meant to capture new onset strokes.
- Baseline depression in CNS function
– Select if there was evidence of chronically depressed CNS function including a motor, cognitive, or functional
baseline deficit (at time of system entry).
- Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Acyanotic (pediatric and
newborn/neonates only - only answer for patients <18 years
old). Includes:
- Aortic Stenosis
- Coarctation of the Aorta
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
- Septal Defects
- Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Cyanotic. This option can be answered for adult patients if present. Includes:
- Tetralogy of Fallot (TET)
- Total Anolmalous Pulmonary Venous Connection (TAPVC or
TAPVR)
- Truncus Arteriosus
- Hypoplastic Left Heart
- Transposition of the Great Vessels
- Congenital Malformation/Abnormality (non-cardiac). This option can be answered for adult patients if present. Includes:
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Tracheal-esophageal fistula
- Known/suspected chromosomal/genetic abnormality – (e.g.,
trisomy 21, 13, 18)
- Congestive heart failure (this admission)
– Select if there is documentation of newly diagnosed congestive heart failure during
this admission and prior to this CPA event.
- Congestive heart failure (prior to this
admission) – Select if there is a documented diagnosis of
congestive heart failure prior to this admission.
- Diabetes mellitus – Select if there
is a documented diagnosis of Type I or Type II diabetes mellitus prior to this CPA event.
- Hepatic insufficiency
– Select if there was evidence of hepatic insufficiency within 24 hours
up to the time of the event, defined by ANY of the following:
- Adult
- Total bilirubin > 2 mg/dL and AST > 2x
normal
- Cirrhosis
- Pediatric/Newborn/Neonate
- Direct bilirubin > 2 mg/dL and AST > 2x
normal
- Cirrhosis
- Hypotension/hypoperfusion – Select
if there was evidence of hypotension within 4 hours up to the time of
the event, defined by ANY of the following:
- Adult [18+]:
- SBP < 90 or MAP < 60 mmHg.
- Vasopressor/inotropic requirement after volume
expansion (except for dopamine ≤ 3 mcg/kg/min).
- Intra-aortic balloon pump
- Pediatric [< 18]:
- SBP < 5th percentile for age, less than [70 + 2
x age in years] for age < 10.
- MAP < 5th percentile for age.
- Vasopressor/inotropic requirement after volume
expansion (except for dopamine ≤ 3 mcg/kg/min).
- Newborn/Neonate:
- Documentation/evidence of symptomatic
hypotension/hypoperfusion.
- Major trauma
– Select if there was evidence of multi-system injury or single system
injury associated with shock or altered mental status during this admission and prior to this CPA event.
- Metastatic or hematologic malignancy
– Select if there is any solid tissue malignancy with evidence of
metastasis, or any blood borne malignancy.
- Metabolic/electrolyte abnormality
– Select if there was evidence of metabolic/electrolyte abnormality
within 4 hours up to the time of the event, defined by ANY of the
following:
- Adult/Pediatric:
- Sodium < 125 or > 150 mEq/L
- Potassium < 2.5 or > 6 mEq/L
- pH < 7.3 or > 7.5, arterial
- Lactate > 2.5 mmol/L,
- Blood glucose < 60 mg/dL
- Newborn/Neonate:
- Acidosis (pH < 7.2 arterial, venous or
capillary)
- Ionized Calcium < 1 mmol/L or < 4 mg/dL
- Glucose < 40 mg/dL
- Sodium < 125 mEq/L
- Magnesium > 4 mEq/L
- Potassium > 6.5 mEq/L
- Myocardial ischemia (acute coronary
syndrome)/infarction (this admission) – Select if there is documentation of a new diagnosis of myocardial ischemia (acute coronary
syndrome)/infarction this admission.
- Myocardial ischemia (acute coronary
syndrome)/infarction (prior to this admission)
– Select if there is a documented past medical history of myocardial ischemia (acute coronary syndrome)/infarction prior to this admission.
- Pneumonia
– Select if there is a documented diagnosis of active pneumonia, where
antibiotics have not yet been started or the pneumonia is still being
treated with antibiotics.
- Recently delivered or currently pregnant during this admission (if selected, maternal in-hospital cardiac arrest section is required):
– Based on the CDC definition of maternal mortality, which is "... pregnancy-related death is defined as the death of a woman while pregnant or within 1 year of the end of pregnancy-regardless of the outcome, durance or site of the pregnancy-from any cause related to or aggravated by the pregancy or its management, but not from accidental or incidental causes", recently delivered is defined as delivery that occured within one year of CPA event.
Suggested data sources: medical history or delivery record.
- Renal insufficiency – Select if there
was evidence of renal insufficiency prior to the event, defined by ANY
of the following:
- Adult [18+]:
- Requiring ongoing dialysis or extracorporeal
filtration therapies.
- Creatinine > 2 mg/dL within 24 hours up to the
time of the event.
- Pediatric [< 18]:
- Requiring ongoing dialysis or extracorporeal
ultrafiltration therapies;
- if < 30 kg: Oliguria (urine output < 1
ml/kg/hr for > 8 hr.)
and creatinine > 1mg/dL within 24 hours up to the time of the
event;
- if > 30 kg: Oliguria (urine output < 0.5
ml/kg/hr for > 8 hr) and creatinine > 2 mg/dL within 24
hours up
to the time of the event.
- Respiratory insufficiency
– Select if there was evidence of acute or chronic respiratory
insufficiency within 4 hours up to the time of the event, defined by
ANY of the following:
- PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300 (in the absence of
pre-existing documented cyanotic heart disease).
- PaO2 < 60 mm Hg (in the absence of pre-existing
documented cyanotic heart disease).
- SaO2 < 90 %, (in the absence of pre-existing
documented cyanotic heart disease);
- PaCO2, EtCO2 or TcCO2 > 50 mm Hg.
- Ages 18+ years – spontaneous respiratory rate >
40/min or < 5/min.
- Ages 9-17 years – spontaneous respiratory rate >
50/min or < 5/min.
- Ages 1-8 years – spontaneous respiratory rate >
60/min or < 5/min.
- Age < 1 year – spontaneous respiratory rate
> 60/min or < 10/min.
- Requiring non-invasive ventilation (e.g.,
Bag-Valve-Mask, Mask CPAP/BiPAP, Nasal CPAP/BiPAP, negative pressure
ventilation).
- Requiring ventilation via invasive airway (e.g.,
T-piece, assist control, IMV, pressure support, high frequency).
- Sepsis
– Select if there is documentation indicating treatment and/or evidence of spesis. The presence of bacteria (bacteremia), other infectious organisms, or toxins created by infectious organisms in the bloodstream with spread throughout the body. Sepsis may be associated with clinical symptoms of systemic illness, such as fever, chills, malaise, low blood pressure, and mental-status changes.
Required: Active or Suspected bacterial or viral infection at admission or during hospitalization
Definition: Indicate if the patient was confirmed or suspected to have Active or Suspected Bacterial or Viral infection at admission or during hospitalization.
Format: Multi-Select (check box)
Allowable Values:
- None
- Bacterial infection
- Emerging Infectious Disease
- SARS-COV-1
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19)
- MERS
- Other Emerging Infectious Disease
- Influenza
- Seasonal cold
- Other viral infection
Notes for Abstraction:
- Influenza (ICD-10-CM code J09.X2 - Flu due to identified novel influenza A virus with other respiratory manifestations)
Select Emerging Infectious Disease when the patient was confirmed or suspected to have:
- SARS-COV-1 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus) (may include ICD-10-CM code B97.21); or
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus) (may include ICD-10-CM code U07.1); or
- MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) (may include ICD-10-CM code B97.29); or
- Other Emerging Infectious Disease
Select one of the Allowable Values options when a confirmed or suspected diagnosis is documented by the provider or when a test result is documented in the patient medical record.
- A confirmed diagnosis includes (but is not limited to) a positive laboratory test provided at a local/state level prior to confirmation from the CDC or when a positive test result is documented in the patient medical record.
- A suspected diagnosis involves instances where the patient meets all the criteria necessary to be considered a Patient Under Investigation, with signs, symptoms, exposure and travel history. Include any documentation by the provider stating if the test was "suspected", "possible", "probable" or "inconclusive" infection.
If the patient is suspected but no lab test has been done, you can record the diagnosis assigned by the hospital's clinical criteria.
Optional: Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) donned by the responders?
Definition: Indicate if Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) was donned by the responders to prevent Transmission-based Precautions. These precautions are designed for patients with confirmed or suspected infections with pathogens for which additional precautions beyond Standard Precautions are needed.
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- The additional PPE's in this instance is specifically to limit the exposure of healthcare workers to pathogens while caring for patients suspected or confirmed to have an Emerging Infectious Disease.
- Additional PPE does NOT include PPE'S worn during Standard Procedures or when applying Standard Precautions, but when Transmission-based Precautions are applied (i.e., Contact Precautions, Droplet Precautions, and Airborne Precautions) to prevent transmission of an infectious agent that is not interrupted by standard precautions alone. These might include:
- Masks/Respirators designed to protect the wearer - e.g. N95 or higher-level respirators (FFP, N99/N100 etc.), a mask with attached shield or a full-face shield, goggles, or visor.
- Coveralls, Isolation/Surgical gowns, or long-sleeved disposable fluid-resistant gown.
- Select Yes when there is documentation in the patient medical record that PPE in addition to the standard protocol/practice was donned by the responders during this event and/or a hospital policy at the time of this event required additional PPE as standard practice.
- Select No/ND if there was no documentation of the additional PPE or a hospital policy regarding additional PPE was not in place at the time of the event.
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Check box (checked for Yes, unchecked for No)
Notes for Abstraction:
- Check the box on this question if there is documentation in the patient medical record of current vaping or e-cigarette use by the patient during the past 12 months.
- Leave the box unchecked if there is no documentation of use or the history includes use prior to the past 12 months.
Vaping and e-cigarette use includes electronic nicotine delivery system or electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), which are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid containing nicotine, propylene glycol, and/or vegetable glycerin and flavorant chemicals to generate an aerosol that the user inhales, or heat-not-burn tobacco products, which are tobacco products that heat tobacco to a lower temperature than required for combustion.
Reference: Dehmer GJ, Badhwar V, Bermudez EA, Cleveland JC Jr, Cohen MG, D'Agostino RS, Ferguson TB Jr, Hendel RC, Isler ML, Jacobs JP, Jneid H, Katz AS, Maddox TM, Shahian DM. 2020 AHA/ACC key data elements and definitions for coronary revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Data Standards (Writing Committee to Develop Clinical Data Standards for Coronary Revascularization). Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020;13:e000059. doi: 10.1161/HCQ.0000000000000059
Table of Contents
2.3
Interventions Already in Place
Intervention(s) ALREADY IN PLACE when the need
for chest
compressions and/or defibrillation was first recognized (check all that
apply).
Select each intervention that was already in
place
at the time of the cardiopulmonary arrest. There is no limit to the
number of interventions that you can select, so you should select all
interventions that apply. To make a selection, click in the circle to
the left of the intervention name.
If either or both endotracheal tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube are selected in CPA 2.3 Intervention Already in Place, please indicate the method of confirmation that was used to ensure proper placement under CPA 4.3 Ventilation. See CPA 4.3 Ventilation for additional coding instructions.
Part A:
- None – Select this option when no
“Part A”
interventions were in place when the need for chest compressions and/or
defibrillation was first recognized.
- Non-invasive assisted ventilation
- Bag-Valve-Mask
- Mask and/or Nasal CPAP
- Mouth-to-Barrier Device
- Mouth-to-Mouth
- Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)
- Other Non-Invasive Ventilation: (specify)
- Invasive assisted ventilation, via an:
- Endotracheal Tube (ET)
- Tracheostomy Tube
- Intra-arterial catheter – Excludes
umbilical arterial catheter (UAC)
- Conscious/procedural sedation
- End Tidal CO2 (ETCO2) Monitoring
- Supplemental oxygen (cannula, mask, hood, or tent)
Suggested Data Sources:
- Respiratory Therapist Notes
- Physician Notes
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) Intervention(s) ALREADY IN PLACE when the need for chest compressions and/or defibrillation was first recognized (check all that apply).
Select each intervention that was already in place at the time of the cardiopulmonary arrest (CPA Event). There is no limit to the number of interventions that you can select, so you should select all interventions that apply. To make a selection, click in the circle to the left of the intervention name.
If either or both endotracheal tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube are selected in CPA 2.3 Intervention Already in Place, please indicate the method of confirmation that was used to ensure proper placement under CPA 4.3 Ventilation. See CPA 4.3 Ventilation for additional coding instructions.
Part A:
- None: Select this option when no "Part A" interventions were in place when the need for chest compressions was first recognized.
- Non-invasive Assisted ventilation: Select this option if assisted ventilation was in place. Also select each type of ventilation used from the following list:
- Bag-Valve-Mask
- Mask and/or Nasal CPAP
- Mouth-to-Barrier Device
- Mouth-to-Mouth
- Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)
- Other Non-Invasive Ventilation (if selected, please specify)
- Invasive assisted ventilation, via an: Select this option if mechanical ventilation was in place when the need for chest compressions was first recognized. Also select from the following list:
- Endotracheal tube (ET)
- Tracheostomy tube)
- Intra-arterial catheter
- Conscious/procedural sedation
- End Tidal CO2 (ETCO2) Monitoring
- Supplemental oxygen
Monitoring (specify):
Vascular Access:
- Yes:
Select "Yes" if any of the following are already in place when the need
for chest compressions and/or defibrillation was first recognized:
- Peripheral vein
- Central vein
- Intraosseous (IO)
- Umbilical vein (UVC)
- Umbilical artery (UAC)
- No/Not
Documented
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) If vascular access in place, type
- Umbilical Venous Catheter (UVC)
- Peripheral IV
Any vasoactive agent in place?
- Yes:
Select "Yes" if any of the following were already in place
when the need for chest compressions and/or defibrillation was first
recognized:
- Dobutamine
- Dopamine
> 3 mcg/kg/min
- Epinephrine
- Nitroglycerin
- Norepinephrine
- Phenylephrine
- Vasopressin
- Other
Vasoactive Agent(s)
- No/Not
Documented: Select "No/Not Documented" if no vasoactive agent was already in
place when the need for chest compressions and/or defibrillation was
first recognized or if started after the need for chest compressions
and/or defibrillation was first recognized.
Note:
This data element needs to be answered independent of the other Part A
interventions.
OPTIONAL: Part B:
- None – Select this option when no
“Part B”
interventions were in place when the need for chest compressions and/or
defibrillation was first recognized.
- IV/IO continuous infusion of antiarrhythmic(s)
; Select if any of
the following were already in place when the need for chest
compressions and/or defibrillation was first recognized:
- Amiodarone/Cordarone
- Lidocaine
- Procainamide
- Other Antiarrhythmic(s) (specify
- Conscious/Procedural sedation
– intravenous narcotics/sedative-hypnotics for procedure
- Dialysis or extracorporeal filtration therapy
ongoing – Hemo- or peritoneal dialysis, continuous
arteriovenous or veno-venous hemofiltration/dialysis ongoing at time of
the event.
- Implantable cardiac defibrillator (ICD)
- End
Tidal CO2 (ETCO2) Monitoring
- Supplemental oxygen – Via nasal
cannula, face mask, hood or tent.
- Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO)
Method(s) of confirmation used to ensure correct placement of Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube placement in trachea (check all that apply):
- Exhaled CO2
- Waveform capnography (waveform ETCO2): Monitor shows waveform as well as number
- Capnometry (numeric ETCO2): Monitor shows number, but NOT waveform display of ETCO2
- Exhaled CO2 colorimetric monitor (ETCO2 by color change): Device changes color (e.g. from purple to yellow) but no number nor waveform is displayed
- Esophageal detection devices: Any device that relies on the ability to readily aspirate gas in the lower airways.
- Revisualization with direct laryngoscopy
- None of the above - Select this option when confirmation was performed and method documented but was not done using any of the above methods. Select this option if only auscultation is performed/documented.
- Not Documented – Select this option when confirmation was documented as performed (other than just auscultation), but the method of confirmation is not documented
Please note that this is a required question if Endotracheal Tube and/or Tracheostomy Tube are is selected in CPA 2.3 Intervention ALREADY IN PLACE and/or CPA 4.3 Ventilation.
Suggested Data Sources:
- Respiratory Therapist Notes
- Physician Notes
Table of Contents
3.1
Event
Age at Event
Enter the age of the patient at the time of the
event. Select
the most appropriate measurement to indicate age om "hour(s)",
"day(s)", "week(s)", "month(s)", or year(s). If Date
of Birth and Event Date have been
provided, the age will be automatically derived.
Estimated
Select if age is estimated by hospital staff.
Note:
If age is not documented and CANNOT be estimated, select "Age
Unknown/Not Documented."
Subject Type
Enter the subject’s relationship with the hospital at the
time of the event onset. Valid entries:
- Ambulatory/Outpatient (includes same-day
surgical)
- Emergency Department
- Hospital Inpatient – (includes Rehab, Skilled
Nursing and Mental Health ‘wards, floors or units’ within a hospital
): note - this response will be auto-populated in the online form for the Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only
- Rehab Facility Inpatient
- Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Inpatient
•
- Mental Health Facility Inpatient (psychiatric,
substance abuse)
- Visitor or Employee – Includes all
healthcare personnel and all other non-patients.
Note:
Some hospitals have rehab, SNF,
mental health units or adjacent facilities to which patients are
‘admitted’ (separate from acute care hospital admission) where the code
team responds. In these instances, Rehab Facility Inpatient, SNF
Inpatient or Mental Health Facility inpatient should be selected. If
the event occurs on a rehab or skilled nursing or mental health 'ward'
(acute care admission), then Hospital Inpatient should be selected.
Illness Category
Enter the most appropriate illness category at the time of
the event onset.
- Medical-Cardiac – Patient with a
primary diagnosis of medical illness that is cardiovascular at the time
of the event.
- Medical-Noncardiac – Patient with a
primary diagnosis of medical illness at the time of the event that is
not cardiovascular.
- Surgical-Cardiac – Patient who is
post-operative following cardiac surgery at the time of the event.
- Surgical-Noncardiac
– Patient who is post-operative with a surgical
illness as the primary diagnosis that is not cardiac surgery at the
time of the event.
- Obstetric – Obstetric patient
(before, during or after delivery) at the time of the event.
- Trauma – Patient with single or
multiple traumas as the primary diagnosis at the time of the event.
- Other (visitor/employee…) – Neither
in-patient nor outpatient, but a visitor or employee at the time of the
event.
Event Location (area)
Select the patient’s location (or type of area) in the
hospital
when the need for chest compression and/or defibrillation was
recognized.
- Ambulatory/Outpatient Area
- Adult Coronary Care Unit (CCU)
- Adult ICU (includes medical, surgical,
cardiovascular, trauma, burn… ICUs)
- Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory
- Delivery Suite -- (includes Labor room (LDRP), obstetrical operating room, newborn stabilization space)
- Diagnostic/Intervention Area (excludes Cath Lab)
– Radiology, Nuclear Medicine, EEG, ECHO, Stress testing, and others.
- Emergency Department
- General Inpatient Area – Excluding
Telemetry units and Step-down units.
- Neonatal ICU (NICU)
- Newborn Nursery
- Operating Room
- Pediatric ICU (PICU) – (includes
medical, surgical, cardiovascular, trauma, burn…ICUs). As of April, 2014, this response excludes the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit.
- Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (PCICU)
- Post Anesthesia Recovery Room (PACU)
- Rehab, Skilled Nursing or Mental Health
Unit/Facility •
- Same-day Surgical Area
- Telemetry Unit or Step-Down Unit
- Other
- Unknown/Not Documented
Note:
Some hospitals have Rehab,
Skilled Nursing or Mental Health areas or adjacent facilities to which
patients are ‘admitted’ (separate from acute care hospital admission)
where the code team responds.
Event Location (name)
Type or select the hospital-specific unit or area name or
number
where the patient was located at the time of the event. Some examples
of unit names include: Surgical ICU, Medical ICU, CVT ICU, CCU-acute,
CCU-step-down, Neonatal CCN, Neonatal ICU, Newborn Nursery East, 3West,
Angiography, CT scan, Cardiac Catheterization lab, Ambulatory Unit A,
on-campus rehab facility.
Note:
This is a dynamic list of
location names that is specific to the selected location area. As new
names are added (manually entered), they become available in the menu
for that particular “location area” for future records. For example, if
“CCU#1” is typed in and saved in record 1, it will appear in the list
for record 2.
Event Witnessed?
Was the onset of the cardiopulmonary arrest directly observed
by
someone (family, lay bystander, employee or health care professional)?
This differs from "monitored."
Was a hospital-wide resuscitation response
activated?
Notes for Abstraction:
- (Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only): Select "Yes" if a resuscitation team was activated. For the neonatal delivery event, a hospital-wide response does not need to be activated to answer "Yes."
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) If team activated, date/time resuscitation team arrival
If a resuscitation team was activated, enter the date and time of arrival of the resuscitation team. Arrival may be classified as present at the bedside. If multiple times are documented, enter the date/time of the arrival of the first member of the resuscitation team.
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Note: The date of the event is required. If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
Table of Contents
4.1
Intl Condition/Defib/Vent
Choose the selection that best describes this
event:
- Patient was PULSELESS when the need for chest compressions
(or defibrillation when initial rhythm was VF or Pulseless VT) was
first recognized.
- Patient initially had a pulse/heart rate (poor perfusion)
requiring chest compressions PRIOR to becoming pulseless.
- Patient had a pulse/heart rate (poor perfusion) requiring
chest compressions, but did NOT become pulseless at any
time during this event.
Note:
While chest compressions are
usually provided to pulseless patients (option 1), patients sometimes
require chest compressions when a poorly perfusing pulse/heart rate is
present (e.g., bradycardia). This occurs more frequently in the
pediatric population. For these events, option 2 or 3 should be
selected.
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) Does patient have a detectable heart rate?
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Yes" if there is documentation that the patient has a detectable heart rate
- Select "No" if there is documentation that the patient’s heart rate is not detectable
- Select "Not Documented" if there is no documentation around heart rate
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) If there is a detectable heart rate, what was the heart rate?
- ≥60 BPM (Greater than or equal to 60 Beats Per Minute)
- < 60 BPM (Less than 60 Beats Per Minute)
- Heart rate Not Documented: Select this response if there is documentation that the patient has a detectable heart rate but the rate itself is not documented.
Notes for Abstraction:
If multiple heart rates are documented, enter the initial heart rate at the time the need for chest compressions was first identified.
Did patient receive chest compressions
(including open chest cardiac massage)?
- Yes
- No/Not Documented
- No – Per Advance Directive
Compression
method(s) used (check all that apply):
- Standard / Manual Compression
- Automatic
Compressor - Includes:
- Mechanical piston CPR
- Active Compression-Decompression DEVICE
(ACD-CPR) –
ACD-CPR is performed with a hand-held device equipped with a suction
cup to actively lift the anterior chest during decompression.
- Load-distributing band (LDB) CPR /
Circumferential CPR – including circumferential thoracic
vest that is cyclically inflated and deflated.
- Interposed Abdominal Compression (IAC-CPR) –
IAC-CPR includes compression of the abdomen during the relaxation phase
of chest compression.
- Unknown/Not Documented
- Open chest CPR – Direct (internal)
cardiac compression.
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) Compression Method used (check all that apply)
- Two Thumb encircling hands: Compression with 2 thumbs with fingers encircling the chest and supporting the back
- Two finger Technique : Compression with 2 fingers with a second hand supporting the back
- Not Documented : Select this response if compressions were provided but the method was not documented
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) Compression to ventilation ratio used (check all that apply)
- 3:1 (90 compressions and 30 breaths)
- 15:2
- Asynchronous
- Not Documented : Select this response if the compression to ventilation ratio was not documented
Date and time compressions started
Enter the date and time compressions were first started. If
the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
If compressions were provided while pulse was
present:
Rhythm when patient with a pulse first received
compressions during the event
What was the first documented rhythm when the patient WITH A
PULSE/HEART RATE first received chest compressions? The rhythm can be
documented by anyone who identifies or records rhythm, not necessarily
team or advanced life support (ALS) provider. For the unmonitored
patient, select the first rhythm identified when monitor applied.
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm (AIVR)
– Wide
complex ventricular arrhythmia with no antegrade P waves, rate 60-100.
If rate < 60 with pulse, code as bradycardia; if rate >
100 with
pulse, code as ventricular tachycardia (VT) with pulse.
- Bradycardia
- Pacemaker
- Sinus – Includes sinus tachycardia.
- Supraventricular tachyarrhythmia (SVTarrhy)
– Includes atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia, and
supraventricular tachycardia.
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT) with pulse
- Unknown/Not Documented
If pulseless at any time during the event:
Date and time pulselessness was first identified
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not
Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
First Documented Pulseless Rhythm
What was the first documented pulseless rhythm? The rhythm can
be documented by anyone who identifies or records rhythm, not
necessarily team or advanced life support (ALS) provider. For the
unmonitored pulseless patient, select the first rhythm identified when
monitor was applied.
- Asystole
- Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
- Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
- Enter the first (initial) cardiac rhythm recorded during the cardiac arrest event.
- The initial rhythm can be obtained from a cardiac monitor, automated external defibrillator strip, or recorded on the code sheet.
- Select Unknown/Not Documented if there is no documentation of the first pulseless rhythm.
- If there is conflicting information documented, e.g. the first pulseless rhythm documented on the code sheet is different than the first rhythm on the monitor strip, enter the first pulseless rhythm on the monitor strip.
- The monitor strip is the preferred data source for this data element.
Table of Contents
4.2 AED and
VF/Pulseless VT
Was Automated External Defibrillator (AED) or
manual defibrillator in AED/Shock Advisory mode applied?
- Yes
- No/Not Documented
- Not Applicable (not used by facility)
Date and time AED or manual defibrillator in
AED/Shock Advisory mode was applied
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not
Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Did patient have ventricular fibrillation or
pulseless ventricular tachycardia at ANY time during the resuscitation
event?
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Yes" if a rhythm of ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia was recorded at ANY time during the resuscitation event. This would include patients whose first (initial) rhythm was some other rhythm but ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia was documented at any time during the event.
- Select "No/Not Documented" if there is no documentation of ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia during the event.
Date and time of first ventricular fibrillation
or pulseless ventricular tachycardia
If patient had ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia at any time during the resuscitation event, enter the date and time that ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia was first recorded. If multiple dates and times are documented, use the earliest date and time.If the time is not documented, select "Time Not
Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Was defibrillation shock provided for
ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia?
- Yes
- No/Not Documented
- No – Per Advance Directive
Total number of shocks
Enter the total number of shocks administered during the cardiac arrest event. If the number of shocks is unknown, select “Unknown/Not
Documented.”
For each defibrillation shock (AED and/or
manual) provide the following information: (Maximum entry of
4 shocks - if more than 4 shocks are provided, enter information from
first 4)
Date/time of shock
If time is not available, select
"Time Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Energy (joules)
If energy level is not available, select "Not
Documented."
Documented reason(s) (patient, medical, hospital related or other) for not providing defibrillation shock for Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) or Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) in first two minutes?
- Yes: There is a documented reason for not providing defibrillation shock for VF or pulseless VT in the first two minutes of the date/time the need for chest compressions (or defibrillation) was first recognized. In order to select yes, the documented reason must fall on the list below (patient, medical, hospital related or other).
- No: There are no specific reasons documented in the medical record why defibrillation shock was not administered within the first two minutes of the date/time the need for chest compressions (or defibrillation) was first recognized.
Notes for Abstraction:
- In order to select "Yes," reasons for not providing defibrillation shock must be documented by a physician, APN, PA, or ACLS certified nurse
Select the specific reason(s) documented in the medical record for not providing defibrillation shock for Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) or Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) in first two minutes
Patient Reasons:
- Initial Refusal (e.g. family refused)
Medical Reasons:
- ICD in place which shocked patient within first 2 minutes of identification of VF or Pulseless VT
- LVAD or BIVAD in place
- Rhythm change to non-shockable rhythm within 2 minutes of identification of VF or Pulseless VT
- Spontaneous Return of Circulation within first 2 minutes of identification of VF or pulseless VT
Hospital Related or Other Reasons:
- Equipment related delay (e.g. defibrillator not available, pad not attached)
- In-hospital time delay (e.g. code team delays, personnel not familiar with protocol or equipment, unable to locate hospital defibrillator)
- Other
Notes for Abstraction:
Table of Contents
4.3
Ventilation
Type(s) of Ventilation/Airway(s) USED During
the event, including those already in place (check all that apply).
Select each type of ventilation/airway used during the event.
There is no limit on the number of types that may be selected.
- None: Select this
option if no assisted ventilation/artificial airway was used
during the event
- Unknown/Not Documented: Select this
option if assisted ventilation/artificial airway was used but
the type is not documented
- Assisted
Ventilation/Artificial Airways Used (select all that apply):
- Bag-Valve-Mask
- Mask
and/or Nasal CPAP/BiPAP
- Mouth-to-Barrier
Device
- Mouth-to-Mouth
- Other
Non-Invasive Ventilation (specify)
- Laryngeal
Mask Airway (LMA)
- Endotracheal
Tube (ET)
- Tracheostomy
Tube
Was
Bag-Valve-Mask ventilation initiated during the event?
- Yes
– There is documentation that Bag-Mask Mask ventilation was initiated during the cardiac arrest event.
- No
– There is no documentation that Bag Mask ventilation was initiated during the cardia arrest event.
Notes for Abstractions: Bag Mask ventilation is also known as bag-valve-mask ventilation
Note: If 'yes' is selected, the following are required/enabled:
If yes, enter date and time:
If Bag Mask ventilation was initiated during the event, enter the date and time if the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24- hour clock (military time)
Was Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) inserted/re-inserted during event?:
If yes, enter Date and Time:
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
Time: HH:MM
24-hour clock (military time)
Time Not Documented
Suggested Data Sources:
- Respiratory Therapist Notes
- Physician Notes
Was
any Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube inserted/Re-inserted
during the event?
- Yes
– There is documentation that an Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube was inserted or re-inserted during the cardiac arrest event.
- No
– There is no documentation that an Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube was inserted or re-inserted during the cardiac arrest event.
Note:
If insertion attempted, but not
achieved, select "No" and you may indicate this in section 7.2
Resuscitation Related Events and Issues
Note:
If Initial Intubation and/or Reintubation is selected, the following
are required/enabled:
Date
and Time Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube inserted if not
already in place and/or Re-inserted during event
If an Endotracheal
Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube
was inserted or reinserted during the event, enter the date and time intubation was achieved, not when the first attempt was made. If the time is not
documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Method(s)
of confirmation used to ensure correct placement of Endotracheal Tube
(ET) or Tracheostomy Tube placement in trachea (check all that apply):
- Exhaled
CO2
- Waveform
capnography (waveform ETCO2): Monitor shows waveform as well as number
- Capnometry
(numeric ETCO2): Monitor shows number, but NOT waveform display of ETCO2
- Exhaled
CO2 colorimetric monitor (ETCO2 by color change): Device changes color
(e.g. from purple to yellow) but no number nor waveform is displayed
- Esophageal
detection devices: Any device that relies on the ability to readily aspirate gas in the lower airways.
- Revisualization
with direct laryngoscopy
- None
of the above - Select this option when confirmation was
not performed or when the method documented but was not done
using any of the above methods. Select this option if only
auscultation is performed/documented.
- Not
Documented – Select this option when confirmation
was documented as performed (other than just auscultation), but the method
of confirmation is not documented
Please note that this is a required question if Endotracheal Tube and/or Tracheostomy Tube are is selected in CPA 2.3 Intervention ALREADY IN PLACE and/or CPA 4.3 Ventilation.
Was any Pulse Oximetry placed during the event?:
If yes, enter Date and Time:
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
Time: HH:MM
24-hour clock (military time)
Time Not Documented
Suggested Data Sources:
- Respiratory Therapist Notes
- Physician Notes
Table of Contents
5.1 Other
Interventions
Was IV/IO Epinephrine bolus administered?
- Yes: There is documentation that an IV/IO epinephrine bolus was administered during the cardiac arrest event.
- No/Not Documented: An epinephrine bolus was not administered during the cardiac arrest event or an epinephrine bolus was administered during the event but was not given IV/IO (e.g. bolus was delivered via endotracheal tube or tracheostomy tube).
Date and time of first IV/IO bolus dose
Enter the date and time that the first IV/IO bolus of epinephrine was administered during the cardiac arrest event.
If the time is not documented, select "Time
Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Total Number of Doses
Enter the total number of IV/IO doses of epinephrine bolus administered during the cardiac arrest event.
If the number of doses is not documented, select "Unknown/Not
Documented."
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) Was any Epinephrine BOLUS administered?
- Yes: There is documentation that any epinephrine bolus was administered during the cardiac arrest event. For the neonatal delivery event, select yes regardless of the route of administration.
- No/Not Documented: An epinephrine bolus was not administered during the cardiac arrest event
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only) Epinephrine Doses
Enter the date/time, dose in milligrams, and delivery route for each Eprinephrine dose administered for the neonatal delivery event. Enter a maximum of 6 doses (if a patient received more than 6 doses, enter the first 6). Delivery route includes: Intravascular (Peripheral, Umbilical Venous Catheter), Intraossous (IO), Endotracheal or Tracheostomy Tube, Other, or Unknown/Not documented.
Was IV/IO bolus administered?
- Yes: There is documentation that an IV/IO vasopressin bolus was administered during the cardiac arrest event.
- No/Not Documented: A vasopressin bolus was not administered during the cardiac arrest event or a vasopressin bolus was administered during the event but was not given IV/IO (e.g. bolus was delivered via endotracheal tube or tracheostomy tube).
Date and time of first IV/IO bolus dose
Enter the date and time that the first IV/IO bolus of vasopressin was administered during the cardiac arrest event.
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not
Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Total Number of Doses
Enter the total number of IV/IO doses of vasopressin bolus administered during the cardiac arrest event.
If the number of doses is not documented, select "Unknown/Not
Documented."
If IV/IO Epinephrine was not administered within the first five minutes of the event, was there a documented patient, medical, hospital related or other reason for not providing Epinephrine bolus?
- Yes: There is a documented patient, medical, hospital related or other reason for not providing IV/IO Epinephrine Bolus within the first five minutes of the cardiac arrest event.
- No: There are no specific reasons documented in the medical record why IV/IO Epinephrine Bolus was not administered within the first five minutes of the cardiac arrest event.
Notes for Abstraction:
- In order to select "Yes," medical reasons for not providing IV/IO Epinephrine bolus must be documented by a physician, APN, or PA
- For pediatric patients, only select "Yes" to this data element if there is documentation that specifically relates to why an IV/IO Epinephrine bolus was not administered.
Select the specific reason(s) documented in the medical record for not providing IV/IO Epinephrine or Vasopressin bolus within the first five minutes of the cardiac arrest event.
Patient Reason:
- Initial Refusal (e.g. family refused)
Medical Reasons:
- Patient already receiving vasopressor (e.g. Epinephrine) as a continuous IV infusion prior to and during arrest
- Spontaneous Return of Circulation within first 5 minutes of date/time pulselessness was first identified (or the need for chest compressions was first recognized (pediatric only)
- Medication Allergy
Hospital Related or Other Reasons:
- In-hospital time delay (e.g. delay in locating medication)
- No route to deliver medication (e.g. no IV/IO access)
- Other
Notes for Abstraction:
Table of Contents
5.2 Other
Drug Interventions
Select all drug interventions that were used
during the event. There is no limit to the number of
interventions that may be selected.
Note:
Check all drug interventions
that were initiated, or, if already in place immediately prior to an
event, were continued during the event. Because drug interventions in
place immediately prior to an event are often stopped at the onset of
an event, they are not automatically carried forward from the
“Interventions in place just prior to the event” screen(s).
- None – Select only after carefully
reviewing all other drug interventions.
- Antiarrhythmic medication(s); Select
from the following:
- Adenosine/Adenocard
- Amiodarone/Cordarone
- Lidocaine
- Procainamide
- Other (specify)
- Vasopressors other than epinephrine bolus; select from following:
- Dobutamine
- Dopamine > 3 mcg/kg/min
- Epinephrine, IV/IO
continuous infusion of epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
- Phenylephrine
- Other vasopressors (specify)
- Atropine
- Calcium chloride/Calcium gluconate
- Dextrose bolus
- Magnesium sulfate
- Reversal agent (Example
naloxone/Narcan, flumazenil/Romazicon, neostigmine/Prostigmin)
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Other drug interventions (specify)
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only)
Select all drug interventions that were used during the event. There is no limit to the number of interventions that may be selected.
- None - Select only after CARFEULLY reviewing all other drug interventions.
- Atropine
- Fluid Bolus for volume expansion: If selected, please choose the type of fluid bolus from the following list:
- Albumin
- Lactate Ringers
- Normal Saline
- O-negative Blood
- Reversal agent (Example naloxone/Narcan, flumazenil/Romazicon, neostigmine/Prostigmin)
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Other drug interventions (specify)
Table of Contents
5.3 Other
Non-Drug Interventions
Select each intervention that was employed during the
resuscitation event.
- None – Select only after CAREFULLY
reviewing all other non-drug interventions.
- Cardiopulmonary bypass/extracorporeal CPR (ECPR)
- Chest tube(s) inserted
- Needle thoracostomy
- Pacemaker, transcutaneous
- Pacemaker, transvenous or epicardial
- Pericardiocentesis
- Other non-drug interventions (specify)
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only)
Select each intervention from the following list that was employed during the resuscitation event.
- None - Select only after CAREFULLY reviewing all other non-drug interventions.
- Chest tube(s) inserted
- Needle thoracostomy
- Paracentesis
- Pericardiocentesis
- Other non-drug interventions (specify)
Table of Contents
6.1 Event
Outcome
Was ANY documented return of adequate
circulation [ROC] (in
the absence of ongoing chest compressions return of pulse/heart rate by
palpation, auscultation, Doppler, arterial blood pressure waveform, or
documented blood pressure) achieved during the event?
Notes for Abstraction:
- Signs of the return of circulation (ROC) include breathing (more than an occasional gasp), coughing, or movement. For healthcare personnel, signs of ROC also may include evidence of a palpable pulse or a measurable blood pressure.
- Select "Yes" when there is documentation of a palpable pulse or a measurable blood pressure in the absence of chest compressions.
- Select "No/Not Documented" if no pulse is recorded.
Date and time of FIRST adequate return of
circulation (ROC)
Enter the date and time of the first adequate return of circulation. If time not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
(Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only): Enter the date and time when spontaneous heart rate of greater than or equal to 60 Beats per Minute was sustained.
Reason resuscitation ended
- Survived
– ROC: restoration of circulation (including pacemaker or
cardiopulmonary bypass), defined as no further need for chest
compression that was sustained for > 20 minutes.
- Died
– Efforts Terminated, No Sustained ROC: Effort terminated;
the patient did not respond to Advanced Life Support (ALS), unable to
achieve sustained ROC, or there was an advance directive limiting ALS,
or there were restrictions placed by the family of the patient during
the event (i.e., family requested event be terminated).
Date and time sustained ROC began lasting
> 20 min OR resuscitation efforts were terminated (End of event)
Enter date and time chest compressions stopped and did not
resume because it was either the beginning
of the sustained return of circulation lasting > 20 min
(Example:
ROC begins, chest compressions stopped at 1300 and not resumed; ROC is
sustained for > 20 min at 1321. Time event ends is 1300), or
because
of other reasons indicated under "Reason resuscitation ended."
Example: Resuscitation stopped at 2301.) If the time is not documented,
select "Time Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Table of Contents
6.2 Post-ROC
Care
Highest
temperature during first 24 hours after return of circulation (ROC)
If
not documented, select "Temperature Not Documented." If
only one temperature is documented during the first 24 hours after
return of circulation (ROC), enter as highest.
Temperature Units for highest documented
temperature during first 24 hrs after ROC
Select "Celsius" or "Fahrenheit"
to indicate the temperature units.
Site of lowest documented temperature during
first 24 hrs after ROC
- Axillary
- Bladder – (from bladder catheter)
- Blood – from intravascular catheter)
- Brain – (from intraventricular
catheter or ICP monitor)
- Oral
- Rectal
- Surface – (Skin, temporal)
- Tympanic –(Ear)
- Other
- Unknown/Not Documented
Date/Time of highest documented temperature
Enter the date/time of highest documented temperature during
first
24 hours after return of circulation (ROC). If not documented, select "Time
Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Table of Contents
7.1 CPR
Quality
Was performance of CPR monitored or guided using any of the following? (Check all that apply)
- None: Select this option if the performance of CPR was not monitored or guided OR if the method used to monitor or guide performance was not documented.
- Waveform Capnography/End Tidal CO2 (ETCO2)
- Arterial Waveform/Diastolic Pressure
- CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device)
- CPR quality coach
- Metronome
- Other: If "Other" is selected, please also specify the type of monitoring for CPR quality in the free text box.
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Waveform Capnography/End Tidal CO2 (ETCO2)" if there is documentation that exhaled CO2 was used to monitor the quality of CPR. Exhaled (End-tidal) CO2 monitors detect and/or measure the quantity of CO2 at the end of exhalation. There are two general types of exhaled CO2 monitors: (1) Capnography graphically displays a number and/or waveform and (2) Colorimetric systems change colors when exhaled CO2 is detected. Only capnography will qualify here.
- Select "Arterial Waveform/Diastolic Pressure" if an arterial line was in place and there is documentation that arterial line diastolic pressure was used to monitor compression quality during the cardiac arrest event.
- Select "CPR mechanics device" if a device with CPR-sensing and feedback technology was used to measure CPR performance. A device or technology may provide feedback on CPR performance characteristics including chest compression rate, depth, and recoil as well as additional parameters such as chest compression fraction and pre-shock pause. CPR feedback devices may include accelerometers, force transducers or TFI devices (Triaxial Field Induction).
- A "CPR quality coach" includes a trained observer providing qualitative information about the quality of CPR performance via direct observation. This individual would have no other (additional) responsibility with regard to providing event intervention(s).
- Select "Metronome" if metronome guidance was used to provide feedback on CPR performance.
- If another means of monitoring the effectiveness of CPR was used (a method that is not on the above list), please select "Other" and specify the type of monitoring in the free text box.
If CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device) used:
Average compression rate: Enter the average compression rate (per minute) as available from the recording device. If average compression rate is not available from the device, select "Not Documented."
Average compression depth: Enter the average compression depth as available from the recording device. Select mm, cm, or inches. If average compression depth is not available from the device, select "Not Documented."
Compression fraction: Enter the compression fraction (enter number between 0 and 1) as available from the recording device. If compression fraction is not available from the device, select "Not Documented."
Percent of Chest Compressions with complete release: Enter the percent of chest compressions with complete release (enter number between 0 and 100) as available from the recording device. If percent of chest compressions with complete release is not available or cannot be calculated directly from data from the device, select "Not Documented."
Average ventilation rate: Enter the average ventilation rate (per minute) as available from the recording device. If average ventilation rate is not available from the device, select "Not Documented."
Longest pre-shock pause: Enter the longest pre-shock pause (in seconds) as available from the recording device. If longest pre-shock pause is not available from the device, select "Not Documented."
Was a team debriefing on the quality of CPR provided completed after the event?
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select "Yes" if there is documentation that a team debriefing on the quality of CPR provided was completed after the arrest event.
- Debriefing refers to a focused discussion after a cardiac arrest event in which individual actions and team performance are reviewed. It may also include a "group huddle."
- Select "No" if there is documentation that a team debriefing on the quality of CPR provided did not occur after the CPR event.
- Select "Not documented" if there is no documentation regarding a team debriefing on the quality of CPR provided.
Table of Contents
OPTIONAL: 7.2
Resuscitation Related Events and Issues
Indicate the specific issues encountered in each category
from the
selections below and enter written comments with respect to the event.
Universal Precautions
- Universal precautions not followed by all team
members
Documentation
- Signature of code team leader not on code sheet
- Missing other signatures
- Initial ECG rhythm not documented
- Medication route(s) not documented
- Incomplete documentation
- Other (specify in comments section)
Alerting Hospital-wide Resuscitation Response
- Delay
- Pager issue(s)
- Other (specify in comments section)
Airway
- Aspiration Related to Provision of Airway
- Delay
- Multiple Intubation Attempts
- Number of Attempts – Enter the
number of times intubation was attempted. If not available, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
- Delayed recognition of misplacement/displacement
- Intubation attempted, but not achieved
- Other (specify in comments section)
Vascular Access
- Delay
- Inadvertent arterial cannulation
- Infiltration/Disconnection
- Other (specify in comments section)
Chest Compression:
- Delay
- No Board
- Other (specify in comments section)
Defibrillation(s)
- Energy level lower than recommended
- Initial delay, personnel not available to
operate defibrillator
- Initial delay, problem with defibrillator access
to patient
- Initial delay, problem with pad or paddle
placement
- Equipment malfunction
- Given, not indicated
- Indicated, not given
- Other (specify in comments section)
Medication(s):
- Delay
- Route
- Dose
- Selection
- Other (specify in comments section)
Leadership:
- Delay in identifying leader
- Knowledge of equipment
- Knowledge of medications/protocols
- Knowledge of roles
- Team oversight
- Too many team members
- Other (specify in comments section)
Protocol Deviation:
- Advanced Life Support (ALS) / Pediatric Advanced
Life Support (PALS)
- Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP)
- Other (specify in comments section)
Equipment:
- Availability
- Function
- Other (specify in comments section)
Was this cardiac arrest event the patient’s index (first) event (during this hospitalization)?
- Yes: This CPA patient record is being completed for the patient’s first (index) event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation during this hospitalization.
- No: This patient record is being completed for an event that is not the patient’s first event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation during this hospitalization (patient had either an out-of-hospital event that lead to this hospitalization or had a proceeding in hospital event during this hospitalization).
Notes for Abstraction:
- For patients that had an out-of hospital arrest that lead to presentation at either your hospital or an outside hospital (for patients transferred to your facility for further management), select “No.”
- Select “Yes” for patients where the CPA form you are currently filling out is representative of the patient’s first (index) CPA event for this hospitalization.
Comments
Use this memo field to document event-related notes.
Note:
Do not include any personal health information/protected health information (PHI) or any other confidential information in the comments section.
Table of Contents
OPTIONAL: 7.3 Maternal In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
If Recently delivered or currently pregnant was selected under Pre-existing conditions, please select one of the following:
- Patient recently delivered fetus: if fetus was delivered one year within the date of the CPA event please enter the delivery date.
- If patient recently delivered fetus, select delivery date: enter date of delivery here.
- Patient is currently pregnant: if patient is currently pregnant, please select this option.
- If patient is currently pregnant, enter EDC/Due Date: enter the due date or estimated date of confinement.
- Gestational age: this is an auto-calculated field, based on the following formula:40 – ("EDC/Due Date" – "Date/Time need for chest compressions FIRST recognized")/7
Suggested sources: medical history or delivery record.
The patient had the following delivery or pregnancy complications:
Please select all of the documented pregnancy complications below.
- Not Documented
- None
- Alcohol use
- Chorioamnionitis
- Cocaine/Crack use
- Gestational Diabetes
- Diabetes
- Eclampsia
- GHTN (Pregnancy induced/gestational hypertension)
- Hypertensive Disease
- Magnesium exposure
- Major trauma
- Maternal Group B Strep (Positive)
- Maternal infection
- Methamphetamine/ICE use<
- Narcotic given to mother within 4 hours of delivery
- Narcotics addiction and/or on methadone maintenance
- Obstetrical hemorrhage
- Pre-eclampsia
- Prior Cesarean
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
- Other (specify): plesae add any conditions that weren't listed above
Suggested sources: medical history or delivery record
Select number of fetuses:
- Single
- Multiple
- Unknown
- Not Documented
Suggested sources: medical history or delivery record
Total # of pregnancies (gravida): enter the total number of confirmed pregnancies the patient has had, regardless of the outcome.
Total # of deliveries (parity): enter the total number of deliveries, including live and still births. Also include a delivery that occurred during this episode of care.
Suggested sources: medical history or delivery record
Delivery mode (disable if patient is still pregnant)
- Vaginal/spontaneous
- Vaginal/operative
- VBAC
- C-section/scheduled
- C-section/emergent
- Unknown/Not Documented: select if the delivery mode is not documented or the patient has not delivered at the time of the event.
Lateral uterine displacement:
- Yes
- Enter time recognized
- No
- Unknown/Not Documented
Select method (all that apply)
- Manual uterine displacement
- Left lateral tilt
- No
- Not Documented/Unknown
Suggested sources: medical history or delivery record
Neonatal outcome
- Delivered: select if neonate was delivered. Enter neonate Agar scores below.
- Undelivered: select if fetus was not delivered, then select one of the following outcomes:
- IUFD: intrauterine fetal death
- Viable: select if patient contineus to be pregnant after the event
- Not documented/Unknown
If delivered, enter Apgar score
- 1 min
- 5 min
- Unknown/Not Documented
Suggested sources: medical history or delivery record
Was a CPA event completed for the newborn?
- Yes: It is recognized that this information is likely to be available only if the delivery happened during the episode of care.
- No: If there is no CPA record for the newborn, select this option. Also select this option is no fetus was delivered.
Table of Contents
OPTIONAL: 7.4 ECMO / ECPR
This form is set up to collect data on all patients who undergo ECMO during a Resuscitation event. Selecting the Cardiopulmonary bypass/ECMO checkbox means that ECMO intervention was employed during this event - from the GWTG-R CPA form (Section 5.3 - Other Drug Interventions).
E-CPR is the rapid deployment of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) - or cardiopulmonary bypass - to provide immediate cardiovascular and oxygenation support for patients in cardiopulmonary arrest during CPR or within 20 min of compressions being applied. It is also when an extracorporeal membrane oxygenation device is implanted in a pulseless patient to be used as an adjunct to standard cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
ENTRY CRITERIA
INCLUDE:
All patients in the CPA Inclusion Criteria who received an Extra-corporeal Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (ECPR) as an intervention during this event.
EXCLUDE:
Patients in the CPA Exclusion Criteria
Patients who did not receive ECMO
ABSTRACTION GUIDELINES
- Do not enter any personal health information/protected health information (PHI) in any free text "Comments" fields or any Custom Field or historic Optional Fields.
- Make use of the Suggested Sources for Abstraction as a guide to help find medical documentation for each data element. Only abstract data which is clearly documented in the medical records.
- When there is a discrepancy in documentation status or a patient's specific variable, refer to the source of medical higher authority relevant to that variable.
- Date Precisions: Date and Time fields have an additional "Precision" drop-down right above the MM/DD/YYYY HH:MI blanks. The Precision is used to indicate how much of the Date and Time data is known and can be abstracted. For most of the HF Date and Time fields, there are three Precision levels.
- The default level is "MM/DD/YYYY HH:MI". This is used if the entire Date and Time information is available. Time should be entered in 24hr/Military format.

- If the Time is ND, select a Precision of "MM/DD/YYYY". The "HH:MI" blanks will become grayed-out.

- If the Date is ND, select a Precision of "Unknown". The whole "MM/DD/YYYY HH:MI" field will become grayed-out.
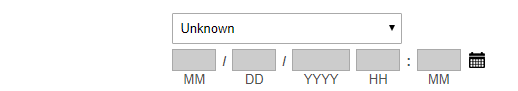
CPA 5.3 OTHER DRUG INTERVENTIONS
Element: Select each intervention that was employed during the resuscitation event:
Definition: Indicate the intervention that was used during this event.
Variable Name: nondrug_none and nondrug_cardiopulmonarybypass
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- None (review options below carefully)
- Cardiopulmonary bypass / ECMO or extracorporeal CPR (ECPR)
Notes for Abstraction:
- If None is selected, do not proceed with this form.
- If Cardiopulmonary bypass / ECMO or extracorporeal CPR (ECPR) is selected, it means that ECMO intervention was employed during this resuscitation event and the rest of the form should be completed in its entirety (except in disabled/greyed-out sections).
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Was ECPR process activated? (Required)
Definition: Indicate if Extra-corporeal Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (ECPR)/ECMO process was activated as an intervention during this event.
Variable Name: ecprocact
Field Type: Single Select
Format: Checkbox
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select only if ECMO/ECPR was activated.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Is there an ELSO record for this patient?(OPTIONAL)
Definition: Indicate if an ELSO record was created for this patient during this arrest/ECMO run.
Variable Name: elsorec
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction: Select Yes only if the ELSO record was created for this arrest/ECMO run, and NOT for prior ECMO runs.
- Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO) maintains a registry of ECMO use in active ELSO centers.
- If your site is an active ELSO center, there may be an ELSO number set up for the patient.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: If yes, enter ELSO Patient Record Number (optional)
Definition: If yes was selected in the previous question above, this element indicates a patient record number unique to the patient and assigned at designated active ELSO centers.
Variable Name: elsorecnum
Format: Integer
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction: Record the ELSO record number for this patient if this information is available. This number is created for patients undergoing ECMO at sites designated as ELSO centers. The number uniquely identifies each patient in the ELSO registry.
NOTE:
- If the site is not an ELSO center and/or has not created an ELSO record number for the patient, then this section can be left blank.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Was Cannulation Attempted?
Definition: Indicate if there was an attempt at cannulation during this event - whether it was successful for not.
Variable Name: canulatmpt
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select Yes if cannulation was attempted
- Select No if there was no attempt at cannulation
- Select No/ND if an attempt at cannulation is unknown or not documented.
- There is a separate question that requires specification as to whether this procedure was successful or not. This one, however, is to show if the process was tried at all, no matter the outcome.
Supporting Definition:
Suggested Data Sources:
Element: Was Cannulation Successful?
Definition: If cannulation was attempted or started, indicate whether the process was successful or not.
Variable Name: canulsuc
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Yes
- No
- Unknown/ND
- Cannulation Initiated but Not Completed
Notes for Abstraction:
- If No is selected here, there's no requirement to continue with the rest of the form. The rest of the questions will be disabled.
- The next set of questions will only be enabled when Yes is selected.
Supporting Definition:
Suggested Data Sources:
Element: Date/Time ECMO Started (REQUIRED)
Definition: Indicates the Date/Time the ECMO started - (when flow was initiated).
Variable Name: ecmostartdt
Format: Date
Allowable Values:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Date: MM = Month (01-12)
- Date: DD = Day (01-31)
- Date: YYYY = Year (2012-Current Year)
- Time: 24 Hour Clock (Military Time)
- Date: HH = Hour (00-23)
- Date: MM = Minutes (00-59)
Notes for Abstraction: Enter the Date/Time ECMO device was connected and pump with blood flow started. This is a required field and refers to the time that extracorporeal blood flow was established through cannulas attached to an ECMO circuit.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Date/Time ECMO Ended (REQUIRED)
Definition: Indicates the Date/Time the ECMO flow was completed/stopped.
Variable Name: ecmoenddt
Format: Date
Allowable Values:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Date: MM = Month (01-12)
- Date: DD = Day (01-31)
- Date: YYYY = Year (2012-Current Year)
- Time: 24 Hour Clock (Military Time)
- Date: HH = Hour (00-23)
- Date: MM = Minutes (00-59)
Notes for Abstraction: Enter the Date/Time ECMO stopped/ended.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Initial Extracorporeal Life Support Mode (Check All that Apply)
Definition: This field collects ECMO mode at the start of the procedure. It specifies the mode of drainage and return of blood in the extracorporeal system.
Variable Name: initlimode
Format: Multi-Select
Allowable Values:
- Venoarterial ECMO
- Venovenous ECMO
- Veno-Venoarterial ECMO
- AVECCO2R
- VVECCO2R
- Other ______________
- Unknown/ND
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select the primary cannulation configuration at the start of the ECMO procedure. If multiple cannulas were placed, select all the options applied during this event.
- Specify in "Other" if another mode was used, different from the ones listed.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Cannulation Anatomical Site (Check All that Apply)
Definition: Indicate the anatomical site where a cannula was placed. (See Appendix for abbreviations/acronyms)
Variable Name: canulselect
Format: Multi-Select
Allowable Values:(See Appendix for Abbreviations)
- RCCA - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- LCCA - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- RIJV - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- RIJVC - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- LIJV - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- RFA - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- LFA - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- RFV - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- LFV - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- LSA - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- LSV - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- RSA - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- RSV - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- Other - Percutaneous? Yes/No
- Aorta
- LA
- PA
- RA
- Unknown/ND
Notes for Abstraction:
- With each choice of an anatomical site, a "Yes/No" must also be selected to indicate if the cannula was done percutaneously (through the skin) or not - EXCEPT for Aorta, LA, PA and RA, which cannot be cannulated percutaneously.
- The "Yes/No" options are for each corresponding anatomical site selected.
- More than one anatomical site may be selected.
- "Other" indicates a site/vessel that is not listed.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: ECMO Cannulation Location (area)
Definition: Indicate the location (in the facility) where the procedure was performed.
Variable Name: ecmocanloc
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Ambulatory/Outpatient Area
- Adult Coronary Care Unit (CCU)
- Adult ICU
- Cardiac Catheterization Lab
- Delivery Suite
- Diagnostic/Intervention. Area (excludes Cath Lab)
- Emergency Department (ED)
- Inpatient Area
- Neonatal ICU (NICU)
- Newborn Nursery
- Operating Room (OR)
- Pediatric ICU (PICU)
- Pediatric Intensive Care Unit
- Post-Anesthesia Recovery Unit (PACU)
- Rehab, Skilled Nursing, or Mental Health Unit/Facility
- Same-day Surgical Area
- Telemetry unit or Step-down unit
- Other (Specify) ______________
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction: N/A
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Team Member(s) Performing ECMO Cannulation:
Definition: Indicate the team member(s) performing the ECMO cannulation. More than one title(s) may be selected where applicable.
Variable Name: ecmocanteam
Format: Multi-Select
Allowable Values:
- Surgeon
- Intensivist
- Anesthesiologist
- Other
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: ECMO circuit priming (select all that apply):
Definition: Indicate what was used in the circuit priming.
Variable Name: ecmocircrys
Format: Multi-Select
Allowable Values:
- Crystalloid
- Saline
- Plasma-Lyte
- Other Crystalloid ____________
- 5% or 25% Albumin
- Plasma
- RBC
- Whole Blood
- Other (Specify) ______________
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction: If Crystalloid is selected, the type of crystalloid used must be specified if the information is available.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Date/Time Series - Rate of Blood Flow (4 hours after cannulation)
Definition: Indicate the date and time that extracorporeal blood flow was flowing through an ECMO circuit at 4 hours after the successful cannulation. Include the rate at which the blood was flowing (mL/minute).
Variable Name: ecmodt
Format: Date and Integer
Allowable Values:
- Date/Time: ____/____/_______ ____:____
(DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM)
- Blood Flow _______
(mL/minute)
- Blood Flow
- ND
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Date/Time Series - Rate of Blood Flow (24 hours after cannulation)
Definition: Indicate the date and time that extracorporeal blood flow was flowing through an ECMO circuit at 24 hours after the successful cannulation. Include the rate at which the blood was flowing (mL/minute).
Variable Name: ecmodt1_24
Format: Date and Integer
Allowable Values:
- Date/Time: ____/____/_______ ____:____
(DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM)
- Blood Flow _______
(mL/minute)
- Blood Flow
- ND
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Date/Time Series - Fraction of Oxygen (4 hours after cannulation)
Definition: Indicate the date, time and fraction of oxygen (FsO2 or FdO2) via oxygenator at 4 hours after the successful cannulation.
Variable Name: ecmodt3
Format: Date and Integer
Allowable Values:
- Date/Time: ____/____/_______ ____:____ , FsO2 _______
(DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM)
- ND
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Date/Time Series - Fraction of Oxygen (24 hours after cannulation)
Definition: Indicate the date, time and fraction of oxygen (FsO2 or FdO2) via oxygenator at 24 hours after the successful cannulation.
Variable Name: ecmodt4
Format: Date and Integer
Allowable Values:
- Date/Time: ____/____/_______ ____:____ , FsO2 _______
(DD/MM/YYYY HH:MM)
- ND
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Head CT Performed?
Definition: Indicate if Computed tomography (CT) of the head was done.
Variable Name: ecmohd
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Yes
- No
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: If Yes, enter Date/Time CT Performed (for first CT post-cannulation if multiple CTs were performed):
Definition: Indicate the first Date and Time a head CT scan was done after cannulation.
Variable Name: ecmoctdt
Format: Date
Allowable Values:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Date: MM = Month (01-12)
- Date: DD = Day (01-31)
- Date: YYYY = Year (2012-Current Year)
- Time: 24 Hour Clock (Military Time)
- Date: HH = Hour (00-23)
- Date: MM = Minutes (00-59)
Notes for Abstraction: ECMO patients can have more than one CT scan. This should be the date/time of the first scan after cannulation. Add comments to indicate if more than one CT scan was done.
Supporting Definition: Head CT scans are usually performed on ECMO patients to assess the frequency of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) and infarction during the treatment. Multiple studies help to reveal or exclude severe intracranial complications where ECMO treatment should be discontinued.
Suggested Data Sources:
Element: Cerebral MRI Performed?
Definition: Indicate if Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed.
Variable Name: ecmomri
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Yes
- No
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: If Yes, enter Date/Time Cerebral MRI performed (for first MRI post-decannulation if multiple MRIs were performed):):
Definition: Indicate the date and time the first MRI was done after decannulation.
Variable Name: ecmomridt
Format: Date
Allowable Values:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Date: MM = Month (01-12)
- Date: DD = Day (01-31)
- Date: YYYY = Year (2012-Current Year)
- Time: 24 Hour Clock (Military Time)
- Date: HH = Hour (00-23)
- Date: MM = Minutes (00-59)
Notes for Abstraction:
- More than one MRI scan can be done.
- This should be the first MRI scan after decannulation.
- Add notes/comments to indicate if multiple MRI scans were done.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: Neurologic injury or events detected during ECMO or after ECMO (Less than 6 weeks after separation from ECMO or by Hospital Discharge, which ever one comes first). (check all that apply):
Definition: Indicate any neurologic injuries or complications that were detected during this ECMO event, or within 6 weeks of separation from ECMO.
Variable Name: ecmonuro
Format: Multi-Select checkbox and Date
Allowable Values:
- None
- Anoxic Brain Injury - Date/Time detected: ____/____/_______ ____:____
- Date/Time Unknown
- Not Documented
- Brain Death - Date/Time detected: ____/____/_______ ____:____
- Date/Time Unknown
- Not Documented
- Cerebral Microbleeds - Date/Time detected: ____/____/_______ ____:____
- Date/Time Unknown
- Not Documented
- Intracranial Hemorrhage - Date/Time detected: ____/____/_______ ____:____
- Date/Time Unknown
- Not Documented
- Ischemic Stroke - Date/Time detected: ____/____/_______ ____:____
- Date/Time Unknown
- Not Documented
- New Clinical Seizure(s) - Date/Time detected: ____/____/_______ ____:____
- Date/Time Unknown
- Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
- For each complication please enter a Date and Time.
- If the date/time is unknown, select "Date/time Unknown/ND". If the date/time was not document, select "Not Documented".
- This element is to assess Neurologic Injuries identified during or after ECMO.
- Record injuries detected less than 6 weeks after separation from ECMO, or those detected by the date of hospital discharge - whichever comes first.
- Reminder: There should ALWAYS be a discharge Cerebral Performance Category (CPC/PCPC).
- Imaging and physician notes regarding neurologic injury/events could be done in parallel at the time of discharge, with the review of information needed to determine the discharge of CPC/PCPC.
Supporting Definition:
- Some of these patients may be in the hospital for very long periods of time. The date/time series captured here is needed to ascertain if this injury/complication might be linked to the arrest/ECPR event.
- For Neurologic Injury:
- Ischemic Stroke refers to arterial ischemic territorial stroke (e.g., middle cerebral artery stroke).
- Intracranial Hemorrhage can include intraventricular hemorrhage, intraparenchymal hemorrhage as well as extra-axial hemorrhage (e.g., subdural hematoma, epidural hematoma, subarachnoid hemorrhage).
- Cerebral Microbleeds refers to diffuse intraparenchymal microbleeds.
Suggested Data Sources:
- Imaging Notes
- Physician Notes
Element: Date/Time ECMO Ended
Definition: Indicates the Date/Time the ECMO was completed/stopped.
Variable Name: ecmoned
Format: Date
Allowable Values:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Date: MM = Month (01-12)
- Date: DD = Day (01-31)
- Date: YYYY = Year (2012-Current Year)
- Time: 24 Hour Clock (Military Time)
- Date: HH = Hour (00-23)
- Date: MM = Minutes (00-59)
Notes for Abstraction: Enter the Date/Time ECMO stopped/ended.
Supporting Definition:
Suggested Data Sources:
Element: EEG performed within in first 24 hours post-ROC?
Definition: Indicate if electroencephalography (EEG) was done within the first 24 hours after return of circulation.
Variable Name: eegperf
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Yes
- No
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: If EEG was performed, was there an indication of electrographic seizure activity?
Definition: Indicate if any electrographic seizure(s) were detected during the EEG.
Variable Name: eegseizind
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Yes
- No
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
Supporting Definition: The EEG is specifically done to detect electrographic seizure activity. Electrographic seizures occurs in some ECMO patients thereby requiring EEG monitoring for identification. Seizures during ECMO have also been associated with cerebral injury and worse outcomes in some patients.
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
Element: If EEG was performed, was an antiepileptic administered?
Definition: Indicate if an antiepileptic was administered to the patient during the ECMO course.
Variable Name: eegantcons
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Yes
- No
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
- Do not select Yes for an antiepileptic that was part of home medications prior to the current hospital admission and if the type and dose of antiepileptic was not changed.
- Do select Yes for any NEW antiepileptic administered during the ECMO course, or if there were dose increases for home antiepileptic.
Supporting Definition: N/A
Suggested Data Sources: N/A
APPENDIX
V-V: Veno-venous support is the application of extracorporeal circulation primarily for respiratory support, in which the extracorporeal circuit drains blood from the venous system and reinfuses into the venous system (or pre-lung). VV ECMO operates in series with the heart and lungs and does not provide bypass of these organs.
V-A: Veno-arterial is the application of extracorporeal circulation often for cardiac or circulatory support, in which the extracorporeal circuit drains blood from the venous system and returns into the systemic arterial system. Without qualification, V-A ECMO refers to support that returns blood to the systemic arterial system, operating in parallel with and providing partial or complete bypass of, the heart and lungs.
V-VA Veno-venoarterial is a hybrid configuration of V-V and V-A extracorporeal support in which the extracorporeal circuit drains blood from the venous system and reinfuses into both the venous and systemic arterial systems. V-VA ECMO provides both pulmonary (V-V component) and cardiac support (V-A component) in patients with combined cardiopulmonary failure.
A-VCO2R Arteriovenous carbon dioxide removal (A-VCO2R) is the provision of pumpless carbon dioxide exchange through the use of an extracorporeal circuit consisting of an artificial lung, and venous and arterial vascular access cannulas using lower blood flows. Blood flow is driven by the patient's arteriovenous pressure gradient.
V-V ECCO2R Venovenous extracorporeal carbon dioxide removal (V-V CO2R) is the provision of carbon dioxide exchange through the use of an extracorporeal circuit consisting of a blood pump, artificial lung, and venous drain and venous return cannulas using lower blood flows Other Indicates a support not listed
Anatomical Site Abbreviations:
| RCCA - Right Common Carotid Artery | RA - Right Atrium |
| LCCA - Left Common Carotid Artery | LA - Left Atrium |
| RIJV - Right Internal Jugular Vein | LV - Left Ventricle |
| RIJVC - Right Internal Jugular Vein Cephalic | LPV - Left Pulmonary Vein |
| LIJV - Left Internal Jugular Vein | PA - Pulmonary Artery |
| RFA - Right Femoral Artery | LSA - Left Subclavian Artery |
| LFA - Left Femoral Artery | LSV - Left Subclavian Vein |
| RFA - Right Femoral Artery | RSA - Right Subclavian Artery |
| LFV - Left Femoral Vein | RSV - Right Subclavian Vein |
Table of Contents
Acute
Respiratory Compromise (ARC) Event
ARC Inclusion Criteria
All patients*, visitors, employees, and staff within the
facility
campus (inpatient areas and ambulatory areas adjacent to the hospital
and surrounding areas).
- Who experience Acute Respiratory Compromise
(ARC), defined as absent, agonal or inadequate respiration
that requires emergency assisted ventilation1
including NEWBORNS receiving at least 2 minutes of assisted
ventilation; 2,3
AND
- The event elicits EITHER a hospital-wide (e.g.,
for general inpatient area) or unit-based (ICU, ED, OR, PACU, delivery
room, newborn nursery, etc.) emergency response
by acute care facility personnel.4
* No minimum hospital stay is required.
- Events must be emergent (e.g.,
elective tracheal intubation for procedure is not included).
- Assisted ventilation is non-invasive
(e.g., mouth-to-mouth,
mouth-to-barrier device, bag-valve-mask, mask/nasal, CPAP/BiPAP) or via
invasive airway (e.g., endotracheal/tracheostomy tube, laryngeal mask
airway) positive (or negative) pressure ventilation. Does not include
nasal cannula, face mask, hood or tent oxygen or oral/nasopharyngeal
airway.
- Events in delivery room, newborn
nursery and neonatal ICU requiring CPAP that do not proceed to
intubation are not included (see exclusion criteria).
- Patient who fails extubation in
PACU, OR, or ICU would not be included, unless an organized team emergency
response
is elicited. Also not included is elective intubation without Acute
Respiratory Compromise (e.g., for CT scan, shock, control of
intracranial pressure).
ARC Exclusion Criteria
The following are excluded:
- Events beginning outside the facility campus, including
during transport to and from the facility.
- ARC stabilized prior to ED arrival
- ARC resuscitation ongoing and continued in ED after
arrival
- ARC resuscitation restarted in ED after arrival prior to
achieving
>20 minutes sustained ROSV (return of spontaneous ventilation)
or
control of ventilation .5,6,7
- Events beginning within the facility campus with response
by facility
first-responders, but ongoing resuscitation transferred to EMS
personnel (e.g., fire, paramedic, ambulance).
- Events in delivery room, newborn nursery and neonatal ICU
requiring CPAP that do not proceed to intubation.
- Events that are not emergency assisted ventilation. 8
- Pre-hospital events are not
considered ‘ended’ until the patient has sustained >20 minutes
ROSV
or control of ventilation. For example, patient stabilized 5 minutes
prior to ED arrival and requires additional ARC resuscitation
interventions 7 minutes after ED arrival would be considered a single,
ongoing event.
- If a subsequent ARC event
occurs in the ED after ROSV or control of ventilation sustained for
>20 minutes, the ARC event is included.
- If the ARC event progresses to a CPA
event, the CPA event is included.
- For example, an elective tracheal
intubation for a patient who needs
deep sedation/intubation for an MRI or CT scan. If that same patient
was emergently intubated for a deterioration in mental status and
transported to CT scan then the patient would be included.
ARC End of Event Definition
Acute Respiratory Compromise ends:
- With return of spontaneous ventilation (ROSV) that is
sustained for > 20 min.
OR
- With control of ventilation with assisted ventilation that
is sustained for > 20 min either:
a. non-invasively (includes
mask
CPAP/BiPAP, nasal CPAP/BiPAP, negative pressure ventilation; excludes
manual bag-valve-mask ventilation)
OR
b. via an invasive airway(e.g., endotracheal/tracheostomy
tube)
- With transfer of newborn out of the delivery room (usually
to Newborn Nursery [NBN], Neonatal ICU [NICU] or Operating Room), when
transfer occurs prior to 20 minutes of spontaneous ventilation (ROSV)
or controlled ventilation.
OR
- When event progressed to CPA; or ARC interventions
terminated because of advance directive.
Note:
Any event that follows after ROSV or control of ventilation > 20
min is defined as a new event.
Table of Contents
OPTIONAL: Local Event ID
This field provided for those facilities using pre-numbered
event
records or another internal event numbering system who wish to include
that reference in their Get With The Guidelines® - Resuscitation
record. Do not enter any personal health information/protected health information (PHI) into this field.
Date/Time the need for emergency assisted
ventilation was first recognized
Enter the date and time that the need emergency assisted
ventilation
was first recognized either by monitoring or direct observation. If the
time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Table of Contents
2.1
Pre-Event Data
OPTIONAL: Was patient discharged from an
Intensive Care Unit (ICU) prior to this ARC event?
OPTIONAL: If yes, enter the date the patient
was admitted to non-ICU unit after ICU discharge PRIOR to this ARC
event.
OPTIONAL: Was patient discharged from a
Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) within 24 hours prior to this ARC
event?
OPTIONAL: Was patient in the ED within 24 hours
prior to this ARC event?
OPTIONAL: Did patient receive
conscious/procedural sedation or general anesthesia within 24 hours
prior to this ARC event?
OPTIONAL:
Enter up
to 4 sets of vital signs taken in the 4 hours
prior to the ARC event (Date, Time, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure,
Respiratory Rate, SpO2, Temperature).
- If
there are more than 4 sets of vital signs taken in the 4 hours prior to
the ARC event, take the 4 complete sets that were taken closest to
the event.
- If
in the 4 hours prior to the ARC event you have a combination
of complete (Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, Respiratory Rate, SpO2, and
Temperature) and incomplete vital signs
(missing one or more of the data elements) you may enter incomplete
vital signs.
- Note:
If no vital signs were taken in the 4 hours prior to the ARC
event, enter the last documented set of vital signs with date and time
prior to the ARC event. If no vital signs are available,
select “None Documented”
- Note
: If systolic blood pressure was obtained via Doppler or pulse, leave
the diastolic blood pressure field blank.
Table of Contents
2.2
Pre-Existing Conditions (This section is
OPTIONAL)
OPTIONAL: Pre-existing conditions at time of
the event (check all that apply)
Select only conditions that existed prior to the event. For those conditions where there is a time interval indicated, only respond affirmatively if the diagnosis is made prior to the ARC event for which you are completing the event form. There is
no
limit on the number of conditions that you can select, so you should
select all of the conditions that apply.
Note:
The following list is specific
to certain conditions of particular interest to Get With The
Guidelines® - Resuscitation and is not meant to be an exhaustive list
of all possible pre-existing conditions. Example:
EMS identifies Hypotension at 0100 at a patient's home, arrives at the
ED at 0130 and the patient arrests at 0200. "Hypotension" should be
selected from the list below (within 4 hours).
- None – Select this option only if
there are no documented pre-existing conditions found in the list below.
- Acute CNS non-stroke event –
Select if there was evidence of decreased mental status, delirium, or
coma not due to acute stroke within 4 hours up to time of the event.
- Acute stroke
– Select if there is a documented diagnosis during this hospitalization of stroke, ischemic stroke, or hemorrhagic stroke. Do not select "acute stroke" here if the patient has a documented past medical history of stroke prior to this admission. This response is meant to capture new onset strokes.
- Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Acyanotic
, (pediatric
and newborn/neonate patients only), such
as
- Aortic Stenosis
- Coarctation of the Aorta
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
- Septal Defects
- Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Cyanotic
, (pediatric
and newborn/neonate patients only), such
as
- Tetralogy of Fallot (TET)
- Total Anolmalous Pulmonary Venous Connection (TAPVC or
TAPVR)
- Truncus
Arteriosus
- Hypoplastic Left Heart
- Transposition of the Great Vessels
- Congenital Malformation/Abnormality (non-cardiac)
, (pediatric
and newborn/neonate patients only), such
as
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Tracheal-esophageal fistula
- Known/suspected chromosomal/genetic abnormality – (e.g.,
trisomy 21, 13, 18)
- Congestive heart failure (this admission)
– Select if there is documentation of newly diagnosed congestive heart failure
during this admission and prior to this ARC event.
- Hypotension/hypoperfusion – Select
if there was evidence of hypotension within 4 hours up to the time of
the event, defined by ANY of the following:
- Adult [18+]:
- SBP < 90 or MAP < 60 mmHg.
- Vasopressor/inotropic requirement after volume
expansion (except for dopamine ≤ 3 mcg/kg/min).
- Intra-aortic balloon pump
- Pediatric [< 18]:
- SBP < 5 th percentile for age, less than [70 +
2 x age in years] for age < 10.
- MAP < 5 th percentile for age.
- Vasopressor/inotropic requirement after volume
expansion (except for dopamine ≤ 3 mcg/kg/min).
- Newborn/Neonate:
- Documentation/evidence of symptomatic
hypotension/hypoperfusion.
- Major trauma
– Select if there was evidence of multi-system injury or single system
injury associated with shock or altered mental status during this admission and prior to this ARC event.
- Pneumonia – Select if there
is a documented diagnosis of active pneumonia, where antibiotics have
not yet been started or the pneumonia is still being treated with
antibiotics.
- Sepsis – Select if there is documentation indicating treatment and/or evidence of sepsis. The presence of bacteria (bacteremia), other infectious organisms, or toxins created by infectious organisms in the bloodstream with spread throughout the body. Sepsis may be associated with clinical symptoms of systemic illness, such as fever, chills, malaise, low blood pressure, and mental-status changes.
Required: Active or Suspected bacterial or viral infection at admission or during hospitalization
Definition: Indicate if the patient was confirmed or suspected to have Active or Suspected Bacterial or Viral infection at admission or during hospitalization.
Format: Multi-Select (check box)
Allowable Values:
- None
- Bacterial infection
- Emerging Infectious Disease
- SARS-COV-1
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19)
- MERS
- Other Emerging Infectious Disease
- Influenza
- Seasonal cold
- Other viral infection
Notes for Abstraction:
- Influenza (ICD-10-CM code J09.X2 - Flu due to identified novel influenza A virus with other respiratory manifestations)
Select Emerging Infectious Disease when the patient was confirmed or suspected to have:
- SARS-COV-1 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus) (may include ICD-10-CM code B97.21); or
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus) (may include ICD-10-CM code U07.1); or
- MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) (may include ICD-10-CM code B97.29); or
- Other Emerging Infectious Disease
Select one of the Allowable Values options when a confirmed or suspected diagnosis is documented by the provider or when a test result is documented in the patient medical record.
- A confirmed diagnosis includes (but is not limited to) a positive laboratory test provided at a local/state level prior to confirmation from the CDC or when a positive test result is documented in the patient medical record.
- A suspected diagnosis involves instances where the patient meets all the criteria necessary to be considered a Patient Under Investigation, with signs, symptoms, exposure and travel history. Include any documentation by the provider stating if the test was "suspected", "possible", "probable" or "inconclusive" infection.
If the patient is suspected but no lab test has been done, you can record the diagnosis assigned by the hospital's clinical criteria.
Optional: Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) donned by the responders?
Definition: Indicate if Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) was donned by the responders to prevent Transmission-based Precautions. These precautions are designed for patients with confirmed or suspected infections with pathogens for which additional precautions beyond Standard Precautions are needed.
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- The additional PPE's in this instance is specifically to limit the exposure of healthcare workers to pathogens while caring for patients suspected or confirmed to have an Emerging Infectious Disease.
- Additional PPE does NOT include PPE'S worn during Standard Procedures or when applying Standard Precautions, but when Transmission-based Precautions are applied (i.e., Contact Precautions, Droplet Precautions, and Airborne Precautions) to prevent transmission of an infectious agent that is not interrupted by standard precautions alone. These might include:
- Masks/Respirators designed to protect the wearer - e.g. N95 or higher-level respirators (FFP, N99/N100 etc.), a mask with attached shield or a full-face shield, goggles, or visor.
- Coveralls, Isolation/Surgical gowns, or long-sleeved disposable fluid-resistant gown.
- Select Yes when there is documentation in the patient medical record that PPE in addition to the standard protocol/practice was donned by the responders during this event and/or a hospital policy at the time of this event required additional PPE as standard practice.
- Select No/ND if there was no documentation of the additional PPE or a hospital policy regarding additional PPE was not in place at the time of the event.
Optional: Pre-Existing Conditions
- Select Emerging Infectious Disease when the patient is known or suspected to have any of the following in their medical history. This does NOT include a current infection:
- SARS-CoV-1 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus); or
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus); or
- MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome); or
- Other Infectious Respiratory Pathogen.
- Select History of vaping or e-cigarette use in the past 12 months if there is documentation in the patient medical record of current vaping or e-cigareete use by the patient or anytime during the past 12 months. Do not select if there is no documentation of use or the history includes prior to the past 12 months.
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Check box (checked for Yes, unchecked for No)
Notes for Abstraction:
- Check the box on this question if there is documentation in the patient medical record of current vaping or e-cigarette use by the patient during the past 12 months.
- Leave the box unchecked if there is no documentation of use or the history includes use prior to the past 12 months.
Vaping and e-cigarette use includes electronic nicotine delivery system or electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), which are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid containing nicotine, propylene glycol, and/or vegetable glycerin and flavorant chemicals to generate an aerosol that the user inhales, or heat-not-burn tobacco products, which are tobacco products that heat tobacco to a lower temperature than required for combustion.
Reference: Dehmer GJ, Badhwar V, Bermudez EA, Cleveland JC Jr, Cohen MG, D'Agostino RS, Ferguson TB Jr, Hendel RC, Isler ML, Jacobs JP, Jneid H, Katz AS, Maddox TM, Shahian DM. 2020 AHA/ACC key data elements and definitions for coronary revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Data Standards (Writing Committee to Develop Clinical Data Standards for Coronary Revascularization). Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020;13:e000059. doi: 10.1161/HCQ.0000000000000059
Table of Contents
2.3
Interventions Already in Place
Intervention(s) ALREADY IN PLACE when the need
for emergency assisted ventilation was first recognized (check all that
apply).
Select each intervention that was already in
place
at the time of the event. There is no limit to the number of
interventions that you can select, so you should select all
interventions that apply. To make a selection, click in the check box
to the right of the intervention name.
Part A:
- Non-invasive Assisted ventilation –
- Bag-Valve-Mask
- Mask and/or Nasal CPAP
- Mouth-to-Barrier Device
- Mouth-to-Mouth
- Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA)
- Other Non-Invasive Ventilation: (specify)
Note to Abstractors: Bag valve mask should only be selected if the patient is not intubated or is extubated and the 'Mask' is used to ventilate the patient. It should not be selected if the bag valve device is used in conjunction with an ET tube or Tracheostomy tube.
- Intra-arterial catheter
- Conciouss/procedural sedation
- End Tidal CO2 (ETCO2) Monitoring
- Supplemental oxygen (cannula, mask, hood, or tent)
- Invasive assisted ventilation
- Endotracheal Tube (ET)
- Tracheostomy Tube
- Select Method(s) of confirmation used to ensure correct placement of Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube placement in trachea (check all that apply):
- Waveform capnography (waveform ETCO2)
- Capnometry (numeric ETCO2)
- Exhaled CO2 colormetric monitor (ETCO2 by color change)
- Esophageal detection devices
- Revisualization with direct laryngoscopy
- None of the above
- Not Documented
Monitoring (specify):
Vascular Access
- Yes:
Select this option when vascular access was already
in place when the need for emergency assisted ventilation was first
recognized. This would include:
- Peripheral
- Central
vein
- Intraosseous
(IO)
- Umbilical
vein (UVC)
- Umbilical
artery (UAC)
- No/Not
Documented: Select this option when no vascular access was already in
place when the need for emergency assisted ventilation was first
recognized or if there is no documentation around vascular
access. If vascular access was not obtained until after the
need for emergency assisted ventilation was recognized, select No/Not
documented.
None – Select this option when no "Part A" interventions were in place when the need for chest compressions and/or defibrillation was first recognized.
OPTIONAL: Part B:
- None – Select this option when no
"Part B"
interventions were in place when the need for chest compressions and/or
defibrillation was first recognized.
- Chest tube(s) – Tube thoracostomy.
- Inhaled nitric oxide therapy –
(newborn/neonate)
- Prostaglandins (continuous infusion –
newborns/neonates)
- Supplemental oxygen – Via nasal
cannula, face mask, hood or tent.
- Other prior interventions in place
– Select this option when an intervention is present that does not
appear on the list.
Table of Contents
3.1
Event
Age at Event
Enter the age of the patient at the time of the event and
indicate "hour(s)", "day(s)", "week(s)", "month(s)", or year(s). If
Date of Birth and Event Date have
been provided, the age will be automatically derived.
Estimated
Select if age is estimated by hospital staff.
Note: If age is not
documented and CANNOT be estimated, select "Age Unknown/Not
Documented."
Subject Type
Enter the subject’s relationship with the hospital at the
time of the event onset. Valid entries:
- Ambulatory/Outpatient (includes
same-day surgical)
- Emergency Department
- Hospital Inpatient
(includes Rehab, Skilled Nursing and Mental Health ‘wards, floors or
units’within a hospital. Some hospitals have rehab, SNF, mental health
units or adjacent facilities to which patients are ‘admitted’ (separate
from acute care hospital admission) where the code team responds. In
these instances, Rehab Facility Inpatient, SNF Inpatient or Mental
Health Facility inpatient should be selected. If the event occurs on a
rehab or skilled nursing or mental health 'ward' (acute care
admission), then Hospital Inpatient should be selected.)
- Rehab Facility Inpatient
- Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Inpatient
- Mental Health Facility Inpatient
(psychiatric, substance abuse )
- Visitor or Employee – Includes all
healthcare personnel and all other non-patients.
Note:
Some hospitals have rehab,
SNF, mental health units or adjacent facilities to which patients are
‘admitted’ (separate from acute care hospital admission) where the code
team responds. In these instances, Rehab Facility Inpatient, SNF
Inpatient or Mental Health Facility inpatient should be selected. If
the event occurs on a rehab or skilled nursing or mental health 'ward'
(acute care admission), then Hospital Inpatient should be selected.
Illness Category
Enter the most appropriate illness category at the time of
the event onset.
- Medical-Cardiac – Patient with a
primary diagnosis of medical illness that is cardiovascular at the time
of the event.
- Medical-Noncardiac – Patient with a
primary diagnosis of medical illness at the time of the event that is
not cardiovascular.
- Surgical-Cardiac – Patient who is
post-operative following cardiac surgery at the time of the event.
- Surgical-Noncardiac
– Patient who is pre-operative or post-operative with a surgical
illness as the primary diagnosis that is not cardiac surgery at the
time of the event.
- Obstetric – Obstetric patient
(before, during or after delivery) at the time of the event.
- Trauma – Patient with single or
multiple trauma as the primary diagnosis at the time of the event.
- Other (visitor/employee…) – Neither
in-patient nor outpatient, but a visitor or employee at the time of the
event.
Event
Location (area)
Select the patient’s location (or type of area) in the
hospital
when the need for emergency assisted ventilation was recognized.
- Ambulatory/Outpatient Area
- Adult Coronary Care Unit (CCU)
- Adult ICU (includes medical, surgical,
cardiovascular, trauma, burn… ICUs)
- Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory
- Delivery Suite
- Diagnostic/Intervention Area (excludes Cardiac
Catherization Lab) – Radiology, Nuclear Medicine, EEG,
ECHO, Stress testing, and others.
- Emergency Department
- General Inpatient Area – Excluding
Telemetry units and Step-down units.
- Neonatal ICU (NICU)
- Newborn Nursery
- Operating Room
- Pediatric ICU (PICU) – (includes
medical, surgical, cardiovascular, trauma, burn…ICUs). As of April, 2014, this response excludes the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit.
- Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (PCICU)
- Post Anesthesia Recovery Room (PACU)
- Rehab, Skilled Nursing or Mental Health
Unit/Facility
- Same-day Surgical Area
- Telemetry Unit or Step-Down Unit
- Other
- Unknown/Not Documented
Note:
Some hospitals have Rehab,
Skilled Nursing or Mental Health areas or adjacent facilities to which
patients are ‘admitted’ (separate from acute care hospital admission)
where the code team responds.
Event Location (name)
Type or select the hospital-specific unit or area name or
number
where the patient was located at the time of the ARC event. Some
examples of unit names include: Surgical ICU, Medical ICU, CVT ICU,
CCU-acute, CCU-step-down, Neonatal CCN, Neonatal ICU, Newborn Nursery
East, 3West, Angiography, CT scan, Cardiac Catheterization lab,
Ambulatory Unit A, on-campus rehab facility.
Note:
This is a dynamic list of
location names that is specific to the selected location area. As new
names are added (manually entered), they become available in the menu
for that particular “location area” for future records. For example, if
“CCU #1” is typed in and saved in record 1, it will appear in the list
for record 2.
Event Witnessed?
Indicate if the onset of the acute respiratory compromise
event was
directly observed by someone (family, lay bystander, employee or health
care professional). This differs from “monitored.”
Was the patient conscious when the need for
emergency assisted ventilation was first identified?
Indicate if the patient was conscious at the onset of the
acute respiratory compromise.
Was the patient breathing when the need for
emergency assisted ventilation was first identified?
Was the patient breathing when the need for emergency
assisted ventilation was first identified?
- Yes – Breathing; or has respiratory
distress, but has intact respiratory effort even if weak or inadequate.
- No – There are no signs of
breathing.
- Agonal – Reflex gasping respiratory
efforts.
- Assisted Ventilation – Receiving
assisted ventilation (non-invasive or invasive).
- Unknown/Not Documented
Rhythm when the need for emergency assisted
ventilation was first identified
What was the first documented rhythm
when the need for emergency assisted ventilation was first identified? The rhythm can be documented by anyone who identifies or records
rhythm, not necessarily team or ALS provider. For the unmonitored
patient, select the first rhythm identified when monitor applied.
- Accelerated idioventricular rhythm (AIVR)
– Wide
complex ventricular arrhythmia with no antegrade P waves, rate 60-100.
If rate < 60 with pulse, code as bradycardia; if rate >
100 with
pulse, code as ventricular tachycardia (VT) with pulse.
- Bradycardia
- Pacemaker
- Sinus – Includes sinus tachycardia.
- Supraventricular tachyarrhythmia (SVTarrhy)
– Includes atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, atrial tachycardia,
supraventricular tachycardia.
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT) with pulse
- Unknown/Not Documented
Was a hospital-wide resuscitation response
activated?
Did patient become apneic or respirations
agonal at ANY time during the ARC event?
Date and time patient became apneic or
respirations became agonal
If the patient became apneic or respirations agonal at any
time
during the resuscitation event, enter the date and time apnea or agonal
respirations were first recognized. If the time is not documented,
select “Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Table of Contents
4.1 Ventilation
Type(s) of Ventilation/Airway(s) USED During
the event, including those already in place (check all that apply).
Select each type of ventilation/airway used during the event.
There is no limit on the number of types that may be selected.
- None: Select this
option if no assisted ventilation/artificial airway was used during the event.
- Unknown/Not Documented: Select this
option if assisted ventilation/artificial airway was used but the type is not documented.
- Assisted
Ventilation/Artificial Airways used (select all that apply):
- Bag-Valve-Mask
- Mask
and/or Nasal CPAP/BiPAP
- Mouth-to-Barrier
Device
- Mouth-to-Mouth
- Other
Non-Invasive Ventilation (specify)
- Laryngeal
Mask Airway (LMA)
- Endotracheal
Tube (ET)
- Tracheostomy
Tube
Note to Abstractors: Bag valve mask should only be selected if the patient is not intubated or is extubated and the 'Mask' is not used to ventilate the patient. It should not be selected if the bag valve device is not used in conjunction with an ET tube or Tracheostomy tube.
Date and Time of FIRST emergency assisted
ventilation during the event (non-invasive or invasive)
Enter the date and time of the first emergency assisted
ventilation during the event. If the time is not documented, select “Time
Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Was
any Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube inserted/re-inserted
during the event?
- Yes
– Initial intubation and/or reintubation achieved during
the event using ET or tracheostomy tube
- No
– No intubation and/or reintubation was achieved during the
event using ET or tracheostomy tube or tube was already in
place
Note:
If insertion attempted, but not
achieved, select "No" and you may indicate this in section ARC 7.1
Resuscitation Related Events and Issues
Note:
If initial Intubation and/or Reintubation is selected, the following
are required/enabled:
Date
and Time Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube inserted if not
already in place and/or re-inserted during event
If an Endotracheal
Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy Tube was inserted or reinserted
during the event, enter the date and time of achievement, not when the
first attempt was made. If the time is not documented, select “Time
Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Method(s)
of confirmation used to ensure correct placement of Endotracheal Tube
(ET) or Tracheostomy Tube (check all that apply):
- Exhaled
CO2
- Waveform
capnography (waveform ETCO2): Monitor shows waveform as well as number
- Capnometry
(numeric ETCO2): Monitor shows number, but NOT waveform display of ETCO2
- Exhaled
CO2 colorimetric monitor (ETCO2 by color change): Device changes color
(e.g. from purple to yellow) but no number nor waveform is displayed
- Esophageal
detection devices
- Revisualization
with direct laryngoscopy
- None
of the above – Select this option when confirmation was performed and method documented but was not done using any of the above methods. Select this option if only auscultation is performed/documented or if no device confirmation was documented as performed.
- Not
Documented – Select this option when confirmation
was documented as performed (other than just auscultation), but the method
of confirmation is not documented
Table of Contents
5.1 Other
Interventions
Drug Interventions
Select all drug
interventions that were used during the event.
There is no limit to the number of interventions that may be
selected.
Note:
Check all drug interventions that
were initiated, or, if already in
place immediately prior to an event, were continued during the event.
Note:
Because drug interventions in place
immediately prior to an event are
often stopped at the onset of an event, they are not automatically
carried forward from the “Interventions in place just prior to the
event” screen(s).
- None – Select only after carefully
reviewing all other drug interventions.
- Bronchodilator – Inhaled
- Bronchodilator – Subcutaneous or
Intravenous/Intraossesous (IV/IO) (e.g., epinephrine, isoproterenol,
terbutaline, albuterol).
- Calcium chloride/Calcium gluconate
- Dextrose bolus
- Fluid bolus for volume expansion
- Magnesium sulfate
- Neuromuscular blocker/muscle relaxant
- Prostaglandin E 1
(PGE)
- Reversal agent – (Example:
naloxone/Narcan, flumazenil/Romazicon, neostigmine/Prostigmin)
- Sedative/induction agent
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Other drug interventions (specify) :
Non-Drug Interventions
Select each non-drug intervention that was
employed during the resuscitation event.
- None – Select only after CAREFULLY
reviewing all other non-drug interventions.
- Central venous catheter/PICC inserted
– including the placement of an Umbilical Venous Catheter (UVC)
- Chest tube(s) inserted
- Needle thoracostomy
- NG/OG Tube
- Thoracentesis
- Tracheostomy/cricothyrotomy – Placed
during event.
- Tracheostomy change/replacement
- Other non-drug interventions (specify):
Table of Contents
6.1 Event
Outcome
Note:
Return of spontaneous ventilation questions are activated only when
patient experiences apnea or agonal respirations.
Was ANY return of
spontaneous respiration
documented during the event (excluding agonal or gasping respiration)?
Select either “Yes” or
“No/Not Documented ”
to indicate if there was any return of spontaneous respiration achieved
during the event – including through invasive airway. Agonal and
gasping respirations are excluded.
Date and time of FIRST return of spontaneous
respiration
Enter the date and time of the first return of respiratory
effort
(excluding agonal or gasping respirations) in a patient previously
apneic or with agonal breathing. If the time is not documented, select
“Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Reason Acute Respiratory Compromise event ended
Select the reason that the event ended.
- Return of spontaneous ventilation (ROSV) (no further need
for assisted ventilation) that is sustained for >20 min.
- Example: Spontaneous
ventilation returns at 1400, requiring no further intervention that is
sustained at 4121, > 20 min. Event ends at 1400.
OR
- Control of ventilation with assisted ventilation that is
sustained for >20 min
a. Non-invasively (includes mask CPAP/BiPAP, nasal
CPAP/BiPAP, negative
pressure ventilation; excludes manual bag-valve-mask ventilation)
OR
b. Via an invasive airway (e.g.,endotracheal/tracheostomy
tube).
OR
- With transfer of newborn
out of the delivery room (usually to Newborn Nursery [NBN], Neonatal
ICU [NICU] or Operating Room), when transfer occurs prior
to 20 minutes of spontaneous ventilation (ROSV) or controlled
ventilation.
OR
- Progressed to Cardiopulmonary Arrest (CPA); or ARC
interventions terminated because of advance directive.
Note:
Any event that follows after ROSV/ or control of ventilation >
20 min is defined as a new event.
Example: ARC event begins at
1725. Endotracheal
tube is successfully placed at 1730. At 1755 endotracheal tub becomes
dislodged. Patient is reintubated at 1757. At 1755 when endotracheal
tube became dislodged, ventilation had been controlled for 25 min; this
event therefore ends at 1730. When endotracheal tube becomes dislodged
at 1755 this starts a new event.
Does CPA Portion of Event Meet Get With The
Guidelines® -
Resuscitation Inclusion Criteria (i.e., received chest compressions
and/or defibrillation of VF or Pulseless VT)?
- Yes
- No, not being entered (e.g., DNAR)
Date and time ARC event ended by any of the
reasons listed above
Enter date and time of the BEGINNING of sustained ROSV or
control
of ventilation , or need for chest compression and/or defibrillation
(CPA) first identified , or ARC interventions terminated because of
advance directive . If the time is not documented, select
“Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
- Example: Control of
ventilation with assisted ventilation begins at 1500 that is sustained
at 1521, > 20 min. Event ends at 1500.
- Example: Emergency assisted
ventilation begins at 1720 for ARC. CPA follows at 1725. Event ends at
1725.
- Example:
Neither sustained ROSV nor sustained control of ventilation has
occurred at 0835, but efforts terminated because of advance directive.
Event ends at 0835.
Table of Contents
7.1
Resuscitation Related Events and Issues
Quality Improvement Issue(s)
Indicate the specific issues encountered in each category
from the
selections below and enter written comments with respect to the event.
Universal Precautions
- Universal precautions not followed by all team
members
Documentation
- Signature of code team leader not on code sheet
- Missing other signatures
- Initial ECG rhythm not documented
- Medication route(s) not documented
- Incomplete documentation
- Other (specify in comments section)
Airway
- Aspiration Related to Provision of Airway
- Delay
- Multiple Intubation Attempts
- Number of Attempts – Enter the number
of times intubation was attempted. If not available, select
“Unknown/Not Documented”
- Delayed recognition of misplacement/displacement
- Intubation attempted, but not achieved
- Other (specify in comments section)
Vascular Access
- Delay
- Inadvertent arterial cannulation
- Infiltration/Disconnection
- Other (specify in comments section)
Medication(s):
- Delay
- Route
- Dose
- Selection
- Other (specify in comments section)
Leadership:
- Delay in identifying leader
- Knowledge of equipment
- Knowledge of medications/protocols
- Knowledge of roles
- Team oversight
- Too many team members
- Other (specify in comments section)
Protocol Deviation:
- Advanced Life Support (ALS) / Pediatric Advanced
Life Support (PALS)
- Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP)
- Other (specify in comments section)
Equipment:
- Availability
- Function
- Other (specify in comments section)
Comments
Use this field to document event-related notes.
Note:
Do not include any personal health information/protected health information or other confidential information in the comments section.
Table of Contents
Medical
Emergency Team (MET) Event
MET
Inclusion Criteria
All patients*, visitors, employees, and staff within the
facility
(in inpatient areas and ambulatory areas adjacent to the hospital and
surrounding areas) for whom the Medical Emergency Team (MET) is
activated. The MET may also be called by other names, such as Medical
Emergency Team, Medical Emergency Response Team, Rapid Response Team,
Critical Care Outreach Team, or Condition Critical Team. It is an
assigned team that often consists of a critical care / emergency nurse
and physician, and a respiratory care practitioner. The team response
is triggered by abnormalities in patient physiology, a subjective
concern on the part of the staff, or family/visitor concerns as defined
by a facility’s activation policies or procedures.
MET Exclusion Criteria
No MET responses are excluded.
Table of Contents
OPTIONAL: Local Event ID
This field provided for those facilities using pre-numbered
event
records or another internal event numbering system who wish to include
that reference in their Get With The Guidelines® - Resuscitation
record. Do not enter any personal health information/protected health information (PHI) into this field.
Date/Time the MET was activated
Enter the date and time that the MET was activated.
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Note:
If the time is not documented, select the MM/DD/YYY option in the online dropdown and check off "Time Not Documented."
Table of Contents
2.1
Pre-Event Data
Was patient discharged from an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) at any point during this admission and prior to this MET call?
- Yes: During this admission the patient was discharged from an ICU prior to this MET call.
- No: Patient was not discharged from an ICU at any point prior to this MET call.
Notes for Abstraction:
- The intent of this data element is to determine whether the patient was discharged from an ICU at any point during their admission and prior to the current MET call.
- Abstract "Yes" if the patient was discharged from an ICU prior to the MET call for which this MET event form is being completed.
Note: ICU includes all Critical Care areas (e.g., ICU, CCU, NICU, PICU,
etc.)
Was patient discharged from an Intensive Care
Unit (ICU) within 24 hrs prior to this MET call?
Notes for Abstraction:
- The intent of this data element is to determine whether the patient was discharged from an ICU within 24 hours prior to the current MET call.
- For patients with multiple ICU stays within a single admission, abstract "Yes" only if the patient was discharged from an ICU within 24 hours prior to the MET call for which this MET event form is being completed.
- If a patient was discharged from an ICU during this admission, but greater than 24 hours prior to this MET call, answer "No."
Was patient discharged from a Post-Anesthesia
Care Unit (PACU) within 24 hours prior to this MET call?
Was patient in the ED within 24 prior to this
MET call?
Did patient receive conscious/procedural
sedation or general anesthesia within 24 hours prior to this MET call?
Enter all vital signs taken in the last 4 hours
prior to this MET
event (Date, Time, Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, Respiratory Rate,
SpO2 (select either 'Room Air' or 'Supplemental O2 (oxygen)'), Temperature).
Note: If no vital signs were taken in the 4 hours prior to the MET
activation, enter the last documented set of vital signs with date and
time prior to the MET activation. If no vital signs are available,
select "Pre-Event VS Unknown/None Documented." If select vital signs are available, enter the available data and select "ND" for only those vital signs that are not documented.
Note: If blood pressure was obtained via Doppler or pulse, leave the
diastolic blood pressure field blank and override the data quality edit
check.
Neurological Assessment – AVPU Scale (most recent within last 4 hours prior to this MET event):
Enter the most recent AVPU Scale recorded within the last 4 hours prior to this MET event.
Notes for Abstraction:
- The AVPU scale has four possible outcomes: Alert, responsive to Voice, responsive to Pain, or Unresponsive.
- If the AVPU scale has not been documented in the medical record, but sufficient information is available from physician or nursing notes, and/or other sources, to allow an AVPU scale to be assigned retrospectively, the retrospectively assigned scale may be entered here.
- If the AVPU scale is not documented and cannot be assigned based on medical record documentation, then select "Not documented."
- AVPU Scale:
- Alert - a fully awake (although not necessarily oriented) patient. This patient will have spontaneously open eyes, will respond to voice (although may be confused) and will have bodily motor function.
- Responsive to Voice - the patient makes some kind of response when you talk to him/her, which could be in any of the three component measures of eyes, voice or motor - e.g. patient's eyes open on being asked "Are you OK?". The response could be as little as a grunt, moan, or slight move of a limb when prompted by the voice of the rescuer.
- Responsive to Pain - the patient makes a response on any of the three component measures on the application of pain stimulus, such as a central pain stimulus like a sternal rub or a peripheral stimulus such as squeezing the fingers. Patients with some level of consciousness (a fully conscious patient would not require a pain stimulus) may respond using their voice, by moving their eyes or through moving part of their body (including abnormal posturing)
- Unresponsive - Sometimes seen noted as 'Unconscious', this outcome is recorded if the patient does not give any eye, voice or motor response to voice or pain.
Table of Contents
2.2
Pre-Existing Conditions
Required: Active or Suspected bacterial or viral infection at admission or during hospitalization
Definition: Indicate if the patient was confirmed or suspected to have Active or Suspected Bacterial or Viral infection at admission or during hospitalization.
Format: Multi-Select (check box)
Allowable Values:
- None
- Bacterial infection
- Emerging Infectious Disease
- SARS-COV-1
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19)
- MERS
- Other Emerging Infectious Disease
- Influenza
- Seasonal cold
- Other viral infection
Notes for Abstraction:
- Influenza (ICD-10-CM code J09.X2 - Flu due to identified novel influenza A virus with other respiratory manifestations)
Select Emerging Infectious Disease when the patient was confirmed or suspected to have:
- SARS-COV-1 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus) (may include ICD-10-CM code B97.21); or
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus) (may include ICD-10-CM code U07.1); or
- MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome) (may include ICD-10-CM code B97.29); or
- Other Emerging Infectious Disease
Select one of the Allowable Values options when a confirmed or suspected diagnosis is documented by the provider or when a test result is documented in the patient medical record.
- A confirmed diagnosis includes (but is not limited to) a positive laboratory test provided at a local/state level prior to confirmation from the CDC or when a positive test result is documented in the patient medical record.
- A suspected diagnosis involves instances where the patient meets all the criteria necessary to be considered a Patient Under Investigation, with signs, symptoms, exposure and travel history. Include any documentation by the provider stating if the test was "suspected", "possible", "probable" or "inconclusive" infection.
If the patient is suspected but no lab test has been done, you can record the diagnosis assigned by the hospital's clinical criteria.
Optional: Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) donned by the responders?
Definition: Indicate if Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) was donned by the responders to prevent Transmission-based Precautions. These precautions are designed for patients with confirmed or suspected infections with pathogens for which additional precautions beyond Standard Precautions are needed.
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
Notes for Abstraction:
- The additional PPE's in this instance is specifically to limit the exposure of healthcare workers to pathogens while caring for patients suspected or confirmed to have an Emerging Infectious Disease.
- Additional PPE does NOT include PPE'S worn during Standard Procedures or when applying Standard Precautions, but when Transmission-based Precautions are applied (i.e., Contact Precautions, Droplet Precautions, and Airborne Precautions) to prevent transmission of an infectious agent that is not interrupted by standard precautions alone. These might include:
- Masks/Respirators designed to protect the wearer - e.g. N95 or higher-level respirators (FFP, N99/N100 etc.), a mask with attached shield or a full-face shield, goggles, or visor.
- Coveralls, Isolation/Surgical gowns, or long-sleeved disposable fluid-resistant gown.
- Select Yes when there is documentation in the patient medical record that PPE in addition to the standard protocol/practice was donned by the responders during this event and/or a hospital policy at the time of this event required additional PPE as standard practice.
- Select No/ND if there was no documentation of the additional PPE or a hospital policy regarding additional PPE was not in place at the time of the event.
Optional: Pre-Existing Conditions
- Select Emerging Infectious Disease when the patient is known or suspected to have any of the following in their medical history. This does NOT include a current infection:
- SARS-CoV-1 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus); or
- SARS-COV-2 (COVID-19) (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome-associated coronavirus); or
- MERS (Middle East Respiratory Syndrome); or
- Other Infectious Respiratory Pathogen.
- Select History of vaping or e-cigarette use in the past 12 months if there is documentation in the patient medical record of current vaping or e-cigareete use by the patient or anytime during the past 12 months. Do not select if there is no documentation of use or the history includes prior to the past 12 months.
Format: Single Select
Allowable Values:
- Check box (checked for Yes, unchecked for No)
Notes for Abstraction:
- Check the box on this question if there is documentation in the patient medical record of current vaping or e-cigarette use by the patient during the past 12 months.
- Leave the box unchecked if there is no documentation of use or the history includes use prior to the past 12 months.
Vaping and e-cigarette use includes electronic nicotine delivery system or electronic cigarettes (e-cigarettes), which are battery-operated devices that heat a liquid containing nicotine, propylene glycol, and/or vegetable glycerin and flavorant chemicals to generate an aerosol that the user inhales, or heat-not-burn tobacco products, which are tobacco products that heat tobacco to a lower temperature than required for combustion.
Reference: Dehmer GJ, Badhwar V, Bermudez EA, Cleveland JC Jr, Cohen MG, D'Agostino RS, Ferguson TB Jr, Hendel RC, Isler ML, Jacobs JP, Jneid H, Katz AS, Maddox TM, Shahian DM. 2020 AHA/ACC key data elements and definitions for coronary revascularization: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Data Standards (Writing Committee to Develop Clinical Data Standards for Coronary Revascularization). Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes. 2020;13:e000059. doi: 10.1161/HCQ.0000000000000059
Table of Contents
3.1
Event
Date/Time of Birth
This field will be auto-populated in the online form from data entered into the Admission and Discharge form.
Enter the patient's date and time of birth. If DOB unknown or not documented, select "DOB Unknown/Not Documented", if time is unknown select "Time Not Documented." Note: In the online form, time is only available for response if the patient is "born this admission (or transferred from birth hospital)."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Age at Event
Enter the age of the patient at the time of the event and
indicate “hour(s)”, “day(s)”,
“week(s)”, “month(s)”, or “year(s)”.
If Date of Birth and Event Date have been provided, the age will be
automatically derived.
Estimated
Select if age is estimated.
Note:
If age is not documented and cannot be estimated, select “Age
Unknown/Not Documented.”
Date/Time 1st MET Team Member Arrived
Enter the date and time the first MET team member arrived. If
the time is not available, select “Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Date/Time Last MET Team Member Departed
Enter the date and time the last MET team member departed
regardless of their role in caring for the patient. If the time is not available, select "Time Not Documented."
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
Example:
- 12:00 MET team is activated
- 12:01 MET team arrives
- 12:05 Code team is activated (but MET members are also
part of code team)
- 12:15 After being successfully resuscitated, the patient is
transferred
to ICU and team members are released. The time the last MET team member
departed would bet 12:15.
Subject Type
Enter the subject's relationship with the hospital at the time of the event onset. Valid entries:
- Ambulatory/Outpatient (includes same-day surgical)
- Emergency Department
- Hospital Inpatient – (includes Rehab, Skilled Nursing and Mental Health 'wards, floors or units' within a hospital )
- Rehab Facility Inpatient
- Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Inpatient
- Mental Health Facility Inpatient (psychiatric, substance abuse)
- Visitor or Employee – Includes all healthcare personnel and all other non-patients.
Note: Some hospitals have rehab, SNF, mental health units or adjacent facilities to which patients are 'admitted' (separate from acute care hospital admission) where the code team responds. In these instances, Rehab Facility Inpatient, SNF Inpatient or Mental Health Facility inpatient should be selected. If the event occurs on a rehab or skilled nursing or mental health 'ward' (acute care admission), then Hospital Inpatient should be selected.
Illness Category
Enter the most appropriate illness category at the time of
the event onset.
- Medical-Cardiac – Patient with a
primary diagnosis of medical illness that is cardiovascular at the time
of the event.
- Medical-Noncardiac – Patient with a
primary diagnosis of medical illness at the time of the event that is
not cardiovascular.
- Surgical-Cardiac – Patient who is
post-operative following cardiac surgery at the time of the event.
- Surgical-Noncardiac
– Patient who is pre-operative or post-operative with a surgical
illness as the primary diagnosis that is not cardiac surgery at the
time of the event.
- Obstetric – Obstetric patient
(before, during or after delivery) at the time of the event.
- Trauma – Patient with single or
multiple trauma as the primary diagnosis at the time of the event.
- Other (visitor/employee…) – Neither
in-patient nor outpatient, but a visitor or employee at the time of the
event.
Event Location (area)
Select the patient's location (or type of area) in the hospital when the need for chest compression and/or defibrillation was recognized.
- Ambulatory/Outpatient Area
- Adult Coronary Care Unit (CCU)
- Adult ICU (includes medical, surgical, cardiovascular, trauma, burn...ICUs)
- Cardiac Catheterization Laboratory
- Delivery Suite – (includes Labor room (LDRP), obstetrical operating room, newborn stabilization space)
- Diagnostic/Intervention Area (excludes Cath Lab) – Radiology, Nuclear Medicine, EEG, ECHO, Stress testing, and others.
- Emergency Department
- General Inpatient Area – Excluding Telemetry units and Step-down units.
- Neonatal ICU (NICU)
- Newborn Nursery
- Operating Room
- Pediatric ICU (PICU) – (includes medical, surgical, cardiovascular, trauma, burn...ICUs). As of April, 2014, this response excludes the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit.
- Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit (PCICU)
- Post Anesthesia Recovery Room (PACU)
- Rehab, Skilled Nursing or Mental Health Unit/Facility
- Same-day Surgical Area
- Telemetry Unit or Step-Down Unit
- Other
- Unknown/Not Documented
Note:
Some hospitals have Rehab, Skilled Nursing or Mental Health areas or adjacent facilities to which patients are 'admitted' (separate from acute care hospital admission) where the code team responds.
Event Location (name)
Type or select the hospital-specific unit or area name or
number
where the patient was located at the time of the event. Some examples
of unit names include: CCU-step-down, Newborn Nursery East, 3West,
Angiography, CT scan, Cardiac Catheterization lab, Ambulatory Unit A,
on-campus rehab facility.
Note:
This is a dynamic list of
location names that is specific to the selected location area. As new
names are added (manually entered), they become available in the menu
for that particular “location area” for future records. For example, if
“3 West” is typed in and saved in record 1, it will appear in the list
for record 2.
Vital Signs at
Time of Event
Enter patient’s heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate,
SpO 2 (select either 'Room Air' or 'Supplemental O2' (oxygen)) and temperature at the time the MET was activated. If one or all vital signs at the time of the event are not documented, select "Unknown/Not documented."
Table of Contents
3.2
MET Activation Triggers
Triggers Initiating MET Activation (record all
that apply)
Based on your hospitals pre-defined set of MET
triggers/conditions,
select the most appropriate triggers/conditions from the list below.
There is no limit to the number of conditions that may be selected.
- Trigger Unknown/Not Documented –
Select this option when you are unable to determine the condition(s)
that triggered this MET activation.
Respiratory:
- Respiratory Depression
- Tachypnea
- New onset of difficulty breathing
- Decreased oxygen saturation
- Other respiratory: If selected, please indicate the specific other respiratory activation trigger in the free text box.
Cardiac:
- Bradycardia
- Tachycardia
- Hypotension
- Hypertensiveurgency/emergency
- Chest pain
- Other cardiac: If selected, please indicate the specific other cardiac activation trigger in the free text box.
Neurological:
- Mental status change
- Unexplained agitation or delirium
- Decreased responsiveness
- Acute Loss of Consciousness (LOC)
- Seizure
- Suspected acute stroke
— Examples: new onset of unilateral paralysis, unilateral numbness,
language disturbance, monocular blindness, vertigo, or ataxia.
- Other neurological: If selected, please indicate the specific other neurological activation trigger in the free text box.
Medical:
- Acute decrease in urine output
- Critical lab abnormality – Example: rising lacate to >4 mEq/L
- Excessive bleeding
- Elevated risk factor score – If selected, please specify the risk factor scale and score (example: MEWS (Modified Early Warning Score) = 5)
- Uncontrolled pain
- Other medical: If selected, please indicate the specific other medical activation trigger in the free text box.
Other:
- Staff member acutely worried about patient.
- Family member/patient activated
- Other: If selected, please indicate the specific other activation trigger in the free text box.
Table of Contents
4.1
Interventions
Check all interventions initiated during the MET event.
- None – Select this response if no drug interventions were initiated during the MET event.
- Albumin (Examples: albumin injection, Albumin, Albuminar, Buminate, Plasbumin)
- Antibiotic (IV)
- Antihistamine (IV) (Examples: Benadryl, diphenhydramine)
- Aspirin
- Antiarrhythmic Agent(s) (Examples:
Adenosine/Adenocard, Amiodarone/Cordarone, Lidocaine, Procainamide)
- Anti-Epileptic (Examples:
Phenytoin/Dilantin, lorazepam/Ativan, diazepam/Valium,
midazolam/Versed)
- Atropine
- Diuretic (IV) (Example:
Furosemide/Lasix)
- Epinephrine – If selected, please also choose the delivery route from inhaled racemic, IM, SQ, or IV
- Fluid Bolus (IV)
- Glucose bolus – Select this response if a glucose bolus was initiated during the MET event in the absence of insulin administration.
- Inhaled Bronchodialator
(Examples: salbutamol,albuterol,
metaproterenol, ipratropium/albuterol.)
- Insulin / Glucose – Select this response if patient was given insulin and required a glucose bolus within the hour for hypoglycemia or was given insulin and glucose for hyperkalemia.
- Nitroglycerin – If selected, please also choose the delivery route from IV or SL
- Reversal Agent (Examples:
naloxone/Narcan, flumazenil/Romazicon, neostigmine/Prostigmin)
- Sedative (Examples: midazolam/Versed, lorazepam/Ativan, Haldol)
- Steroids
- Vasoactive Agent Infusion (not bolus) (Examples: Dobutamine, Dopamine > 3 mcg/kg/min, Epinephrine,
Norepinephrine, Phenylephrine)
- Other Drug Intervention(s): Other text – If “Other”
is selected, enter the other drug intervention(s).
Table of Contents
4.2
Non-Drug Interventions
Note:
Check all interventions that
were initiated, or, if already in place immediately prior to the event,
were continued during the event.
Respiratory Management:
- Supplemental O2
- Suctioning
- Non-Invasive Ventilation – Select this option if non-invasive ventilation was initiated or continued during the event. This would include a bag-valve-mask, CPAP/BiPAP, Nasal Airway, Oral Airway, or another form of non-invasive ventilation.
- Bag-Valve-Mask
- Mask CPAP/BiPAP – If 'mask CPAP/BiPAP' is selected, please also indicate if the mask was already in place immediately prior to the event (and continued during the event) or if it was newly initiated during the MET event.
- Nasal Airway
- Oral Airway
- Other Non-Invasive Ventilation – If selected, please specify the type of non-invasive ventilation used in the free text box
- Invasive Ventilation – Select this option if invasive ventilation was initiated or continued during the event. This would include Endotracheal Tubes, Tracheostomy Tubes, or other.
- Endotracheal Tube (ET) – If Endotracheal Tube (ET) is selected, please also indicate if the ET was already in place immediately prior to the event (and continued during the event) or if it was inserted/re-inserted during the MET event.
- Tracheostomy Tube – If Tracheostomy Tube is selected, please also indicate if the Tracheostomy tube was already in place immediately prior to the event (and continued during the event) or if it was inserted/re-inserted during the MET event.
- Other Invasive Ventilation – If selected, please specify the type of invasive ventilation used in the free text box
If Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy tube placed during MET event, method(s) of confirmation used to ensure correct placement of ET or Tracheostomy Tube (check all that apply):
- Exhaled CO2
- Waveform capnography (waveform ETCO2): Monitor shows waveform as well as number
- Capnometry (numeric ETCO2): Monitor shows number, but NOT waveform display of ETCO2
- Exhaled CO2 colorimetric monitor (ETCO2 by color change): Device changes color (e.g. from purple to yellow) but no number nor waveform is displayed
- Esophageal detection devices: Any device that relies on the ability to readily aspirate gas in the lower airways.
- Revisualization with direct laryngoscopy
- None of the above – Select this option when confirmation was performed and method documented but was not done using any of the above methods. Select this option if only auscultation is performed/documented.
- Not Documented – Select this option when confirmation was documented as performed (other than just auscultation), but the method of confirmation is not documented
Monitoring:
For response selected, also indicate if "continued," meaning the intervention was already in place immediately prior to the event and continued during the event OR "initiated," during the event.
- Apnea/bradycardia
- Continuous ECG/Telemetry
- Continuous pulse oximetry
- Other continuous monitoring – If selected, please also indicate the type of other continuous monitoring in the free text box.
Vascular access:
For each response selected, also indicate if "already in place" meaning the intervention was already in place immediately prior to the event and continued during the event OR "place during the MET event."
- Central vein
- Peripheral vein
- Intraosseous (IO)
- Other vascular access – If selected, please also indicate the type of other vascular access in the free text box.
Stat Consult:
- Critical Care
- Other Stat Consult – If selected, please also indicate the type of other stat consult in the free text box.
Other Interventions initiated during the event:
Note: Only select other interventions from the list below if the intervention was initiated during the MET event.
- 12 lead ECG
- Cardioversion/Pacing
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Imaging
- Nedside Cardiac Ultrasound (Echo)
- Chest X-ray
- Head CT (stat)
- Neonatal Head Ultrasound
- STAT labs
- Transfusions of blood products
- Other Non-Drug Interventions – If selected, please also indicate the type of other non-drug interventions initiated during the event in the free text box.
Table of Contents
5.1
MET Outcome
Did patient require emergency assisted
ventilation for
acute respiratory compromise (ARC) or chest compressions and/or
defibrillation for cardiopulmonary arrest (CPA) during the MET event?
- No
- Yes, Acute Respriatory Compromise (ARC) event
- Yes, Cardiopulmonary Arrest (CPA) event
Did the ARC event meet Get With The Guidelines®
- Resuscitation Inclusion Criteria?
- Yes
- No (e.g. DNAR)
- N/A (not collecting ARC data in Get With The
Guidelines® - Resuscitation)
Did the CPA event meet Get With The Guidelines®
- Resuscitation Inclusion Criteria?
- Yes
- No (e.g. DNAR)
- N/A (not collecting CPA data in Get With The
Guidelines® - Resuscitation)
Patient Transferred To:
- Not Transferred (remained on unit)
- ICU (Example: Critical care areas,
including coronary care (e.g., ICU, CCU, Neonatal ICU, Pediatric ICU…)
- Post-MET ICU Length of Stay For This ICU Admission (days)
- Cardiac Catheterization/Lab
- Telemetry/Step-Down
- Operating Room
- Emergency Department
- Other Hospital
- Other (please specify if selected)
Did patient die during event?
Was MET response scope limited by
patient/family end of life decisions or physician decision of medical
futility?
Indicate if therapy was limited by patient/family end of life decisions or medical futility.
Was patient made DNAR during MET event?
Table of Contents
6.1
Review of MET Response
Select the specific issues encountered during the MET
response.
- No/Not Documented
- MET trigger(s) present, but team not immediately activated MET Response Delay
- Incorrect team activated
- MET response delay
- MET criteria/process not known or misunderstood by those calling MET MET communication system not working (e.g., phone, operator, pager)
- Other (specify)
- Essential Patient Data Not Available
- Incomplete or inaccurate information communicated
- Medication Delay
- Equipment Issue: (specify equipment)
- Function Issues Between MET and Other Caregivers/Departments
- Prolonged MET Event Duration
Table of Contents
7.1
Comments
Use this memo field to document event-related notes.
Note:
Do not include any confidential information or patient identifiers in the comments section.
Table of Contents
Post Cardiac Arrest Care (PCAC)
General
Information
This form is intended to capture post cardiac arrest care provided to
both out of hospital and in-hospital cardiac arrest event
patients. Sites are encouraged to enter 100% of appropriate
patients.
The following can be included:
- Patients who survived an out of hospital cardiac arrest
event.
- Patients who survived an in-hospital cardiac arrest event
that occurred within your facility.
- Patients who survived an in-hospital cardiac arrest event
that occurred at an outside facility and who were then transferred to
your hospital for continued management of that event.
- Patients in whom therapeutic hypothermia was induced.
If more than 1 cardiac arrest event occurred, the data from the initial/first
event (requiring chest compressions and/or
defibrillation) should always be used when completing this form. This
holds true for both cooled and non-cooled patients with multiple arrest
events. Note, if completing this form on an out of hospital
arrest patient that then re-arrests in the hospital the data entered
here should be for the initial/first event and will differ from that
entered on the CPA form.
Example:
A patient with pre-hospital CPA is stabilized in the field with ROSC at
10:00. The patient arrives to your ED at 10:10. The
patient again requires chest compressions and/or defibrillation in the
ED at 10:30. Data collection should be based off of the
initial pre-hospital CPA event.
Example:
A patient with an in-hospital CPA is stabilized with ROSC at 13:00 and
again requires chest compressions and/or defibrillation at
13:36. Data collection should be based off of the initial
in-hospital CPA event.
Example:
A patient with an out of hospital CPA is stabilized with ROSC at
15:00. Active cooling is not initiated. The patient
again requires chest compressions at 17:00 for a repeat event at which
point a therapeutic hypothermia protocol is initiated. Data
collection should be based off of the initial out of hospital CPA event
(ROSC at 15:00)
Intro
Where did the
event occur?
Select where the FIRST event requiring chest compressions and/or
defibrillation occurred.
- Out of hospital:
The first event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation
began outside the facility campus, including during transport to and
from the facility.
- In-hospital: The
first event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation occurred
within the facility campus (including inpatient areas and ambulatory
areas adjacent to the hospital and surrounding areas). This
event should also be entered into GWTG-Resuscitation CPA form.
Notes for Abstraction:
- If more than 1 cardiac
arrest event occurred, the location of the initial event (requiring
chest compressions and/or defibrillation) should be used in completing
this form.
- Out-of-Hospital events
include:
- CPA stabilized prior to ED
arrival
- CPA resuscitation ongoing
and continued in ED after arrival
- CPA resuscitation restarted
in ED after arrival, but prior to achieving >20 minutes
sustained ROSC.
- Events beginning within the
facility campus with response by facility first-responders, but ongoing
resuscitation transferred to EMS personnel (e.g., fire, paramedic,
ambulance).
- If completing the record
for a patient who had an out of hospital cardiac arrest event, even if
the patient has subsequent in-hospital event(s), select “Out of
Hospital”.
- If completing the record
for a patient whose initial cardiac arrest event occurred within the
facility campus of an outside hospital and was then transferred to your
hospital for continuing care, select “In-hospital”.
Did patient have subsequent cardiac arrest event(s) during the course of hospitalization?
- Yes: The patient had more
than one cardiopulmonary resuscitation event (defined as either
pulselessness or a pulse with inadequate perfusion requiring chest
compressions and/or defibrillation).
- No: The patient had only one cardiopulmonary
resuscitation event for which they are being hospitalized.
- Not Documented: If there is no documentation around subsequent events.
Notes for Abstraction:
- If the patient has more
than one cardiopulmonary resuscitation event, regardless of whether or
not multiple events occur in or out of hospital, select “Yes.”
- Repeat events are defined
as those that occur after ROSC is sustained for >20
minutes.
Example: A
patient with pre-hospital CPA is stabilized with ROSC at 12:00. At
12:12, 7 minutes after ED arrival, patient requires additional CPA
resuscitation interventions (chest compression and/or defibrillation).
ROSC was not sustained > 20 min. This would be considered a
single, ongoing out of hospital event.
Example: A
patient with pre-hospital CPA is stabilized with ROC at 10:00 and
requires no additional CPA resuscitation interventions in ED, with ROSC
sustained > 20 min at 10:21. This out of hospital event has
ended and would be considered the first (index) event. If patient again
requires chest compression and/or defibrillation in the ED at 10:30, 9
min after ROSC sustained for >20 minutes, that event would be
considered a repeat cardiac arrest event.
System Entry
Date/Time
Enter the date and time the patient entered the system, based on
subject type (below).
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military
time)
If the time is not available, select “Time Not
Documented.”
Notes for Abstraction:
- Hospital Inpatient –
Date/time the patient was admitted to the hospital, including direct
admissions and admissions through the ED (used when first event occurs
as hospital inpatient).
- Ambulatory/Outpatient –
Date/time the patient registered in the Ambulatory/Outpatient area.
- Rehab Facility Inpatient*
(separate admission) – Date/time the need for chest compression and/or
defibrillation was first recognized.
- Skilled Nursing Facility
Inpatient* (separate admission) – Date/time the need for chest
compression and/or defibrillation was first recognized.
- Mental Health Facility
Inpatient* (separate admission) – Date/time the need for chest
compression and/or defibrillation was first recognized.
- Visitor or Employee
(includes healthcare personnel and other non-patients) – Date/time the
need for chest compression and/or defibrillation was first recognized.
- Out of Hospital Cardiac
Arrest – Date/time the need for chest compression and/or defibrillation
was first recognized.
- Transfer Patients (includes
patients that are transferred to your facility from another acute care
hospital for continued management of a cardiac arrest event) –
Date/time the need for chest compression and/or defibrillation was
first recognized for the cardiac arrest event for which they were
transferred to your facility.
*Note: Some hospitals have Rehab, Skilled Nursing and/or
Mental Health areas or adjacent facilities to which patients are
admitted (separate from hospital admission) where the code team
responds.
Table of Contents
PCAC 2.1 Pre-Existing Conditions
This field is provided for those facilities using pre-numbered event records or another internal event numbering system who wish to include that reference in their Get With The Guidelines® - Resuscitation Post Cardiac Arrest Care record. Do not include any personal health/protected health information (PHI) in this field.
Pre-existing
conditions at time of the event (check all that apply)
Select only conditions that existed prior to the event. For those conditions where there is a time interval indicated, only respond affirmatively if the diagnosis is made prior to the CPA event for which you are completing the event form. There is
no
limit on the number of conditions that you can select, so you should
select all of the conditions that apply.
Note:
The following list is specific
to certain conditions of particular interest to Get With The
Guidelines® - Resuscitation and is not meant to be an exhaustive list
of all possible pre-existing conditions. Additionally, where a time
interval is indicated, it is NOT limited
to the current admission.
Example: If EMS identifies Hypotension at 1:00 at a patient’s home,
arrives at the ED at 1:30 and the patient arrests at 2:00,
“Hypotension” should be selected from the list below (within 4 hours).
- None – Select this option only if
there are no documented pre-existing conditions found in
the list below.
- Acute stroke
– Select if there is a documented diagnosis during this hospitalization of stroke, ischemic stroke, or hemorrhagic stroke. Do not select "acute stroke" here if the patient has a documented past medical history of stroke prior to this admission. This response is meant to capture new onset strokes.
- Acute CNS non-stroke event – Select
if there was evidence of decreased mental status, delirium, or coma not
due to acute stroke within 4 hours up to time of the event.
- Baseline depression in CNS function
– Select if there was evidence of chronically depressed CNS function including a motor, cognitive, or functional
baseline deficit (at time of system entry).
- Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Cyanotic (pediatric and newborn/neonate only).
- Tetralogy of Fallot (TET)
- Total Anolmalous Pulmonary Venous Connection (TAPVC or
TAPVR)
- Truncus Arteriosus
- Hypoplastic Left Heart
- Transposition of the Great Vessels
- Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Acyanotic (pediatric and
newborn/neonates only). Includes:
- Aortic Stenosis
- Coarctation of the Aorta
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
- Septal Defects
- Congenital Malformation/Abnormality (non-cardiac (pediatric and newborn/neonate only). Includes:
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Tracheal-esophageal fistula
- Known/suspected chromosomal/genetic abnormality – (e.g.,
trisomy 21, 13, 18)
- Congestive heart failure (this admission)
– Select if there is documentation of newly diagnosed congestive heart failure during
this admission and prior to this CPA event.
- Congestive heart failure (prior to this
admission) – Select if there is a documented diagnosis of
congestive heart failure prior to this admission.
- Diabetes mellitus – Select if there
is a documented diagnosis of Type I or Type II diabetes mellitus prior to this CPA event.
- Hepatic insufficiency
– Select if there was evidence of hepatic insufficiency within 24 hours
up to the time of the event, defined by ANY of the following:
- Adult
- Total bilirubin > 2 mg/dL and AST > 2x
normal
- Cirrhosis
- Pediatric/Newborn/Neonate
- Direct bilirubin > 2 mg/dL and AST > 2x
normal
- Cirrhosis
- Hypotension/hypoperfusion – Select
if there was evidence of hypotension within 4 hours up to the time of
the event, defined by ANY of the following:
- Adult [18+]:
- SBP < 90 or MAP < 60 mmHg.
- Vasopressor/inotropic requirement after volume
expansion (except for dopamine ≤ 3 mcg/kg/min).
- Intra-aortic balloon pump
- Pediatric [< 18]:
- SBP < 5th percentile for age, less than [70 + 2
x age in years] for age < 10.
- MAP < 5th percentile for age.
- Vasopressor/inotropic requirement after volume
expansion (except for dopamine ≤ 3 mcg/kg/min).
- Newborn/Neonate:
- Documentation/evidence of symptomatic
hypotension/hypoperfusion.
- Major trauma
– Select if there was evidence of multi-system injury or single system
injury associated with shock or altered mental status during this admission and prior to this CPA event.
- Metabolic/electrolyte abnormality
– Select if there was evidence of metabolic/electrolyte abnormality
within 4 hours up to the time of the event, defined by ANY of the
following:
- Adult/Pediatric:
- Sodium < 125 or > 150 mEq/L
- Potassium < 2.5 or > 6 mEq/L
- pH < 7.3 or > 7.5, arterial
- Lactate > 2.5 mmol/L,
- Blood glucose < 60 mg/dL
- Newborn/Neonate:
- Acidosis (pH < 7.2 arterial, venous or
capillary)
- Ionized Calcium < 1 mmol/L or < 4 mg/dL
- Glucose < 40 mg/dL
- Sodium < 125 mEq/L
- Magnesium > 4 mEq/L
- Potassium > 6.5 mEq/L
- Myocardial ischemia (acute coronary
syndrome)/infarction (this admission) – Select if there is documentation of a new diagnosis of myocardial ischemia (acute coronary
syndrome)/infarction this admission.
- Myocardial ischemia (acute coronary
syndrome)/infarction (prior to this admission)
– Select if there is a documented past medical history of myocardial ischemia
(acute coronary syndrome)/infarction prior to this admission.
- Metastatic or hematologic malignancy
– Select if there is any solid tissue malignancy with evidence of
metastasis, or any blood borne malignancy.
- Pneumonia
– Select if there is a documented diagnosis of active pneumonia, where
antibiotics have not yet been started or the pneumonia is still being
treated with antibiotics.
- Renal insufficiency – Select if there
was evidence of renal insufficiency prior to the event, defined by ANY
of the following:
- Adult [18+]:
- Requiring ongoing dialysis or extracorporeal
filtration therapies.
- Creatinine > 2 mg/dL within 24 hours up to the
time of the event.
- Pediatric [< 18]:
- Requiring ongoing dialysis or extracorporeal
ultrafiltration therapies;
- if < 30 kg: Oliguria (urine output < 1
ml/kg/hr for > 8 hr.)
and creatinine > 1mg/dL within 24 hours up to the time of the
event;
- if > 30 kg: Oliguria (urine output < 0.5
ml/kg/hr for > 8 hr) and creatinine > 2 mg/dL within 24
hours up
to the time of the event.
- Respiratory insufficiency
– Select if there was evidence of acute or chronic respiratory
insufficiency within 4 hours up to the time of the event, defined by
ANY of the following:
- PaO2/FiO2 ratio < 300 (in the absence of
pre-existing documented cyanotic heart disease).
- PaO2 < 60 mm Hg (in the absence of pre-existing
documented cyanotic heart disease).
- SaO2 < 90 %, (in the absence of pre-existing
documented cyanotic heart disease);
- PaCO2, EtCO2 or TcCO2 > 50 mm Hg.
- Ages 18+ years – spontaneous respiratory rate >
40/min or < 5/min.
- Ages 9-17 years – spontaneous respiratory rate >
50/min or < 5/min.
- Ages 1-8 years – spontaneous respiratory rate >
60/min or < 5/min.
- Age < 1 year – spontaneous respiratory rate
> 60/min or < 10/min.
- Requiring non-invasive ventilation (e.g.,
Bag-Valve-Mask, Mask CPAP/BiPAP, Nasal CPAP/BiPAP, negative pressure
ventilation).
- Requiring ventilation via invasive airway (e.g.,
T-piece, assist control, IMV, pressure support, high frequency).
- Sepsis
– Select if there is a documented bloodstream infection where
antibiotics have not yet been started or the infection is still being
treated with antibiotics. Documentation of "presumed sepsis," without confirmatory positive blood cultures, would NOT constitute septicemia.
- Prior CPR event – Select if the patient has a history of cardiac arrest or CPR event prior to the events precipitating or during this hospitalization
Table of Contents
PCAC 3.1 Cardiac Arrest Event
Date/Time of Birth
(Will be auto-populated from Admission/Discharge Form)
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military
time)
- DOB Unknown/Not Documented
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
Notes for Abstraction:
- Because this data element is critical in determining the population for all measures, the abstractor should NOT assume that the claim information for the birthdate is correct. If the abstractor determines through chart review that the date is incorrect, she/he should correct and override the downloaded value. If the abstractor is unable to determine the correct birthdate through chart review, she/he should default to the date of birth on the claim information.
Event Witnessed?
Did patient
receive chest compressions (including open chest cardiac massage)?
- Yes
- No/Not Documented
- No, Per Advance Directive
Date/Time
compressions started
Enter the date and time compressions were first started by EMS
personnel, hospital staff, or bystander.
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military
time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Duration of CPR
(in minutes):
If the FIRST event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation
occurred out-of-hospital, enter the total time that CPR was
performed. You should be looking for notes documenting
estimated or actual CPR time.
If duration of CPR is not documented, select the “Not documented”
checkbox.
Notes for Abstraction:
- If CPR is transferred from
EMS personnel to in-hospital staff, include the total time that CPR was
performed by all providers.
- If CPR is started and
stopped due to return of circulation that is NOT sustained for greater
than 20 min and CPR is started again enter the total time that CPR is
performed until the end of the event (sustained ROSC > 20 min or
efforts terminated).
Sustained Return of Spontaneous Circulation (ROSC) achieved?
- Yes: There is documentation of restoration of circulation that is sustained for > 20 minutes with no further need for chest compressions, including with pacemaker or cardiopulmonary bypass/extracorporeal CPR
- No: There is documentation that ROSC was not achieved or there was no restoration of circulation that is sustained for > 20 minutes
- Not Documented: There is no documentation as to whether or not ROSC was achieved
Notes for Abstraction:
- Sustained ROSC is deemed to have occurred when chest compressions are not required for 20 consecutive minutes and signs of circulation persist (or sustained ROSC if extracorporeal oxygenation or biventricular assist device is applied).
For out-of-hospital events, ROSC attained?
For out-of-hospital cardiac arrest events, enter location where ROSC was obtained.
- At scene
- En-route
- After arrival to hospital
- Not Documented
Date/Time sustained ROSC
began (lasting > 20 min) OR resuscitation efforts were
terminated (End of event):
Enter date and time chest compressions stopped and did not resume
because it was either the beginning of the sustained return of
circulation lasting > 20 min (Example: ROSC begins, chest
compressions stopped at 1300 and not resumed; ROSC is sustained for
> 20 min at 1321. Time event ends is 1300), or because of other
reasons indicated under “Reason resuscitation ended.” Example:
Resuscitation stopped at 2301.) If the time is not documented, select
“Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military
time)
If time is estimated by EMS personnel, select “Time Estimated”
Table of Contents
PCAC 4.1 Arrival Information
Arrival Date/Time
Enter the earliest documented month, day, and year, and the time the
patient arrived at this hospital (emergency room, on the floor for
inpatient care).
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Notes for Abstraction:
- For times that include
“seconds”, remove the seconds and record the time as is.
- Example: 15:00:35 would be recorded as 15:00
- The arrival date/time may
differ from the admission date/time.
- The arrival date/time may
differ from system entry date/time.
- For arrival date/time, when
reviewing ED records do NOT include any documentation from external
sources (e.g., ambulance records, physician office record, laboratory
reports or ECG/EKGs) obtained prior to arrival.
- Do not use preprinted
dates/times on a vital sign graphic record to determine arrival
date/time.
- If the patient is in either
an outpatient setting of the hospital (e.g., dialysis, chemotherapy,
cardiac cath) or a SNF unit of the hospital, and is subsequently
admitted to acute inpatient, use the date/time the patient arrived at
the ED or on the floor for acute inpatient care as the arrival
date/time.
- Direct Admits:
- If the patient is a “Direct Admit” to the cath lab, use
the earliest date/time the patient arrived at the cath lab (or cath lab
staging/holding area) as the arrival date/time.
- For “Direct Admits” to acute inpatient use the earliest
date/time the patient arrived at the nursing floor or in observation as
the arrival date/time.
- If the patient was
transferred from your hospital’s satellite/free-standing ED or from
another hospital within your hospital’s system (as an inpatient or ED
patient), and the two facilities are geographically distinct from one
another, use the arrival date/time at the receiving facility.
- For cardiac arrests that
occur while the patient is an inpatient in acute care, enter the actual
hospital arrival date/time and not the date/time of cardiac
arrest.
Neurological Assessment Findings:
If not assessed or assessment findings are not documented, select "Not
documented".
Are pupils fixed and dilated
- Yes: The patient's pupils are fixed and dilated.
- No: The patient's pupils are not fixed or dilated.
- Not Documented: There is no documentation of the patient's pupils being fixed and dilated.
Status of patient (if not sedated/paralyzed)?
- Conscious: The patient is conscious.
- Unconscious/Comatose: The patient is unconscious or comatose.
- Not Documented: There is no documentation around the ability of the patient to follow commands at the time of the initial neurological assessment
Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) within 1-hr of ROSC? Do not complete this section if the patient is paralyzed.
Record the GCS performed within 1 hour of ROSC.
If you record GCS scores for motor, eye and verbal response,
the total score will automatically be generated.
If only a total score is documented (and not the individual
components), only fill in the "Total GCS" score response option.
If assessment of any individual component of the GCS or total
GCS is limited or unable to be performed due to sedation or paralytic
drug received within 1 hour prior to exam select "Sedation/Paralytic"
If the score for the individual components of the GCS are not
documented or the GCS was not done, select "Unknown/Not Documented"
- Motor:
- Intubated
- Sedation
- Unknown/ Not Documented
Glasgow
Coma Scale (Adults)
|
Motor
Response
|
Obeys
commands for movement
|
6 points
|
|
Purposeful
movement to painful stimulus
|
5
points
|
|
Withdraws
from pain
|
4
points
|
|
Abnormal
(spastic) flexion, decorticate posture
|
3
points
|
|
Extensor
(rigid) response, decerebrate posture
|
2
points
|
|
None
|
1
point
|
|
Eye
Opening Response
|
Spontaneous--open
with blinking at baseline
|
4
points
|
|
Opens
to verbal command, speech, or shout
|
3
points
|
|
Opens
to pain, not applied to face
|
2
points
|
|
None
|
1
point
|
|
Verbal
Response
|
Oriented
|
5
points
|
|
Confused
conversation, but able to answer questions
|
4
points
|
|
Inappropriate
responses, words discernible
|
3 points
|
|
Incomprehensible
speech
|
2
points
|
|
None
|
1 point
|
Glasgow
Coma Scale and Modification for Children
|
Sign
|
Glasgow Comas Scale
|
Modification for children
|
Score
|
|
Eye
Opening
|
Spontaneous
|
Spontaneous
|
4
|
|
To
Command
|
To
sound
|
3
|
|
To
pain
|
To
pain
|
2
|
|
None
|
None
|
1
|
|
Verbal
Response
|
Oriented
|
Age
appropriate verbalization, orients to sound, fixes and follows, social smile
|
5
|
|
Confused
|
Cries,
but consolable
|
4
|
|
Disoriented
- Inappropriate words
|
Irritable,
uncooperative, aware of environment - Irritable, persistent cries,
inconsistently consolable
|
3
|
|
Incomprehensible
sounds
|
Inconsolable
crying, unaware of environment or parents, restless, agitated
|
2
|
|
None
|
None
|
1
|
|
Motor
Response
|
Obeys
commands
|
Obeys
commands, spontaneous movement
|
6
|
|
Localizes
pain
|
Localizes
pain
|
5
|
|
Withdraws
|
Withdraws
|
4
|
|
Abnormal
flexion to pain
|
Abnormal
flexion to pain
|
3
|
|
Abnormal
extension
|
Abnormal
extension
|
2
|
|
None
|
None
|
1
|
|
Best
Total Score
|
|
|
15
|
Notes for Abstraction:
- This data element is looking to capture
the GCS within 1 hour of ROSC for this cardiac arrest event regardless
of whether it is done at your facility or not. If the patient
is transferred to your hospital from another acute care hospital ED or
inpatient floor enter the GCS recorded within 1 hour of ROSC at that
hospital or during transport by the transport team.
-
If the patient is located at the
transferring hospital and/or is in transport during the first hour post
ROSC, but the GCS from the transferring hospital is not available,
enter the first one done at your hospital.
-
If the only GCS recorded within 1 hour
of ROSC is obtained by EMS, it is acceptable to enter that score.
-
If there are multiple GCS recorded
within 1 hour of ROSC enter the best score.
-
If patient has an endotracheal tube in
place at the time GCS measured leave the verbal score blank and select
the Intubated check-box (this is equivalent to documentation of
"T").
-
For cardiac arrests that occur while
the patient is an inpatient in acute care record the GCS performed
within 1 hour of the cardiac arrest event for which the PCAC record is
being completed.
-
GCS may be documented by anyone trained
in performing GCS which may include any physician, advanced practice
nurse, physician assistant, or nurse.
-
See Table 1 for a list of Sedative
drugs.
-
See Table 2 for a list of
Paralytic drugs.
Table of Contents
PCAC 4.2 Targeted Temperature Management
Was targeted temperature management (TTM) utilized?
-
Yes: Targeted temperature management was used for the FIRST cardiac arrest event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation.
- No: Targeted temperature management was not used for the FIRST cardiac arrest event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation OR was initiated for subsequent repeat cardiac arrest event.
- Unknown/Not documented: The use of targeted temperature management cannot be determined from medical record documentation.
Notes for Abstraction:
- Targeted Temperature Management (TTM) involves maintaining a patient's core temperature within a documented targeted range and refers to strict temperature control following cardiac arrest.
- Select "Yes" only if there is a documented targeted temperature in the medical record.
- TTM is intentional, controlled reduction of a patient's core temperature to a target of 32-36 degrees Celsius and includes the terms therapeutic hypothermia, induced hypothermia, and targeted temperature management.
- Select "Yes" only if targeted temperature management was used during or after the first or initial cardiac arrest for which the PCAC record is being completed.
- Do not select "Yes" if targeted temperature management was initiated during or following a subsequent re-arrest event.
Initial patient temp
If yes, what was the targeted temperature (choose one)?
Select the documented targeted temperature from the following list.
ADULT
- Below 32.0°C
- 32°C - 36°C
- Above 36°C
- Other (Specify):
- Unknown/Not documented
PEDIATRIC/INFANT
- Initial continuous hypothermia (32°C - 34°C)
- Continuous nomothermia (36°C - 37.5°C)
- Other (Specify):
- Unknown/Not documented
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select only one response. If, for example, documentation in the medical record states a targeted temperature of 32°C, select the response of "Below 32.0°C."
Temperature control method (select all that apply):
If Targeted Temperature Management (TTM) was used for the first or initial cardiac arrest
event, select all cooling methods that were used.
- Antipyretics: Include fever reducing medications such as ibuprofen and aspirin
- Cold IV Saline Bolus: Infusion of iced
isotonic fluid to initiate core
cooling.
- Intranasal: Nasal catheter that sprays
rapid evaporating cooling liquid or cold air into the nasal cavity for
cooling the brain. The catheter itself may be cooled.
- Intravascular device or catheter
(continuous): i.e. used as access for an extra corporeal cooling circuit
- Surface Cooling: Includes cooling pads,
circulating cold water blankets and cold air-forced blankets, ice packs
and other external methods.
- Other: Any other method not
captured under previously selections.
- None
Duration of continuous hypothermia:
- Hours
- Days
- Not Documented
Date/Time targeted temperature management initiated
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented"
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Was goal temperature met?
-
Yes: There is documentation that the targeted goal temperature was met.
-
No: There is documentation that the targeted goal temperature was not met (e.g. the targeted goal temperature was 33 degrees Celsius and documentation indicates that the patient only reached 34 degrees Celsius)
-
Not Documented: There is no documentation around target temperatures OR the information cannot be determined from medical record documentation.
(REQUIRED for patients that are not treated with targeted temperature management) Clinical rationale
documented by medical team why targeted temperature management was not initiated (check all
that apply):
If Targeted Temperature Management (TTM) was not utilized for the
first or initial cardiac arrest event, select the reason(s) why it was
not initiated.
- Arrhythmias/QTc prolongation: Patient experienced arrhythmias/QTc prolongation.
- Awake, alert, following commands:
Patient is awake, alert and following commands.
- Clinician preference: There is documentation that the clinical team is concerned with the evidence related to this therapy.
- DNAR with limitation on technologic
support: Patient is DNAR, DNAI status, has Advanced Directives that
would exclude therapeutic hypothermia, or patient is comfort measures
only.
- Facility does not routinely treat patients with targeted temperature management
- Hemodynamic instability: Patient has
hemodynamic instability.
- Increased risk of bleeding: Patient has
a condition that increases risk of bleeding.
- Known /Suspected Septic Shock: Patient experiences septic shock.
- Limited life expectancy: Life
expectancy less than 1 year, terminal cancer or other end
stage terminal disease, severe comorbid illness or other conditions
which severely life expectancy.
- Not intubated: Patient is not intubated.
- Poor functional status pre-arrest
(including dementia): The patient has poor functional status,
dementia or other severe cognitive impairment prior to
arrest.
- Pregnancy: Patient
is pregnant.
- Recent surgery: Patient's recent surgery.
- Other (specify): There are reason(s)
other than those specified above documented as to why cooling was not
initiated.
- Unknown/Not Documented: There
are no reason(s) documented as to why cooling was not
initiated.
Notes for Abstraction:
- This data element seeks to determine
the clinical rationale of the medical team as to why the patient was
not managed using TTM and is not an endorsement of the reasons listed as absolute
contraindications.
-
Reasons for not using TTM must be mentioned in the context of post cardiac arrest active cooling, therapeutic hypothermia or targeted temperature management. It is the intent that the abstractor will not make inference as to the why TTM was not used based upon the presence of certain patient clinical characteristics and conditions in the record, but will only abstract reasons that are specifically documented in the medical record as the reason for not using this therapy. The one exception is "Facility does not routinely treat patients with targeted temperature management." For this one response, you may answer based on your facility's practice.
-
Reasons for not using TTM must be explicitly documented by a physician, advance practice
nurse or physician assistant.
-
It is not acceptable to use
documentation of reasons for using TTM from outside hospital notes
that played a factor in the decision-making process for not initiating
at your facility.
-
The following may help abstractors
classify reasons:
- Awake, alert, following commands may
include documentation that cooling was not initiated because the motor
component of Glasgow Coma Score was greater than 5.
- Increased risk of bleeding may
include: Uncontrolled or active bleeding, known or ongoing
bleeding diathesis, multisystem, significant trauma
increasing bleeding risk (i.e. intra-abdominal such as splenic or liver
laceration), severe coagulopathy, major surgery within 14 days,
Intracranial pathology (i.e. intracranial hemorrhage, ischemic stroke),
subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH).
- Hemodynamic instability may include:
severe cardiovascular instability (i.e. uncontrollable dysrhythmia,
severe cardiogenic shock, or refractory hypotension, unable to maintain
BP with pressors, (i.e. 90mmHg systolic or MAP less than 60 despite
vasoactive medications), or profound Bradycardia ≤40.
- Poor functional status
pre-arrest (including dementia): Dementia,
Pre-arrest cognitive status severely impaired (i.e. could not perform
ADL independently), prolonged duration of arrest (e.g. pulseless
greater than 60 min, time to ROSC greater than 30 minutes),
prolonged duration between ROSC and initiation of cooling. (i.e.
greater than 12 hours post ROSC)
- Other may include: coma due to drug
intoxication from barbiturates, benzodiazepines, and other CNS
depressants including antidepressants. If “Other” is
selected, please specify the reason.
For all patients:
Was there ever a documented temperature of ≥38 degrees Celsius?
Is there a recorded temperature of greater than or equal to 38 degrees Celsius (100.4 degrees Fahrenheit) documented in the medical record any time during the hospitalization?
This data element needs to be answered for both patients in whom active cooling is initiated and also those that are not cooled.
If yes, when was a temperature of ≥38 degrees Celsius documented? (Check all that apply)
If a temperature of greater than or equal to 38 degrees Celsius (100.4 degrees Fahrenheit) was documented any time during the hospitalization, indicate on what day(s) a temperature of greater than or equal to 38 degrees Celsius was recorded.
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select "Unknown/Not Documented"
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented"
Table of Contents
PCAC 5.1 Measurements &
Medications
On invasive mechanical ventilator?
- Yes: Patient is on invasive mechanical ventilator.
- No: Patient is not on invasive mechanical ventilator.
- PCO2: mm Hg
- (Arterial) Pa02: mm Hg
If not documented, select "Not Documented."
Was there a PaO2 in the first 24 hours of >300mmHg?
Was there a PaO2 after the initial value and within 24 hours of ROSC
that was greater than 300 mm Hg?
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If initial PaO2 value is in this range,
do NOT select “Yes”. Only select “Yes” if there is
a subsequent PaO2 value AFTER the initial value and within 24 hours of
ROSC that is greater than 300 mm Hg.
If yes, FiO2 at time PaO2 assessed(%)
If there was a PaO2 value of greater than 300 mm Hg, what was the FiO2
at the time of blood gas draw closest to when the PaO2 value was
obtained?
Was there a PaO2 in the first 24 hours of <60mmHg?
Was there a PaO2 after the initial value and within 24 hours of ROSC
that was less than 60 mm Hg?
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If initial PaO2 value is in this range,
do NOT select “Yes”. Only select “Yes” if there is
a subsequent PaO2 value AFTER the initial value and within 24 hours of
ROSC that is less than 60 mm Hg.
If yes, FiO2 at time PaO2 assessed(%)
If there was a PaO2 value of less than 60 mm Hg, what was the FiO2 at
the time of blood gas draw closest to when the PaO2 value was
obtained?
Serial Measurements
Serial Blood Pressure Measurements:
Enter lowest Systolic BP for each of the following time periods:
- Hours 0 -6 post ROSC
- Hours 6 - 12 post ROSC
- Hours 12 - 24 post ROSC
- Hours 24 - 72 post ROSC
If a systolic blood pressure measurement is not measured or not
documented during any time period select the "Not Documented” checkbox.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
Do NOT use the initial measurement to
respond to the 0 to 6 hours post ROSC time period.
If there is not a subsequent value measured after the initial value
within 6 hours post ROSC, select “Not Documented” rather than enter the
initial value again.
-
For each time period, use the lowest
documented Systolic Blood Pressure (BP) between the two time
periods. Do not record values exactly at or beyond the upper
limit of the time period.
- Examples:
- 0 to 6 hour time period would include
all values after the initial value and up to 5 hours and 59 minutes
post ROSC.
- For the medication data elements in this section, answer based on the medications administered up to, but not beyond, the upper limit of the time period. If a patient receives a medication at the exact upper limit of the time period, enter that medication for the following time period. For example, a patient receives dobutamine at exactly 6 hours post ROSC. Check yes for the time period of 6-12 hours post ROSC.
Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 0-6 hours post ROSC:
Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 6-12 hours post ROSC:
Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 12-24 hours post ROSC:
Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 24-72 hours post ROSC:
Table of Contents
PCAC 5.2 Clinical Study Data
Did patient go to the cath lab at any time during this
admission?
-
Yes: The patient went to the cath lab
at any time during this admission
- No: The
patient did not go to the cath lab at any time during this
admission
- Not Documented: There was no documentation that the patient went to the Cath lab any time during this admission.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the patient has an in-hospital
cardiac arrest, only select “Yes” if the patient went to the Cath lab
after the cardiac arrest event.
-
If the patient has the initial cardiac
arrest event while in the cath lab, select “Yes.”
Date/Time at Cath lab
Enter the date/time that the patient arrived at the Cath lab.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the patient went to the Cath lab
multiple times during the hospitalization, enter the date/time the
patient arrived at the Cath lab for the first encounter.
-
If date and time of arrival at the Cath
lab is not specifically documented, use the earliest documented date
and time that indicates the patient was in the Cath lab (i.e. date and
time vital signs in the Cath lab).
Reason went to Cath lab:
Select the reason(s) the patient went to the Cath lab. Select
all that apply.
- Abnormal ECG (not including STEMI)
- Cardiogenic shock
- Elevated cardiac biomarkers
- Focal wall motion abnormality on echocardiogram
- New BBB
- Routine cath post arrest
- ST elevation
- VF arrest
- Unknown/Not Documented: The
patient went to the Cath lab but the reason is unknown or not
documented.
- Other (specify): The reason the patient
went to the cath lab cannot be accurately captured under or is
something other than the previous selections.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the patient went to the Cath lab
multiple times during the hospitalization, select the reason the
patient went to the Cath lab for the first encounter.
-
Reasons that the patient went to the
Cath lab must be documented by a physician, advance practice nurse or
physician assistant
Cath lab interventions:
Select the intervention(s) the patient received in the cath
lab.
- No intervention: The patient went to
the cath lab but did not receive an intervention.
- Atrial Decompression: Patient received atrial decompression.
- Balloon pump: Patient received
intra-aortic balloon pump.
- Stent/PCI: Patient received
percutaneous coronary intervention with or without placement of bare
metal or drug eluting stents.
- Ventricular Assist Device: Patient received any left
ventricular assist device (e.g. Impella®) or other ventricular assist device.
- Unknown/Not Documented: The patient
went to the Cath lab but it is either not known or not documented what
type of intervention the patient received.
- Other (specify): The intervention the patient went to the Cath lab to receive or is something other than the previous selections.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the patient received an intervention
not listed select “No Intervention”.
-
PCI Includes techniques capable of
relieving coronary narrowing (rotational atherectomy, directional
atherectomy, extraction atherectomy, laser angioplasty, implantation of
intracoronary stents and other catheter devices for treating coronary
atherosclerosis).
-
If the patient went to the Cath lab
multiple times during the hospitalization, select the interventions the
patient received in the Cath lab for the first encounter.
Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placed during this admission?
Did the patient have an implantable cardiac defibrillator placed during
this admission?
-
Yes: ICD therapy was placed during this
hospitalization,
- No: ICD
therapy was NOT placed during this hospitalization or cannot be
determined from medical record documentation.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the patient had cardiac
resynchronization therapy pacemaker with defibrillator (CRT-D) or
biventricular pacemaker with defibrillator placed during this
hospitalization select “Yes”.
For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only
EEG (spot) performed within the first 24 hours post ROSC?
- Yes: There was spot EEG monitoring from time of ROSC up to 24 hours post ROSC.
- No: There was no spot EEG monitoring from time of ROSC up to 24 hours post ROSC.
- Not documented: EEG (spot) cannot be determined from medical record documentation.
If yes, Start Date/Time of EEG (spot):
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
EEG (continuous) performed within the first 24 hours post ROSC?
- Yes: There was continuous or routine EEG monitoring from time of ROSC up to 24 hours post ROSC.
- No: There was no continuous or routine EEG monitoring from time of ROSC up to 24 hours post ROSC.
If yes, Start Date/Time of EEG (continuous):
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
If yes, End Date/Time of EEG (continuous):
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
Brain imaging (CT/MRI) performed within the first 5 days post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient did receive a CT/MRI within the first 5 days post ROSC.
- No: Patient did NOT receive a CT/MRI within the first 5 days post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- If a CT/MRI was performed prior to cardiac arrest event and a subsequent CT/MRI is NOT performed AFTER the cardiac arrest event, select "No".
- If the only CT/MRI performed was done at an outside hospital prior to transfer, select "Yes" and record the date/time of that CT/MRI in the subsequent data element "Date/Time of initial CT/MRI."
If yes, or at any point within 10 days, Date/Time of CT/MRI:
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
Notes for Abstraction:
- Enter the date and time of the first CT/MRI post ROSC.
- If a CT/MRI was performed at an outside hospital prior to transfer, and that information is available, you may record that date/time.
- Enter date and time of the initial CT/MRI from the DICOM header information. This is the date and time printed on the hard copy of the film or available when reviewing the image digitally. Use the time indicated on the radiology report only if it clearly indicates the time of study initiation or completion and NOT time of scheduling, dictation or reporting.
PCAC 6.1 Outcome Data
Discharge Modified Rankin
Scale:
If a Modified Rankin Scale (mRS) was measured, what is the scale
recorded by hospital personnel closest to discharge.
If a score is not available or unknown, check the "Not Documented”
checkbox.
Modified Rankin Scale
0 – No symptoms at all
1 – No significant disability despite symptoms: ability to carry out
all usual activities
2 – Slight disability
3 – Moderate disability: Requiring some help but able to walk without
assistance
4 – Moderate to severe disability: Unable to walk without assistance
and unable to attend to own bodily needs without assistance
5 - Severe disability: Bedridden, incontinent and requiring constant
nursing care and attention
6 – Death
Notes for Abstraction:
-
This mRS assessment is intended to
measure disability at the time of discharge. If there is more than 1
measured, use the mRS measured closest to hospital discharge. Ideally
the mRS will be measured at discharge.
-
If a mRS measurement has not been
documented in the medical record, but sufficient information is
available from the physical therapy (PT) notes, occupational therapy
(OT) notes, and/or other sources to allow a mRS to be assigned
retrospectively, the retrospectively assigned mRS score may be entered
into the case report form.
-
If the mRS is not measured or
documented and a mRS cannot be assigned retrospectively, then leave
this field blank. .
-
It is recommended that the mRS be
measured by qualified individuals.
-
Two formal scoring methods for the mRS
are the Simplified Questionnaire (SQ) and the Rankin Focused Assessment
(RFA). The Simplified Questionnaire may be most appropriate for use in
the pre-discharge setting. The more detailed Rankin Focused Assessment
may be more appropriate for use at post-discharge visits, but also may
be helpful to use selectively for cases in which pre-discharge scoring
based on the SQ is uncertain. Also potentially helpful is the Rankin
training and certification program at www.rankinscale.org. Instructions
for the SQ and RFA are provided in the dynamic PMT resources section
under Print Blank Forms.
Table of Contents
PCAC Historic
Note: PCAC elements moved to Historic on December 14, 2022
PCAC 2.1 Pre-Event
OPTIONAL: Local Event ID
This field is provided for those facilities using pre-numbered event
records or another internal event numbering system who wish to include
that reference in their Get With The Guidelines® - Resuscitation Post
Cardiac Arrest Care record. Do not include any personal health/protected health information (PHI) in this field.
Did pt. receive chest
compressions and/or defibrillation during this event?
- Yes
- No/Not Documented (does NOT meet inclusion criteria)
Notes for Abstraction:
- Event is defined here as the first event requiring chest
compressions and/or defibrillation
- If response here is “No/Not documented,” do not complete
PCAC form as the patient does not meet inclusion criteria.
Date/Time the need for
chest compressions (or defibrillation when initial rhythm was VF or
Pulseless VT) was first recognized.
Enter the date and time that the need was first recognized by telemetry
or direct observation, by EMS personnel, medical staff, or lay
bystander. The date of the event is required. If the time is not
documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military
time)
Notes for Abstraction:
- In absence of additional
definitive information, for an out of hospital event, if the patient
had no signs of life reported to the 911 operator use the date and time
of call to 911.
PCAC 3.1 Cardiac Arrest Event
Age at Event (Will
be auto-populated from Admission/Discharge Form)
Was out of
hospital CPR performed?
- Yes: CPR was started
outside the facility campus for the first event requiring chest
compressions and/or defibrillation, including during transport to and
from the facility.
- No: CPR was started within
your facility by acute care facility personnel for the first event
requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation (this would be a
patient that would also fall into the CPA patient population).
- Not Documented: Unable to
determine from medical record documentation if CPR was started for the
first event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation out of
hospital or
in-hospital.
Notes for Abstraction:
- Select “Yes” if CPR was
started for the following types of events:
- CPA stabilized prior to
ED arrival
- CPA resuscitation ongoing
and continued in ED after arrival
- CPA resuscitation
restarted in ED after arrival, but prior to achieving >20
minutes sustained ROSC.
- Events beginning within
the facility campus with response by facility first-responders, but
ongoing resuscitation transferred to EMS personnel (e.g., fire,
paramedic, ambulance).
- For patients with initial
events occurring within the facility campus of another acute care
hospital (and for whom CPR was started by acute care facility personnel
at that facility) and who are then transferred to your facility for
further management, select “No.”
If yes, out of
hospital CPR performed first by:
If CPR was performed out of hospital, select who first started CPR on
the patient for the FIRST event requiring chest compressions and/or
defibrillation.
- Healthcare provider/EMS: A healthcare provider includes a physician, APN, PA, RN,
LPN, RT or alternate individual with Healthcare BLS
knowledge. EMS Personnel includes any emergency medical
responders including, paramedic, EMT, firefighter, law enforcement
officer or volunteer with BLS knowledge.
- Layperson: A
layperson includes anyone other than the healthcare provider and EMS
defined above, or individual providing compression-only
CPR.
- Not Documented:
Documentation does not specify if the person who first started CPR was
a healthcare provider, EMS personnel, or layperson.
Notes for abstraction
- This data element is
looking to capture the person who first started
CPR.
- If CPR is started by a
healthcare provider or EMS personnel who is off duty or not functioning
in their professional role at the time of starting CPR, select
healthcare provider/EMS.
- If CPR is started by a
layperson and transferred to EMS when they arrive on the scene, select
Layperson.
Condition that
best describes this event:
Choose the selection that best describes the patient when the need for
chest compressions and/or defibrillation was first identified:
- Patient was PULSELESS when
need for chest compressions and/or need for defibrillation of initial
rhythm VF/Pulseless VT was first identified
- Patient had a pulse (poor
perfusion) requiring chest compressions PRIOR to becoming pulseless
- Patient had a pulse (poor
perfusion) requiring chest compressions, but did NOT become pulseless
at any time during this event
Note: While chest compressions are usually provided to pulseless
patients (option 1), patients sometimes require chest compressions when
a poorly perfusing pulse/heart rate is present (e.g., bradycardia).
This occurs more frequently in the pediatric population. For these
events, option 2 or 3 should be selected
If pulseless at ANY time
during event:
Date/Time pulselessness
was first identified:
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
- Date: MM/DD/YYYY
- Time: HH:MM
- 24-hour clock (military
time)
Notes for Abstraction:
- This Date/Time is the
Date/Time that pulselessness was first identified or confirmed by EMS
personnel, medical provider or hospital staff.
- For out of hospital arrest
events, this information is often documented on the run report provided
by EMS.
- If conflicting information
is present for out of hospital events, use Date/time of 911 call to
approximate Date/time pulselessness was first identified.
First documented
pulseless rhythm:
What was the first documented pulseless rhythm?
- Asystole
- Pulseless Electrical
Activity (PEA)
- Pulseless Ventricular
Tachycardia
- Ventricular Fibrillation
(VF)
- Unknown/Not Documented
Notes for Abstraction:
- The rhythm can be
documented by anyone who identifies or records rhythm, not necessarily
team or advanced life support (ALS) provider.
- For the unmonitored
pulseless patient, select the first rhythm identified when monitor was
applied.
Total time
patient without a pulse prior to CPR (in minutes):
If the FIRST event requiring chest compressions and/or defibrillation
occurred out-of-hospital, enter the total Time in minutes the patient
was without a pulse prior to the start of chest compressions.
If the duration of time the patient was without a pulse prior to the
start of CPR is not documented or cannot be calculated, select the “Not
documented” checkbox.
Notes for
Abstraction:
- If the data elements of
Date/time chest compressions started AND Date/time pulselessness was
first identified are completed, this data element will be
autopopulated.
PCAC 4.1 Arrival Information
Was patient transferred
from another hospital?
- Yes: Patient was
transferred to your hospital from another acute care
hospital
- No: Patient was not
transferred to your hospital from another acute care hospital
Notes for
Abstraction:
- If the patient has an event
at another acute care hospital and is transferred to your hospital
select "Yes."
- If the patient has an out
of hospital cardiac arrest and is transported to another hospital and
then subsequently transferred to your hospital select "Yes."
- If a patient is first seen
in a satellite, free standing ED that is part of your hospital but is
geographically separate, select "Yes."
Neurological Assessment performed within 1-hr of ROSC?
Was a neurological assessment performed as part of the initial
evaluation (within 1 hour of ROSC)?
- Yes: There is documentation of a
neurological assessment within 1 hour of ROSC
-
No/Not Documented: There is
no documentation of neurological assessment in the medical record or a
neurological assessment was performed greater than 1 hour after ROSC.
-
Neurological Assessment obtained at
transferring facility: The patient was located at a
transferring facility 1 hour post ROSC AND the results of the
neurological assessment performed at that hospital within 1 hour of
ROSC are available.
Notes for Abstraction:
- This data element is looking to capture
the initial neurological assessment within 1 hour of ROSC for this
cardiac arrest event regardless of whether it is done at your facility
or not. If the patient is transferred to your hospital from
another acute care hospital ED or inpatient floor and a neurological
assessment was performed at that hospital within 1 hour of ROSC select
“Neurological Assessment obtained at transferring facility” and record
the findings of that assessment under “Neurological Assessment
Findings”.
-
If the patient is located at the
transferring hospital and/or is in transport during the first hour post
ROSC AND the initial neurological assessment from the transferring
hospital is not available it is acceptable to select “Yes” if an
initial neurological assessment is performed at your
hospital.
-
For a cardiac arrest event that
occurred while the patient an inpatient in acute care look
for the first neurological assessment performed after the
cardiac arrest FIRST event requiring chest compressions and/or
defibrillation.
-
Neurological assessment may be
documented by a physician, advanced nurse practitioner or physician
assistant.
Date/Time initial neurological assessment:
Enter the date and time of the first neurological assessment
performed.
If time is unknown select the "Time Not Documented"
checkbox.
If date and time are unknown or not documented, select the “Unknown/Not
Documented", checkbox.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
Notes for Abstraction:
- If the initial neurological assessment
within 1 hour of ROSC is performed at another acute care hospital prior
to transfer to this hospital, enter the date/time of the neurological
assessment performed at the transferring hospital and record the
results under “Neurological Assessment Findings”.
Pupils
equal
Left pupil
reaction
Right pupil
reaction
Follows commands at time of initial assessment?
- Yes: There is documentation that the patient follows verbal commands at the time of the initial neurological assessment
- No: There is documentation that the patient could not follow verbal commands at the time of the initial neurological assessment
- Not Documented: There is no documentation around the ability of the patient to follow commands at the time of the initial neurological assessment
Notes for Abstraction:
- Documentation of a Motor Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of 6, or equivalent, at the time of the initial neurological assessment is sufficient to select "Yes."
PCAC 4.2 Targeted Temperature Management
Where was targeted temperature management initiated?
If Targeted Temperature Management (TTM) was initiated for the first or initial cardiac arrest
event, select where it was started.
-
Pre-hospital (by
EMS): TTM was initiated by EMS in the field prior
to arrival at any acute care hospital.
-
In-hospital (either at another hospital prior to transfer or in my hospital): TTM was initiated at another hospital prior to transfer or was initiated in your hospital's ED (the hospital at which the PCAC record is being completed) or was initiated in an inpatient floor/unit of your hospital (the hospital at which the PCAC record is being completed).
-
Unknown/Not documented
Notes for Abstraction:
- If TTM was initiated at your
hospital’s satellite/free-standing ED or from another hospital within
your hospital’s system (as an inpatient or ED patient), and there is
one medical record for the care provided at both facilities select “In-hospital.”
If yes, Date/Time goal temperature met:
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select "Time Not Documented."
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select "Unknown/Not
Documented"
Date/Time re-warming started?
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
Notes for Abstraction:
- The date/time cooling efforts are
discontinued would also be equivalent to the date/time re-warming
started in the absence of alternate documentation.
Date/Time re-warming completed?
Enter date/time a temperature of greater than or equal to 36.5 degrees
Celsius was FIRST documented.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
Notes for Abstraction:
- Re-warming is considered completed when
the patient has reached a temperature of greater than or equal to 36.5
degrees Celsius.
Was there a documented temperature of ≤ 31.0 degrees Celsius 6 hours after the initiation of the temperature controlled period?
-
Yes : There was a documented temperature of ≤ 31.0 degrees Celsius 6 hours after the initiation of the temperature controlled period.
-
No : There was no documented temperature of ≤ 31.0 degrees Celsius 6 hours after the initiation of the temperature controlled period.
-
Not Documented : There is no documentation around temperatures during the temperature controlled period OR the information cannot be determined from medical record documentation.
Notes for Abstraction:
- The temperature controlled period is defined as the time period between the date/time the target temperature is first recorded and the date/time that re-warming is started and generally 12 to 72 hours after target temperature is met depending upon facility protocol.
-
This element is looking only at the time period starting 6 hours after the initiation of the temperature controlled period through the date/time re-warming is started (e.g. maintenance phase). Please refer to that time frame only when abstracting this data element.
- You must take documentation in the medical record at face value. If conflicting information is present, and even one value that is ≤ 31.0 degrees Celsius is documented in the time period starting 6 hours after the initiation of the temperature controlled period, select "Yes."
Did patient receive a paralytic drug during induction?
Did the patient receive a paralytic drug any time between date/timeTargeted Temperature Management (TTM) was initiated and date/time the targeted temperature was first recorded (for the first or
initial cardiac arrest event)?
-
Yes
-
No
-
Not Documented: Patient received a
paralytic drug but there is no documentation that it was given between
date/time TTM was initiated and the date/time the targeted temperature was first recorded
Notes for Abstraction:
-
See Table 2 for a list of
paralytic drugs.
If a temperature of greater than or equal to 38 degrees Celsius was documented, was patient following commands at time of fever?
For each day a temperature of greater than or equal to 38 degrees Celsius (100.4 degrees Fahrenheit) was documented, answer whether or not the patient was following commands at the time of the fever.
- Yes: There is documentation that the patient follows verbal commands at the time the fever was recorded
- No: There is documentation that the patient did not follow verbal commands at the time the fever was recorded or there is no documentation around the ability of the patient to follow commands at the time of the fever.
Notes for Abstraction:
- Documentation of a Motor Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) of 6 at the time of the initial neurological assessment is sufficient to select “Yes.”
Documented Adverse Events (check all that apply)
Indicate if any adverse events were documented as a result of the post
ROSC management of cardiac arrest. Select all that
apply.
-
None: There is specific
documentation that there were no adverse events related to post ROSC
management of cardiac arrest.
-
Bleeding requiring blood product
transfusion: Bleeding during the first 72 hours of care after ROSC AND
greater than 2 units transfused blood AND physician note attributing
bleeding problem to cooling, rewarming or cardiac arrest as reason for
transfusion.
-
Skin breakdown: There is documentation
of new skin breakdown within 7 days of ROSC.
-
Hemodynamically significant
bradycardia, heart block, and/or pacemaker requirement: There is
documentation of any of these conditions during the first 72 of care
after ROSC AND physician, advance practice nurse or physician
assistant note attributing the condition to cooling,
rewarming, or cardiac arrest.
-
Other: There is documentation
of some other adverse event as a result of cooling, rewarming or
cardiac arrest. If “Other” is selected, please specify the
reason.
-
Not Documented: There is no
documentation related to adverse events in the medical
record.
Notes for Abstraction:
- This data element is looking to capture
any adverse events related to post ROSC management of cardiac arrest
with or without cooling.
-
Other may include infectious
complications such as new onset sepsis, pneumonia, catheter associated
infection or blood stream infection after the cardiac arrest
event. If “other” is selected, please specify the adverse
event.
-
DO NOT select “Skin breakdown” if there
is documentation of skin breakdown prior to the cardiac arrest
event. This data element is looking for new skin breakdown as
a result of the post ROSC management of cardiac arrest.
-
Skin breakdown may be documented by a
physician, advance practice nurse, physician assistant, RN or wound
care specialist.
PCAC 5.1 Measurements & Medications
If patient was transferred to your hospital, vital signs prior to
transfer?
If the patient arrived to your hospital as a transfer from another
acute care hospital, is there documentation of any vital signs
(temperature, heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate or pulse
oximetry saturation) obtained at the transferring hospital prior to
patient transfer available in the medical record?
-
Yes: There is documentation of vital
signs obtained at the transferring hospital prior to patient
transfer.
-
No: There is no documentation of vital
signs obtained at the transferring hospital prior to patient
transfer.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If ANY vital signs are available from
the transferring hospital select “Yes.” There does not need
to be documentation of ALL vital signs listed under “Vital Signs prior
to transfer” in order to select “Yes”.
-
Vital signs taken during transport to
your hospital by the transport team or EMS are NOT acceptable to select
“Yes.”
-
Documentation of vital signs from the
transferring hospital must be part of the patient’s medical record at
your hospital.
If yes, Date/Time of vital signs prior to transfer:
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If there is more than 1 set of vital
signs available from transferring hospital prior to patient transfer,
enter the date/time the first vital signs post ROSC were
measured.
-
If individual vital signs (temperature,
heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate or pulse oximetry
saturation) were obtained at different times, enter the time that the
first measurement was obtained.
Vital signs prior to transfer:
Enter the first vital signs post ROSC measured at the transferring
hospital.
Temperature:
Enter the patient’s first temperature measurement post ROSC from
transferring hospital. Select “Celsius” or “Fahrenheit” to
indicate the temperature units. If temperature prior to transfer is not
documented select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Site:
Select the site of the initial temperature.
-
Axillary
-
Bladder – (from bladder catheter)
-
Blood – (from intravascular catheter)
-
Brain – (from intraventricular catheter or ICP monitor)
-
Oral
-
Rectal
-
Surface – (Skin, temporal)
-
Tympanic –(Ear)
-
Other
-
Unknown/Not Documented: If the site at which temperature was obtained
is unknown or not documented.
Heart Rate (bpm)
Enter the patient’s heart rate in beats per minute. Enter the patient’s
first heart rate post ROSC obtained at the transferring
hospital. If heart rate prior to transfer is not documented
select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Systolic BP/ Diastolic BP (mmHg)
Enter the patient’s blood pressure (systolic/diastolic) in mmHg. Enter
the patient’s first blood pressure measurement post ROSC obtained at
the transferring hospital. If blood pressure prior to transfer is not
documented select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Respiratory Rate (breaths/min)
Enter the patient’s respiratory rate in breaths/min. Enter
the patient’s first respiratory rate post ROSC obtained at the
transferring hospital. If respiratory rate prior to transfer
is not documented select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Intubated or on mechanical ventilator?
If a respiratory rate is documented, select whether or not the patient
was intubated and/or on a mechanical ventilator at the time the
respiratory rate was recorded.
Pulse Oximetry Saturation (SpO2): (%)
Enter the patient’s oxygen saturation obtained from pulse oximetry as a
percentage. Enter the patient’s first SpO2 post ROSC obtained
at the transferring hospital. If Sp02 prior to transfer is not
documented select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Initial Measurements
Vital Signs:
Enter the first vital signs measured within 1 hour of ROSC that were
obtained after arrival to your hospital.
Ideally these should be the first vital signs measured at your hospital
within 1 hour of ROSC. If the patient is not at your hospital
within 1 hour of ROSC, enter the first vital signs obtained after
arrival to your hospital.
Date/Time of initial vital sign measurements after arrival to your
hospital
Enter the date/time the first vital signs after ROSC were measured at
your hospital.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the individual vital signs of
(temperature, heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, MAP, and
pulse oximetry saturation) were obtained at different times, enter the
date/time that the first measurement was obtained.
-
If the patient is not at your
hospital within 1 hour of ROSC, enter the date and time the first vital
signs were obtained after arrival to your hospital.
-
For inpatient cardiac arrest event,
enter the first vital signs obtained after ROSC.
Temperature:
Enter the first temperature measured within 1 hour of ROSC at your
hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital within 1
hour of ROSC, enter first heart temperature obtained after arrival to
your hospital. Select “Celsius” or “Fahrenheit” to
indicate the temperature units. If initial temperature is not
documented select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Site:
-
Axillary
-
Bladder – (from bladder catheter)
-
Blood – from intravascular catheter)
-
Brain – (from intraventricular catheter
or ICP monitor)
-
Oral
-
Rectal
-
Surface – (Skin, temporal)
-
Tympanic –(Ear)
-
Other
-
Unknown/Not Documented: If site
temperature was obtained from is unknown or not documented.
Heart Rate (bpm)
Enter the patient’s heart rate in beats per minute. Enter the first
heart rate obtained within 1 hour of ROSC at your hospital. If the
patient is not at your hospital within 1 hour of ROSC, enter the first
heart rate obtained after arrival to your hospital.
If initial heart rate is not documented select the “Not documented”
checkbox.
Respiratory Rate (breaths/min)
Enter the patient’s respiratory rate in breaths/min. Enter the first
respiratory rate obtained within 1 hour of ROSC at your hospital. If
the patient is not at your hospital within 1 hour of ROSC, enter first
respiratory rate obtained after arrival to your
hospital. If initial respiratory rate is not documented
select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Intubated or on mechanical ventilator?
If a respiratory rate is documented, select whether or not the patient
was intubated and/or on a mechanical ventilator at the time the
respiratory rate was recorded.
Systolic BP/ Diastolic BP (mmHg)
Enter the patient’s blood pressure (systolic/diastolic) in mmHg. Enter
the first blood pressure measurement with 1 hour of ROSC at your
hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital within 1 hour of ROSC,
enter the first BP obtained after arrival to your hospital.
If blood pressure prior to transfer is not documented select the “Not
documented” checkbox.
MAP (mmHg):
Enter the first MAP measured within 1 hour of
ROSC at your hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital
within 1 hour of ROSC, enter the first MAP obtained after arrival to
your hospital. If a MAP is not documented
for any time period, check the "Not Documented” checkbox.
Pulse Oximetry Saturation (SpO2): (%)
Enter the patient’s oxygen saturation obtained from pulse oximetry as a
percentage. Enter the first oxygen saturation obtained with 1
hour of ROSC at your hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital
within 1 hour of ROSC, enter the first SpO2 obtained after arrival to
your hospital. If initial SpO2 is not documented select the
“Not documented” checkbox.
FiO2 at time SpO2 assessed: (%)
Enter the patient's FiO2 at the time the SpO2 was assessed. For patients without an oxygen delivery device, abstractors can input 21%.
Electrolytes and Labs
Date/Time of initial electrolyte & lab measurements (at your
hospital):
Enter the date/time the first serum creatinine (Scr), bicarbonate/CO2,and glucose were obtained after arrival to
your hospital.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the measurements for serum
creatinine (Scr), bicarbonate/CO2, and glucose were obtained at different times, enter the date/time that
first value was obtained.
-
For inpatient cardiac arrest event,
enter the date/time of the first measurements obtained after
ROSC.
Serum Creatinine:
Enter the first SCr measured within 2 hours
of ROSC at your hospital. Indicate whether the value is in mg/dL or
µmol/L. If the patient is not at your hospital within 2 hours
of ROSC, enter the first SCr obtained after arrival to your
hospital. If initial Scr is not documented select the “Not
documented” checkbox.
Bicarbonate/CO2:
Enter the first bicarbonate/CO2 measured within 2
hours of ROSC at your hospital. Indicate whether the value is
in mmol/L or mEq/L. If the patient is not at your hospital
within 2 hours of ROSC, enter the first bicarbonate/CO2 obtained after
arrival to your hospital. If initial bicarbonate/CO2 is not
documented select the “Not documented” checkbox.
Glucose:
Enter the first glucose measured within 2 hours of ROSC at
your hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital within
2 hours of ROSC, enter the first glucose obtained after
arrival to your hospital. If a glucose is not documented for
any time period, select the "Not Documented” checkbox.
Date/Time of initial Lactate:
Enter the date/time that the first lactate was measured after arrival
to your hospital.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
Notes for Abstraction:
-
For inpatient cardiac arrest event,
enter the date/time of first lactate obtained after ROSC.
Lactate:
Enter the first lactate measured within 2 hours of ROSC at your hospital. Indicate whether the value is in mmol/L or mg/dL. If the patient is not at your hospital within 2 hours of ROSC, enter the lactate obtained after arrival to your hospital. If a lactate is not documented, check the "Not Documented" checkbox.
Date/Time of initial Troponin:
Enter the date/time that the first troponin was measured after arrival
to your hospital.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
For inpatient cardiac arrest event,
enter the date/time of first troponin obtained after ROSC.
Troponin:
Enter the first troponin measured within 2 hours of ROSC at
your hospital. Indicate whether the value is in ng/dL or
mcg/L and if the tests were Troponin I or T. If the patient
is not at your hospital within 2 hours of ROSC, enter the first
troponin obtained after arrival to your hospital. If initial
troponin is not documented, select the "Not Documented” checkbox.
Date/Time of initial blood gas measurements (at your hospital)
Enter the date/time that the first pH, pCO2, and PaO2, were measured
after arrival to your hospital.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
If the date and time are unknown or not documented, select “Unknown/Not
Documented”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the blood gas values for pH, PCO2,
and PaO2 were obtained at different times, enter the date/time that the
first value was obtained.
-
For inpatient cardiac arrest event,
enter the date/time of the first blood gas measurements obtained after
ROSC
pH:
Enter the first pH measured within 2 hours of ROSC at your
hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital within 2
hours of ROSC, enter the pH obtained after arrival to your
hospital. If pH is not documented, select the "Not
documented" checkbox.
pCO2 (mmHg):
Enter the first pCO2 measured within 2 hours of
ROSC at your hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital
within 2 hours of ROSC, enter the first pCO2 obtained after arrival to
your hospital. If pCO2 is not documented, select the "Not
documented” checkbox.
Was there a pCO2 in the first 24 hours of <30 or >50mmHg?
Was there a pCO2 after the initial value and within 24 hours of ROSC
that was less than 30 or greater than 50 mm Hg?
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the initial pCO2 value is in this
range, DO NOT select "Yes". Only select "Yes" if
there is a subsequent pCO2 value AFTER the initial value and within 24
hours of ROSC that is less than 30 or greater than 50 mm Hg.
PaO2 (mmHg):
Enter the first PaO2 measured within 2 hours of ROSC at
your hospital. If the patient is not at your hospital within
2 hours of ROSC, enter the first PaO2 obtained after arrival to your
hospital. lf PaO2 is not documented, select the "Not
documented” checkbox.
Is there documentation that Central Venous Saturation (ScvO2) or mixed
venous saturation was tracked within the first 24 hours?
Was central venous saturation or mixed venous return tracked during the
first 24 hours post ROSC?
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If there is documentation of at least
one ScvO2 or mixed venous saturation value in the first 24 hours select
“Yes.”
Serial Measurements
For lactate and glucose enter the measurement obtained
closest to but not after:
-
6 hours post ROSC
-
24 hours post ROSC
-
48 hours post ROSC
-
72 hours post ROSC
Note: In the online tool, the date/time fields will autopopulate with
the date and time corresponding to the specified number of hours post
ROSC to help you to best identify the time period.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
For each specified time period, enter
the value obtained closest to but not after the date/time that is
autopopulated.
-
Do NOT use the initial measurement to
respond to the 6 hours post ROSC time period. If
there is not a subsequent value measured after the initial value within
6 hours post ROSC, select “Not Documented” rather than enter the
initial value again.
-
If none of the measurements were
obtained for a given time period, select the “Not Documented”
checkbox.
- If a patient did not survive to the specified number of hours post ROSC time period, check off the patient did not survive check box. This check box is present for each time period, and when checked off, will disable the remaining serial measurements. For example, for a patient that dies 12 hours post ROSC, complete the 6 hr post ROSC serial measurements section and for the "24hr post ROSC" measurement section check off the box that states "Patient did not survive 24hr post ROSC."
Lactate:
Indicate whether the value is in mmol/L or mg/dL. If
a lactate is not documented for any time period, select the "Not
Documented” checkbox.
Glucose (mg/dL):
If a glucose is not documented for any time
period, select the "Not Documented" checkbox.
Did patient receive any sedatives in the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received sedation in the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive sedation OR patient received sedation but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received sedation but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all sedatives in the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 1 for a list of sedative drugs
- Select yes if sedative drug is administered by either IV bolus or continuous infusion up to 6 hours post ROSC.
- If a drug was administered via IV bolus or if the continuous infusion is started at exactly hour 6, select “No” here and respond “Yes” to the data element of Did patient receive any sedatives in the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of sedative treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a sedative is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering sedation may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
- It is not expected that in routine situations the physician will explicitly identify which reasons were relevant for each time period. Most likely, this will only be documented once. It is acceptable to assume the same reason(s) for non-treatment to be valid for each time period post ROSC unless otherwise specified.
Did patient receive any paralytics in the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received paralytics in the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive paralytics OR patient received paralytics but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received paralytics but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all paralytics in the 0-6 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 2 for a list of paralytic drugs
- Select yes if paralytic drug is administered by either IV bolus or continuous infusion up to 6 hours post ROSC.
- If a drug was administered via IV bolus or if the continuous infusion is started at exactly hour 6, select “No” here and respond “Yes” to the data element of Did patient receive any paralytic in the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of paralytic treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a paralytic is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering paralytics may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
- It is not expected that in routine situations the physician will explicitly identify which reasons were relevant for each time period. Most likely, this will only be documented once. It is acceptable to assume the same reason(s) for non-treatment to be valid for each time period post ROSC unless otherwise specified.
Did patient receive any sedatives in the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received sedation in the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive sedation OR patient received sedation but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received sedation but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all sedatives in the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 1 for a list of sedative drugs
- Look for drugs administered up to but not beyond 24 hours post ROSC.
- Select yes if sedative drug is administered by either IV bolus or continuous infusion up to 24 hours post ROSC.
- If a drug was administered via IV bolus or if the continuous infusion is started at exactly hour 24, select “No” here and respond “Yes” to the data element of Did patient receive any sedatives in the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of sedative treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a sedative is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering sedation may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
Did patient receive any paralytics in the 6-24hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received paralytics in the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive paralytics OR patient received paralytics but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received paralytics but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all paralytics in the 6-24 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 2 for a list of paralytic drugs
- Look for drugs administered up to but not beyond 24 hours post ROSC.
- Select yes if paralytic drug is administered by either IV bolus or continuous infusion up to 24 hours post ROSC.
- If a drug was administered via IV bolus or if the continuous infusion is started at exactly hour 24, select “No” here and respond “Yes” to the data element of Did patient receive any paralytics in the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of paralytic treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a paralytic is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering paralytics may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
Did patient receive any sedatives in the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received sedation in the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive sedation OR patient received sedation but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received sedation but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all sedatives in the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 1 for a list of sedative drugs
- Look for drugs administered up to but not beyond 48 hours post ROSC.
- Select yes if sedative drug is administered by either IV bolus or continuous infusion up to 48 hours post ROSC.
- If a drug was administered via IV bolus or if the continuous infusion is started at exactly hour 48, select “No” here and respond “Yes” to the data element of Did patient receive any sedatives in the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of sedative treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a sedative is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering sedation may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
Did patient receive any paralytics in the 24-48hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received paralytics in the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive paralytics OR patient received paralytics but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received paralytics but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all paralytics in the 24-48 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 2 for a list of paralytic drugs
- Look for drugs administered up to but not beyond 48 hours post ROSC.
- Select yes if paralytic drug is administered by either IV bolus or continuous infusion up to 48 hours post ROSC.
- If a drug was administered via IV bolus or if the continuous infusion is started at exactly hour 48, select “No” here and respond “Yes” to the data element of Did patient receive any paralytics in the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of paralytic treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a paralytic is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering paralytics may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
Did patient receive any sedatives in the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received sedation in the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive sedation OR patient received sedation but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received sedation but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all sedatives in the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 1 for a list of sedative drugs
- Look for drugs administered up to but not beyond 72 hours post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of sedative treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a sedative is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering sedation may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
Did patient receive any paralytics in the 48-72hour time period post ROSC?
- Yes: Patient received paralytics in the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC
- No: Patient did not receive paralytics OR patient received paralytics but there is documentation that the drug(s) were administered outside of the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC
- Not Documented: Patient received paralytics but there is no documentation as to the time that the medication(s) were administered.
- None Contraindicated: There is a documented contraindication to all paralytics in the 48-72 hour time period post ROSC.
Notes for Abstraction:
- See Table 2 for a list of paralytic drugs
- Look for drugs administered up to but not beyond 72 hours post ROSC.
- If reasons for not treatment are not mentioned in the context of paralytic treatment, do not make inferences (e.g. do not assume that a paralytic is not being prescribed because of a contraindication unless documentation explicitly states so).
- Documented reasons for not administering paralytics may include (list is not all-inclusive):
- Patient/family refusal
- Allergy/sensitivity/adverse reaction.
Serial Blood Pressure Measurements:
Were there at least two consecutive systolic blood pressure readings of <90mmHg separated by at least one hour in the first 0-6 hours post ROSC?
MAP (mmHg):
If a MAP is not documented for any time period, select the "Not Documented" checkbox.
Select all vasopressors/inotropes patient was on during the first 0-6 hours post ROSC:
Select drugs delivered by IV bolus or continuous infusion.
- None: Select if patient received none of the vasopressors/inotropes on the following list in the first 0-6 hours post ROSC
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
- Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
- Dopamine
- Isoproterenol (Isuprel)
- Milrinone (Primacor)
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine (Levophed))
- Phenylephrine (NeoSynephrine)
- Vasopressin (Pitressin)
Were there at least two consecutive systolic blood pressure readings of <90mmHg separated by at least one hour 6-24 hours post ROSC?
MAP (mmHg):
If a MAP is not documented for any time period, select the "Not Documented" checkbox.
Select all vasopressors/inotropes patient was on during hours 6-24 post ROSC:
Select drugs delivered by IV bolus or continuous infusion.
- None: Select if patient received none of the vasopressors/inotropes on the following list in the first 0-6 hours post ROSC
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
- Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
- Dopamine
- Isoproterenol (Isuprel)
- Milrinone (Primacor)
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine (Levophed))
- Phenylephrine (NeoSynephrine)
- Vasopressin (Pitressin)
Select all vasopressors/inotropes patient was on during hours 24-48 post ROSC:
Select drugs delivered by IV bolus or continuous infusion.
- None: Select if patient received none of the vasopressors/inotropes on the following list in the first 0-6 hours post ROSC
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
- Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
- Dopamine
- Isoproterenol (Isuprel)
- Milrinone (Primacor)
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine (Levophed))
- Phenylephrine (NeoSynephrine)
- Vasopressin (Pitressin)
Select all vasopressors/inotropes patient was on during hours 48-72 post ROSC:
Select drugs delivered by IV bolus or continuous infusion.
- None: Select if patient received none of the vasopressors/inotropes on the following list in the first 0-6 hours post ROSC
- Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
- Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
- Dopamine
- Isoproterenol (Isuprel)
- Milrinone (Primacor)
- Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine (Levophed))
- Phenylephrine (NeoSynephrine)
- Vasopressin (Pitressin)
Did patient receive any anticonvulsants in the 0-72 hour time period
post ROSC?
-
Yes: The patient received
anticonvulsant medication any time between date/time of ROSC and up to
72 hours after ROSC.
-
No: The patient did NOT receive
anticonvulsant medication any time between date/time of ROSC and up to
72 hours after
ROSC.
-
Not Documented: The patient
received anticonvulsant medication however it is unclear from medical
record documentation the time period during which the medication was
administered.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
See Table 5 for a list of
anticonvulsant medications.
PCAC 5.2 Clinical Study Data
Was a 12-lead ECG performed?
Was a 12-lead ECG performed at any time?
Notes for Abstraction:
- If a 12-lead ECG is performed by EMS for this event select “Yes.”
- If a 12-lead ECG is performed for this event at another hospital prior to transfer, select “Yes.”
ECG interpretation:
Indicate which of the following findings were present on the first ECG. Select all that apply.
- STEMI
- Ischemic changes (not a STEMI)
- New Left Bundle Branch Block (BBB)
- Other: The 12 lead ECG interpretation cannot be accurately captured under or is something other than previously selections.
- Unknown/Not Documented: A 12 lead ECG was performed, but the interpretation is unknown or not documented.
Notes for Abstraction:
ECG interpretation must be confirmed by a physician. Abstractors should not make interpretation based upon an ECG present in the medical record.
Date/Time of cath lab intervention
Enter the date/time of the first cath lab intervention.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If multiple interventions are performed
in the cath lab, enter the date and time of the first
intervention.
-
For Stent/PCI, enter the earliest
date/time of the first balloon inflation or date/time of the first
stent deployment or date/time of the first treatment of lesion with
another device (time Angiojet or other thrombectomy device used, time
of aspiration, time of suction, time of device pass, time Rotablator
used).
-
For balloon pump, enter the date/time
balloon placement is noted to be optimal.
-
For LVAD, enter the date/time of device
placement and confirmed function.
Echo Studies
Echo performed?
-
Yes: An echo study was performed.
-
No/Not Documented: An echo study was
not performed or cannot be determined from medical record documentation
Date/Time of First Echo
Enter the date and time the FIRST echo study was performed for Day
1-Day 4 post ROSC.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Echo findings:
Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction (LVEF)(%)
If LVEF value is not available or unknown, check the "Not Documented "
checkbox.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If both a numeric value and narrative
description are documented in reference to the same LVF/LVEF
assessment, use the numeric value.
-
The numeric EF may be documented as a
percentage (%), whole number, or decimal. Convert all decimals to
percentages (e.g., 0.40 = 40). The value should be between 5 and 80.
-
If EF was reported as a range, use the
midpoint and consider this an estimated value (e.g., LVEF of 35-45%.
Use 40% as an estimated EF value).
-
If the LV Function has been determined
more than once for a specified day, enter the results of the first test
of that the day.
-
If two or more numeric values or
descriptions are provided in reference to the same LVF/LVEF assessment,
use the lowest value or most severe description.
-
If both calculated and estimated values
are documented, use the calculated value.
-
If the EF is documented as less than
(<) or greater than (>) a given number, use the value one
whole number below or above the given number (e.g., EF < 40% -
Use 39%; EF > 40% - Use 41%).
-
If the EF is not documented as a whole
number, round fractions to the nearest whole number (e.g., 39.5% = 40%,
39.4% = 39%)
Head CT performed?
Was a head CT performed post ROSC?
-
Yes: Patient did receive head CT post
ROSC for the first or initial cardiac arrest event.
-
No/Not Documented: Patient did NOT
receive head CT post ROSC for the first or initial cardiac arrest
event.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If a head CT was performed prior to
cardiac arrest event and a subsequent head CT is NOT performed AFTER
the cardiac arrest event, select “No/Not Documented”.
-
If the only head CT performed was done
at an outside hospital prior to transfer, select “Yes” and record the
date/time of that head CT in the subsequent data element “Date/Time of
initial head CT.”
Date/Time of initial head CT
Enter the date and time the first head CT post ROSC was
performed.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
Enter the date and time of the first
head CT post ROSC.
-
If a head CT was performed at an
outside hospital prior to transfer, and that information is available,
you may record that date/time.
-
Enter date and time of the initial CT
of the head from the DICOM header information. This is the date and
time printed on the hard copy of the film or available when reviewing
the image digitally. Use the time indicated on the radiology report
only if it clearly indicates the time of study initiation or completion
and NOT time of scheduling, dictation or reporting.
Head CT findings:
Indicate the findings present on the initial head CT. Select
all that apply.
-
Normal
-
Cerebral edema
-
Intracranial hemorrhage
-
Herniation
-
Other: Finding(s) other than the
specified options were documented in the medical record.
-
Unknown/Not Documented: A head CT was
performed but findings are unknown or not documented in the medical
record.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
Findings must be documented in the
radiology report or by a physician. Abstractors should not
make a determination of findings based upon CT images present in the
medical record.
-
Unless indicated, only select new
(acute) findings.
Cerebral MRI performed?
Was a cerebral MRI performed post ROSC?
-
Yes: Patient did receive cerebral MRI
post ROSC for the first or initial cardiac arrest
event.
-
No/Not Documented: Patient did NOT
receive cerebral MRI post ROSC for the first or initial cardiac arrest
event.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If a cerebral MRI was performed prior
to cardiac arrest event and a subsequent cerebral MRI is NOT performed
AFTER the cardiac arrest event, select “No/Not Documented”.
-
If the only cerebral MRI performed was
done at an outside hospital prior to transfer, select “Yes”.
Date/Time of initial MRI:
Enter the date and time the first cerebral MRI post ROSC was
performed.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Notes for Abstraction:
-
Enter the date and time of the first
cerebral MRI post ROSC.
-
If a cerebral MRI was performed at an
outside hospital prior to transfer, and that information is available,
you may record that date/time.
-
Enter date and time of the initial MRI
of the head post ROSC from the DICOM header information. This is the
date and time printed on the hard copy of the film or available when
reviewing the image digitally. Use the time indicated on the radiology
report only if it clearly indicates the time of study initiation or
completion and NOT time of scheduling, dictation or reporting.
EEG performed within the first 24 hours post ROSC?
Was any EEG monitoring performed from ROSC up to 24 hours post
ROSC?
-
Yes: There was continuous or
routine EEG monitoring from time of ROSC up to 24 hours post
ROSC.
-
No/Not documented: There was
no EEG monitoring from time of ROSC up to 24 hours post ROSC or cannot
be determined from medical record documentation.
If EEG performed, was there evidence of any seizure activity?
Notes for Abstraction:
-
EEG interpretation must be confirmed and documented by a physician.
If evidence of seizure activity, was their evidence of Status Epilepticus (sustained seizures)?
Notes for Abstraction:
-
EEG interpretation must be confirmed and documented by a physician.
If yes, was an anticonvulsant administered?
If there was evidence of electrographic seizures, was an anticonvulsant
administered during EEG monitoring?
Notes for Abstraction:
-
See Table 5 for a list of
anticonvulsant medications.
PCAC 6.1 Outcome Data
Did patient survive to hospital discharge?
-
Yes, patient lived
-
No, patient died
Note: This data element will autopopulate from the Admission/Discharge
Form data element Discharge Disposition.
Date/Time of discharge from ICU
Enter the date and time the patient was discharged from the
ICU.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select the “Time Not Documented
checkbox.”
If patient was not discharged from ICU, select the “Patient was not
discharged from ICU” checkbox.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
If the patient does not survive to be
discharged from the ICU, select “Patient was not discharged from ICU”
checkbox.
-
If the patient was discharged from ICU
and readmitted to the ICU later in the hospital stay, enter the date
and time of the patients first discharge from the
ICU.
Did patient ever follow commands?
Is there documentation that the patient followed commands any time
during the hospital stay?
-
Yes: There is documentation
that the patient follows verbal commands at any time during the
hospital stay.
-
No: There is documentation in the
medical record that the patient did NOT follow verbal commands at any
time during the hospital stay.
-
Not Documented: There is no
documentation regarding the patient’s ability to follow verbal commands
during the hospital stay.
Notes for Abstraction:
-
Documentation of components of the
Glasgow Coma Score (GCS) are acceptable.
Date/Time of first documented following of commands:
Enter the date and time the patient first followed commands.
-
Date: MM/DD/YYYY
-
Time: HH:MM
-
24-hour clock (military time)
If the time is not documented, select “Time Not Documented.”
Table of Contents
Optional Fields
The Optional fields can be used to track any additional information not
already collected in the Patient Management Tool. To use these, your
Stroke team will need to decide on consistent representations for the
fields you will use. For instance, Optional 1 will always be used to
track the hospital floor.Do not enter any personal health/protected health information (PHI) into the Optional Fields.
Optional 1 through Optional 10 are text fields that can hold up to 20
alphanumeric characters.
Optional 1
Optional 2
Optional 3
Optional 4
Optional 5
Optional 6
Optional 7
Optional 8
Optional 9
Optional 10
Table of Contents
Table 1: Sedatives
| clonazepam
(Klonopin) |
| dexmedetomidine
(Precedex) |
| diazepam
(Valium) |
| fentanyl (Duragesic, Subsys) |
| fosopropofol
disoudium (Lusedra) |
| haloperidol (Haldol) |
| hydromorphone hydrochloride (Dilaudid) |
| ketamine
(Ketalar) |
| lorazepam (Ativan) |
| methadone |
| midazolam
(Versed) |
| morphine |
| propofol
(Diprivan) |
| Other
sedative |
Table 2: Paralytics
|
Neuromuscular
blockade |
| atracurium
(Tracrium) |
| choline
chloride succinate |
| cisatracurium
(Nimbex) |
| doxacurium
(Nuromax) |
| pancuronium
(Pavulon) |
rocuronium
(Zemuron) |
| succinylcoline
(Anectine, Quelicin) |
| vecuronium
(Norcuron) |
| Other
paralytic |
Table 3: Inotropes/Vassopressors
| adrenaline |
| amrinone
(Inocor) |
| digitoxin (Crystodigin) |
| digoxin
(Lanoxin) |
| dobutamine
(Dobutrex) |
| dopamine |
| ephedrine
sulfate |
| epinepherine |
| inamrinone
lactate |
| isoproterenol
(Isuprel) |
| milrinone
(Primacor) |
| noradrenaline |
| norepinephrine
(Levophed) |
| phenylphrine
(NeoSynephrine) |
| vasopressin
(Pitressin) |
Table 4: Vasodilators
| Nitroglygerin |
| amrinone (Inocor) |
| ciloprost, lloprost (Ventavis) |
| Fenoldopam mesylate (Corlopam) |
| Hydralazine (Apresoline) |
| milrinone (Primacor) |
| Nesiritide (Natrecor) |
| Nicardipine (Cardene) |
| Sodium Nitroprusside (Nipride) |
| Other vasodilator |
Table 5: Anticonvulsants
| carbamazepine (Tegretol) |
| clonazepam (Klonopin) |
| diazepam (Diastat, Valium) |
| phenytoin (Dilantin, Fosphenytoin) |
| felbamate (Felbatol) |
| gabapentin (Neurontin) |
| lacosamide |
| lamotrigine (Lamictal) |
| levetiracetam (Keppra) |
| Phenobarbital |
| topiramate (Topamax) |
| Trileptal |
| valproate (Depakene, Depakote) |
| Other anticonvulsant |
Table of Contents
Scoring
Definitions
Cerebral Performance Categories
Adult Cerebral Performance Categories/CPC
Scale
- Evaluate only cerebral performance capabilities,
estimating potential
performance if non-cerebral organ systems were (are) normal.
- Example – a conscious, mentally active, bedridden,
post-CPR patient with severe heart disease would have a CPC of 1.
- Differences in CPC scores exist only for categories
1, 2 and 3, while
categories 4 and 5 are determined solely by cerebral status.
Note:
If patient is anesthetized, or paralyzed with neuromuscular blockade,
or intubated, use “as is” clinical condition to calculate scores.
- CPC 1
: Good cerebral performance* – Conscious, alert, able to
work, might have mild neurologic or psychologic deficit.
- CPC 2
: Moderate cerebral disability* – conscious, sufficient
cerebral function for independent activities of daily life. Able to
work in sheltered environment.
- CPC 3
: Severe cerebral disability
– Conscious, dependent on others for daily support because of impaired
brain function. Ranges from ambulatory state to severe dementia or
paralysis.
- CPC 4
: Coma or vegetative state
– Any degree of coma without the presence of all brain death criteria.
Unawareness, even if appears awake (vegetative state) without
interaction with environment; may have spontaneous eye opening and
sleep/awake cycles. Cerebral unresponsiveness.
- CPC 5
: Brain death – Apnea, areflexia, EEG silence, etc.
*Note:
Differences between “Good Performance” and “Moderate Disability” are
often too subtle to distinguish from the information in the medical
record. Make the selection based on your “best guess.”
From Table
8.6, page 178 in. Safar P. Resuscitation after Brain
Ischemia, in Grenvik A and Safar P Eds – Brain Failure and
Resuscitation, Churchill Livingstone, New York, 1981; 155-184.
|
Pediatric/Neonate Cerebral Performance
Categories/PCPC Scale
- PCPC 1
: Normal
- Age-appropriate level of functioning; preschool child developmentally
appropriate; school-age child attends regular classes.
- NEONATE
: Normal - No obvious neurological abnormalities.
- PCPC 2
: Mild cerebral disability
- Able to interact at an age-appropriate level; minor neurological
disease that is controlled and does not interfere with daily
functioning (e.g., seizure disorder that is well controlled with
medication); preschool child may have minor developmental delays, but
more than 75% of all daily living developmental milestones are above
the 10 th percentile; school-age child attends regular school, but
grade is not appropriate for age, or child is failing appropriate grade
because of cognitive difficulties.
- NEONATE
: Mild cerebral disability
- Minor neurological abnormality; neurological disease that is
controlled and does not interfere with daily functioning (e.g., seizure
disorder that is well controlled with medication).
- PCPC 3
: Moderate cerebral disability
- Below age-appropriate functioning; neurological disease that is not
controlled and severely limits activities; most activities of preschool
child’s daily living developmental milestones are below the 10th
percentile; school-age child can perform activities of daily living,
but attends special classes because of cognitive difficulties and/or
has a learning deficit.
- NEONATE
: Moderate cerebral disability
- Neurological disease that is not controlled (e.g., breakthrough
seizures despite medications which affect responsiveness to
environment).
- PCPC 4
: Severe cerebral disability
- Preschool child’s activities or daily living milestones are below the
10th percentile, and child is excessively dependent on others for
provision of activities of daily living; school-age child may be so
impaired as to be unable to attend school; school-age child is
dependent on others for provision of activities of daily living;
abnormal motor movements for both preschool and school-age child may
include non-purposeful, decorticate, or decerebrate responses to pain.
- NEONATE
: Severe cerebral disability
- Obvious severe neurological disorder: Abnormal motor movements may
include non-purposeful, decorticate or decerebrate response to pain.
- PCPC 5
: Coma or vegetative state - Coma; unawareness.
- NEONATE
: Coma or vegetative state - Coma; unawareness.
- PCPC 6
: Brain death
- NEONATE :
Brain death
|
Table of Contents
Data Dictionary for IHCA Site Characteristics
Why are we collecting this information?
Denomiator Data
In 2015, the Institute of Medicine's report, "Strategies to Improve Cardiac Arrest Survival: A Time to Act (2015)", initiated a call to action, specifically Recommendation #4: Set National Accreditation Standards for Cardiac Arrest for Hospital and Health Care Systems and #5: Adopt continuous quality improvement programs. Currently, survival for in-hospital cardiac arrests (IHCA) is low at about 19%-38% (Merchant RM et al. Incidence of treated cardiac arrest in hospitalized patients in the United States. Crit Care Med. 2011;39;2401-2406).
In order to increase the rate of survival for IHCA, we must first understand that root causes when patients do not survive the IHCA, including the impact of arrest location on survival, which requires measurement of data. Get With The Guidelines-Resuscitation provides the numerator for measurement in participating hospitals. Additionally, we need to collect the denominator in order to develop a new measure and conduct feasibility testing of an IHCA incidence measure.
Goals
- Identify disparities and highlight improvement opportunities for IHCA survival
- Measurement & reporting of key metrics are essential in order to benchmark care, address challenges of resuscitation and highlight opportunities for improvement
- Data entry is optional for the 2019 recognition submission period. We are considering making this a requirement for Get With The Guidelines-Resuscitation Recognition going forward.
- Data for the previous year should be entered by February 15, 2019.
Where can you find this information?
The owner of this information may vary by institution. If you do not know who owns this information, we recommend starting with your Finance Office, then if not available there, contacting your Quality and/or Nursing Departments. Other departments which may have this information include but are not limited to: CFO or Finance Office, VP Quality, CNO Office, Administration, and/or Business Intelligence (BI).
Example: The finance department may maintain this as a standard report provided to each unit for budgeting purposes.
Example: The information is provided by Unit Managers via the midnight census to Administration.
Example: In some institutions, this information may have been developed by HIM as part of their overall finance and billing.
What are the data being collected?
Note: All inpatients and observation patients should be included.
Med/surg bed days: The number of occupied bed days in the Adult med/surg units (non-procedural, non-critical, and non-licensed beds) January 1 through December 31.
Ped ward bed days: The number of occupied bed days in the Pediatric med/surg units (non-procedural, non-critical, and non-licensed beds) January 1 through December 31.
Total adult admissions: Enter the total adult admissions from January 1 through December 31 for patients 18 years or older.
Total ped admissions: Enter the total pediatric (patients ≥1 year old to <18 years old) admissions from January 1 through December 31.
Total neonate/infant admissions: Enter the total neonate/infant (patients >24 hours old to <1 years old) admissions from January 1 through December 31.
Total newly born admissions: Enter the total newly born (born this admission or <24 hours old) admissions from January 1 through December 31.
Adult ICU bed days: The number of occupied bed days in all the Adult Intensive Care Units from January 1 through December 31.
Ped ICU bed days: The number of occupied bed days in all Pediatric Intensive Care Units from January 1 through December 31.
NICU (neonatal intensive care unit) bed days: The number of occupied bed days in all Neonatal Intensive Care Units from January 1 through December 31.
Table of Contents
Summary of Changes
Section |
Title |
Change |
| |
|
Update 04/2014: Added text stating not to enter any personal health information/protected health information (PHI) in the "Local Event ID" and "Comments" section across all forms. |
| 1.1 Admit |
System Entry Date/Time |
Update 5/2015: Added "Emergency Department- Date/Time the patient was admitted/registered into the Emergency Department" |
| 1.1 Admit |
Date/Time of Birth |
Update 4/2014: Added clarification for abstraction that stated: "Note: In the online form, time is only available for response if the patient is "born this admission (or transferred from birth hospital)." |
| 1.1 Admit |
Patient Gender Identity |
Update 2/2021: Added new element |
| 1.1 Admit |
Patient-Identified Sexual Orientation |
Update 2/2021: Added new element |
| 1.1 Admit |
Race |
Update 03/2016: Removed multi-select instructions |
| 1.1 Admit |
Born this admission or transferred from birth hospital? |
Update 12/2014: Moved data element beneath Age at System Entry |
| 1.1 Admit |
Canada Sex |
Update 12/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Canada Gender |
Update 12/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Canada Date of Birth |
Update 12/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Canada Patient Postal Code |
Update 12/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Canada Providence or Territory |
Update 12/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Canada Race |
Update 12/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Birth Weight (patients <30 days only) |
Update 10/2013: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Weight same as birth weight |
Update 10/2013: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form |
| 1.1 Admit |
Weight |
Update 4/2014: Label of element updated to state Weight (required for pediatric and newborn/neonate patients only). Label update made to clarify required status of element for pediatric and newborn/neonate patients only.
Update 12/2014: Replaced "weight at admission" to "weight weight at time of the first (or index) event" in first sentence of coding instructions for this element. |
| 1.1 Admit |
Patient Gender Identity |
Update 05/2021: New response options added |
| 1.1 Admit |
Patient-Identified Sexual Orientation |
Update 05/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form |
| 1.1 Admit |
Length (patients <30 days old only) |
Update 10/2013: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form |
| 1.1 Admit |
Head Circumference (patients <30 days only) |
Update 10/2013: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form |
| 1.1 Admit |
COVID-19 Vaccination |
Update 01/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form
Update 06/2021: Link to element added to "Vaccinations & Testing" section |
| 1.1 Admit |
COVID-19 Vaccination Date |
Update 01/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form
Update 06/2021: Updated allowable values and notes for abstraction. Link to element added to "Vaccinations & Testing" section. |
| 1.1 Admit |
COVID-19 Vaccine Manufacturer |
Update 06/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form |
| 1.1 Admit |
Did the patient receive both doses of vaccine? (if applicable) |
Update 06/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form |
| 1.1 Admit |
Is there documentation that this patient was included in a COVID-19 vaccine trial? |
Update 01/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form
Update 06/2021: Link to element added to "Vaccinations & Testing" section |
| 1.1 Admit |
Influenza Vaccination |
Update 01/2021: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form
Update 06/2021: Link to element added to "Vaccinations & Testing" section |
| 1.2 Newborns/Neonates |
Did mother receive prenatal care |
Update 10/2013: Not documented response option added |
| 1.2 Newborns/Neonates |
Fetal monitoring |
Update 10/2013: Unknown/Not documented response option added |
| 1.2 Newborns/Neonates |
Delivery mode |
Update 10/2013: Vaginal "assisted" changed to vaginal "operative." C-section response divided into scheduled and emergent |
| 1.2 Newborns/Neonates |
Apgar Scores |
Update 10/2013: Unknown/Not Assigned response categories added. 10, 15, and 20 minute apgar scores added |
| 1.2 Newborns/Neonates |
Special circumstances recognized at birth |
Update 10/2013: "Known at time of delivery" removed. Response options added: Abdominal wall defects, CCAM/CPAM, CDH. Response options to indicate if the diagnosis was made prior to brith (prenatal or antenatal) or after birth (postnatal) added |
1.3 Induced Hypothermia |
Was induced hypothermia initiated? |
Update 4/2013: Element added to Admission and Discharge Form
Update 4/2014: Following Note for Abstraction added: If the "MET-only Admission" check box is checked off, N/A will be auto-populated in the online form for this field. |
| 1.4 Discharge |
During this admission, was a standardized health related social needs form or assessment completed? |
Update 01/2021: Added new element. |
| 1.4 Discharge |
If yes, identify the areas of unmet social needs (select all that apply): |
Update 01/2021: Added new element.
Update 12/2023: Updated definition and notes for abstraction.
Update 01/2024: Updated element.
|
| 1.4 Discharge |
Was there Active or Suspected COVID-19 diagnosis in the 2 weeks prior to admission or during this hospitalization? |
Update 06/2020: Added new element. |
| 1.4 Discharge |
Method of Diagnosis |
Update 06/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Updated display label. Updated allowable values and notes for abstraction. |
| 1.4 Discharge |
Date/Time of Diagnosis |
Update 06/2020: Added new element. |
| |
CPA Criteria |
Update 10/2013: Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only definition added
Update 04/2016: Updated "Neonatal" to "Newly born" |
| |
Neonatal delivery event |
Update 10/2013: Element added to create Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| CPA 2.1 Pre-Event |
Was patient discharged from an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) within 24 hours prior to this CPA Event? |
Update 04/2014: Updated data element and definition to specify a time frame of 24 hours prior to the event. The change to the data element included the addition of the following: "within 24 hours prior to this CPA Event." |
| CPA 2.1 Pre-Event |
OPTIONAL: Was patient in the ED within 24 prior to this CPA event? |
Update 12/2014: Added Notes for Abstraction section for this data element |
CPA 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
|
Update 10/2012: Section changed to required
Update 04/2013: Added new data element of Did patient have an out-of-hospital arrest leading to this admission?
Update 04/2014:
Added the following statement: "For those conditions where there is a time interval indicated, only respond affirmatively if the diagnosis is made prior to the CPA event for which you are completing the event form."
Updated 'Acute Stroke' to specify that this response is meant to capture new onset strokes.
Updated Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Cyanotic and Non Cardiac to note that the response can be answered for adult patients if present.
Clarified timing of diagnosis on the response options of: Major Trauma & Myocardial ischemia.
Update 12/2014: Added following sentence to the definition for Septicemia: "Documentation of "presumed sepsis," without confirmatory positive blood cultures, would NOT constitute septicemia."
Update 02/2018: Added new option for "Pre-existing Conditions at Time of Event"
Update 08/2018: Updated "septicemia" to "sepsis" |
| CPA 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Active or suspected bacterial or viral infection at admission or during hospitalization |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Updated allowable values and notes for abstraction.
Update 07/2020: Updated definition and allowable values. |
| CPA 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Emerging Infectious Disease |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 06/2020: Removed the duplicated element that was labeled as "Optional"
Update 07/2020: Added new code option "Other Emerging Infectious Disease". |
| CPA 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) donned by the responders |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Updated definition. Updated notes for abstraction. |
| CPA 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
History of vaping or e-cigarette use in the past 12 months |
Update 04/2020: Added new element. |
| CPA 2.3 Interventions Already in Place |
Interventions ALREADY IN PLACE when need for chest compressions and/or defibrillation was first recognized |
Update 12/2014: Added Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) as an option under "Part B"
Update 2/2016: Updated code options for Part A of Interventions Already in Place
Update 04/2017: Added note before Part A referencing CPA 4.3, updated options in Part A |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 2.3 Interventions already in place |
Intervention(s) ALREADY IN PLACE when the need for chest compressions and/or defibrillation was first recognized |
Update 10/2013: Definition updated for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group
Update 04/2017: Added note before Part A referencing CPA 4.3, updated options in Part A |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 2.3 Interventions already in place |
If vascular access in place, type |
Update 10/2013: Element added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 3.1 Event |
If team activated, date/time resuscitation team arrival |
Update 10/2013: Element added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| CPA 3.1 Event |
Illness Category |
Update 12/2014: Removed Newborn option from Illness Category |
| CPA 3.1 Event |
Event Location |
Update 04/2014: Added new response option of "Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit" and included the following statement under the PICU definition: Pediatric ICU (PICU) – (includes medical, surgical, cardiovascular, trauma, burn...ICUs). As of April, 2014, this response excludes the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. |
| CPA 3.1 Event |
Illness Category |
Update 10/2018: Removed "pre-operative or" from "Surgical-Noncardiac" section. |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 4.1 Initial Condition/Defib/Vent |
Does patient have a detectable heart rate |
Update 10/2013: Element added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 4.1 Initial Condition/Defib/Vent |
If there is a detectable heart rate, what was the heart rate |
Update 10/2013: Element added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 4.1 Initial Condition/Defib/Vent |
Compression method used |
Update 10/2013: Element responses added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 4.1 Initial Condition/Defib/Vent |
Compression to ventilation ratio used |
Update 10/2013: Element added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| CPA 4.1 Initial Condition/Defib/Vent |
First documented pulseless rhythm |
Update 10/2013: Notes for abstraction added (five bullets)
Update 05/2015: Added "Unknown/Un-Documented" |
| CPA 4.2 AED and VF/Pulseless VT |
Did patient have ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia at ANY time during the resuscitation event |
Update 10/2013: Notes for abstraction added (two bullets) |
| CPA 4.2 AED and VF/Pulseless VT |
Date and time of first ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia |
Update 10/2013: Added sentence: If patient had ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia at any time during the resuscitation event, enter the date and time that ventricular fibrillation or pulseless ventricular tachycardia was first recorded. If multiple dates and times are documented, use the earliest date and time. |
| CPA 4.2 AED and VF/Pulseless VT |
Total Number of Shocks |
Update 10/2013: Added sentence: Enter the total number of shocks administered during the cardiac arrest event. |
| CPA 4.2 AED and VF/Pulseless VT |
Documented reason(s) (patient, medical, hospital related or other) for not providing defibrillation shock for Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) or Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) in first two minutes |
Update 10/2013: Element Added
Update 12/2014: Added "or ACLS certified nurse" to Notes for Abstraction |
| CPA 4.3 Ventilation |
Was Bag-Valve Mask ventilation intiated during the event? |
Update: Added Bag Mask instructions
Update 12/2016: Updated label |
| Was Laryngeal Mask Airway (LMA) inserted/re-inserted during event? |
Update 12/2016: Added elements |
| Was any Pulse Oximetry placed during the event? |
Update 12/2016: Added elements |
| CPA 5.1 Other Interventions |
Was IV/IO Epinephrine bolus administered |
Update 10/2013: Element updated to add "IV/IO." Removed words "during the event." Clarity added for Yes and No/Not documented response options.
Update 2/2017: Removed references to "Vasopressin bolus" |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 5.1 Other Interventions |
Was any Epinephrine BOLUS administered |
Update 10/2013: Element added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 5.1 Other Interventions |
Epinephrine Doses |
Update 10/2013: Element added for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| CPA 5.1 Other Interventions |
Was IV/IO Vasopressinbolus administered |
Update 10/2013: Element updated to add "IV/IO." Removed words "during the event." Clarity added for Yes and No/Not documented response options. |
| CPA 5.1 Other Interventions |
If IV/IO Epinephrine or Vasopressin BOLUS was not administered within the first five minutes of the event, was there a documented patient, medical, hospital related or other reason for not providing Epinephrine or Vasopressin bolus |
Update 10/2013: Element Added |
CPA 5.2 Other Drug Interventions |
|
Update 4/2013: Added new response option of Vasopressin, IV/IO continuous infusion |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 5.2 Other Drug Interventions |
Select all drug interventions that were used during the event |
Update 10/2013: Element updated for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 5.3 Other Drug Interventions |
Select each intervention that was employed during the resuscitation event |
Update 10/2013: Element updated for Neonatal Delivery CPA Event form group |
| CPA 6.1 Event Outcome |
Was ANY documented return of adequate circulation [ROC] (in the absence of ongoing chest compressions return of pulse/heart rate by palpation, auscultation, Doppler, arterial blood pressure waveform, or documented blood pressure) achieved during the event |
Update 10/2013: Notes for abstraction added (three bullets) |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 6.1 Event Outcome |
Was ANY documented return of adequate circulation [ROC] (in the absence of ongoing chest compressions return of pulse/heart rate by palpation, auscultation, Doppler, arterial blood pressure waveform, or documented blood pressure) achieved during the event |
Update 10/2013: Neonatal Delivery Event Only definition added |
CPA 6.2 Post-ROC Care |
|
Update 4/2013: Removed data element of Was induced hypothermia initiated after return of circulation (ROC) was achieved? |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was continuous end tidal CO 2 monitoring (exhaled CO2) used to monitor quality of CPR |
Update 10/2013: Added "(exhaled CO2)". Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
If yes, was an end tidal CO2 value of >10 mmHg achieved |
Update 10/2013: Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 7.1 CPR Quality |
If yes, (>10 mmHg achieved), was an end tidal CO2 value of >20 mmHg achieved |
Update 10/2013: Neonatal Delivery CPA Event only element added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was arterial line diastolic pressure used to monitor compression quality |
Update 10/2013: Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was a device or technology used to monitor compression quality |
Update 10/2013: Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 7.1 CPR Quality |
If yes, device |
Update 10/2013: Neonatal Delivery CPA Event only element added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was a compression rate of greater than 100/minute maintained during CPR |
Update 10/2013: Changed to "greater than 100/minute" (previously had been "about 100/minute"). Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was a compression rate of at least 90/minute maintained during CPR |
Update 10/2013: Neonatal Delivery CPA Event only element added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Were compressions interrupted (hand off period) for > 10 seconds at any time during CPR |
Update 10/2013: Removed "(other than for interventions such at ET placement)" from the definition. Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Were compressions interrupted >15 seconds (>30 seconds for neonates) for interventions such as invasive airway placement during CPR |
Update 10/2013: Updated from "20" to "30 seconds" for neonates. Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Did ventilation rate exceed 10/minute for ped patients (20/minute for neonates), excluding the initial confirmation of tracheal tube placement |
Update 10/2013: Separated out No from Not Documented to create two response options: No and Not Documented. Notes for abstraction added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
| Neonatal Delivery CPA Event Only 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was a ventilation rate of about 30/minute maintained during CPR |
Update 10/2013: Neonatal Delivery CPA Event only element added
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic section. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was performance of CPR monitored or guided using any of the following? (Check all that apply) |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
If CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device) used: Average compression rate |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
If CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device) used: Average compression depth |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
If CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device) used: Compression fraction |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
If CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device) used: Percent of chest compressions with complete release |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
If CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device) used: Average ventilation rate |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
If CPR mechanics device (e.g. accelerometer, force transducer, TFI device) used: Longest pre-chick pause |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.1 CPR Quality |
Was a team debriefing on the quality of CPR provided completed after the event? |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
CPA 7.2 Resuscitation Related Events and Issues |
|
Update 4/2013: Added new data element of Was this cardiac arrest event the patient’s index (first) event (during this hospitalization)?
Update 4/2014: Removed the following sentence: "Note: Written comments will not be sent to Get With The Guideline-Resuscitation registry but can be used by each institution for internal QI review." |
CPA 7.3 Maternal In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest |
|
Update 02/2018: Added new section
|
CPA 7.4 ECMO / ECPR |
|
Update 05/2020: Added new section
|
CPA 7.4 ECMO / ECPR |
Neurologic injury or events detected during ECMO or after ECMO (Less than 6 weeks after separation from ECMO or by Hospital Discharge, which ever one comes first). (check all that apply): |
Update 06/2020: Updated element name, notes for abstraction, and suggested data sources
|
CPA 7.4 ECMO / ECPR |
Date/Time ECMO Started |
Update 06/2020: Moved element below "Was Cannulation Successful?"
|
CPA 7.4 ECMO / ECPR |
Date/Time ECMO Ended |
Update 06/2020: Moved element below "Was Cannulation Successful?"
|
CPA 7.4 ECMO / ECPR |
If yes, enter ELSO Patient Record Number |
Update 06/2020: Updated definition and notes for abstraction
|
| ARC 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
|
Update 04/2014:
Added the following statement: "For those conditions where there is a time interval indicated, only respond affirmatively if the diagnosis is made prior to the ARCevent for which you are completing the event form."
Updated 'Acute Stroke' to specify that this response is meant to capture new onset strokes.
Update 12/2014: Added following sentence to the definition for Septicemia: "Documentation of "presumed sepsis," without confirmatory positive blood cultures, would NOT constitute septicemia."
Update 08/2018: Updated "septicemia" to "sepsis"
|
| ARC 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Active or suspected bacterial or viral infection at admission or during hospitalization |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Updated allowable values and notes for abstraction.
Update 07/2020: Updated definition and allowable values. |
| ARC 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Emerging Infectious Disease |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Added new code option "Other Emerging Infectious Disease". |
| ARC 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) donned by the responders |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Updated definition. Updated notes for abstraction. |
| ARC 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
History of vaping or e-cigarette use in the past 12 months |
Update 04/2020: Added new element. |
| ARC 2.3 Interventions Already in Place |
|
Update 10/2018: Added "Note to Abstractors" and updated response options |
| ARC 3.1 Event |
Illness Category |
Update 12/2014: Removed Newborn option from Illness Category |
| ARC 3.1 Event |
Event Location |
Update 04/2014: Added new response option of "Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit" and included the following statement under the PICU definition: "Pediatric ICU (PICU) – (includes medical, surgical, cardiovascular, trauma, burn...ICUs). As of April, 2014, this response excludes the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive" Care Unit. |
| ARC 4.1 Ventilation |
Type(s) of Ventilation/Airway(s) USED During th event, including those already in place |
Update 10/2018: Added "Note to Abstractors" |
| ARC 4.1 Ventilation |
Method(s) of confirmation used to ensure correct placement of Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Trachestomy Tube |
Update 10/2018: Updated description for "None of the above" |
| MET 2.1 Pre-Event Data |
Was patient discharged from an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) at any point during this admission and prior to this MET call? |
Update 4/2014: Element label updated to include "at any point during this admission." Two notes for abstraction added. |
| MET 2.1 Pre-Event Data |
Was patient discharged from an Intensive Care Unit (ICU) within 24 hrs prior to this MET call? |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
| MET 2.1 Pre-Event Data |
If yes, enter the date the patient admitted to non-ICU discharge PRIOR to this MET call |
Update 4/2014: Element retired and moved to historic. |
| MET 2.1 Pre-Event Data |
Pre-event vital signs |
Update 4/2014: Added "ND" response for each vital sign. Added selection of "Room Air" or "Supplemental O2" next to the SpO2 value. |
| MET 2.1 Pre-Event Data |
Neurological Assessment – AVPU Scale (most recent within last 4 hours prior to this MET event) |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
| MET 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Active or suspected bacterial or viral infection at admission or during hospitalization |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Updated allowable values and notes for abstraction.
Update 07/2020: Updated definition and allowable values. |
| MET 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Emerging Infectious Disease |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Added new code option "Other Emerging Infectious Disease". |
| MET 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) donned by the responders |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Updated definition. Updated notes for abstraction. |
| MET 2.2 Pre-existing conditions |
History of vaping or e-cigarette use in the past 12 months |
Update 04/2020: Added new element. |
| MET 3.1 Event |
Subject Type |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
| MET 3.1 Event |
Illness Category |
Update 12/2014: Removed Newborn option from Illness Category |
| MET 3.1 Event |
Event Location |
Update 4/2014: Added new response option of "Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit" and included the following statement under the PICU definition: "Pediatric ICU (PICU) – (includes medical, surgical, cardiovascular, trauma, burn...ICUs). As of April, 2014, this response excludes the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive" Care Unit. |
| MET 3.2 Activation Triggers |
|
Update 4/2014:
Retired the following response options: reversal agent without immediate response, bleeding into airway, symptomatic hypertension with end organ signs/symptoms, chest pain unresponsive to nitroglycerine, rising lactate to >4 mEq/L, >1 stat page required to summon patient's regular team for acute problem.
Changed "uncontrolled" bleeding to "excessive" bleeding.
Moved 'unexplained agitation or delirium' under 'mental status change.'
Added the following response options: other respiratory & specify, hypertensive urgency/emergency, chest pain, other cardiac & specify, decreased responsiveness, other neurological & specify, critical lab abnormality, elevated risk factor score & specify, uncontrolled pain, other medical & specify, and family member/patient activated.
|
| MET 4.1 Drug Interventions |
|
Update 4/2014: Changed section to state "check all NEW drug interventions initiated during MET event." Prior to 4/2014, the section stated: "check all interventions that were initiated, or if already in place immediate prior to the event, were continued during the event."
Moved the response option of Albumin from MET 4.2 to this section.
Retired the following response options: calcium, heparin/LMWH, magnesium, mannitol, sodium bicarbonate, thrombolytic
Added the following response options: antibiotic IV, antihistamine IV, Epinephrine & route, sedative, steroids
|
| MET 4.2 Non-Drug Interventions |
Respiratory Management: |
Update 4/2014:
Retired the response options of: elective intubation for airway protection, tracheostomy care/replacement.
Updated section to categorize interventions as "non-invasive ventilation" and "invasive ventilation" and added response options to denote if the intervention was already in place and continued during the MET event or placed during the MET event.
Added the following element: If Endotracheal Tube (ET) or Tracheostomy tube placed during MET event, method(s) of confirmation used to ensure correct placement of ET or Tracheostomy Tube (check all that apply):
|
| MET 4.2 Non-Drug Interventions |
Monitoring: |
Update 4/2014:
Retired the response option of: non-invasive blood BP (NIBP) monitor. Removed label of "stand alone" next to the "apnea/bradycardia response."
Updated "ECG" to "continuous ECG/Telemetry"
Updated "pulse oximetry" to "continuous pulse oximetry"
Added an "Other monitoring & specify" response
Added option of "continued" or "initiated" next to each response option.
Moved 12 lead ECG to "Other interventions initiated during the event" section
|
| MET 4.2 Non-Drug Interventions |
Vascular access: |
Update 4/2014:
Retired the response options of: Umbilical Artery (UAC) and Umbilical Vein (UAV).
Added option of "already in place" or "placed during MET event" next to each response option.
|
| MET 4.2 Non-Drug Interventions |
Stat consult: |
Update 4/2014:
Retired the response options of: cardiology, neurology, pulmonary, and surgery.
Added Other stat consult & Specify
|
| MET 4.2 Non-Drug Interventions |
Transfusion: |
Update 4/2014:
Retired the response options of: fresh frozen plasma, packed red blood cells, platelets. Moved Albumin to section 4.1.
|
| MET 4.2 Non-Drug Interventions |
Other interventions initiated during the event: |
Update 4/2014:
Retired the response options of: bronchoscopy, chest tube, coma position, CPR, cricothyotomy, defibrillation of VF/pulseless VT, foley catheter, gastric lavage, gastrointestinal endoscopy upper GI, gastrointestinal endoscopy lower GI, hyperventilation, NG/OG tube, neonatal head ultrasound (Echo), pacemaker, pericardiocentesis, serum lactate, throacentesis.
Added response options of: STAT labs, transfusion of blood products
|
| MET 5.1 MET Outcome |
Patient transferred to: |
Update 4/2014: Added: Emergency Department. Retired and moved to historic Morgue (died) response. |
| MET 5.1 MET Outcome |
Was patient made DNAR during MET Event |
Update 4/2014: Element added. |
| MET 6.1 Review of MET Response |
|
Update 4/2014: Added Incorrect team activated; updated MET response delay. |
PCAC |
Form creation |
Update 10/2012: PCAC form release |
PCAC General |
Intro |
Update 02/2023: Added PCAC Intro section header |
PCAC General |
Did patient have subsequent cardiac arrest event(s) during the course of hospitalization? |
Update 02/2023: Updated response options |
PCAC General |
System Entry Date/Time |
Update 02/2023: Moved note for "Time Not Documented" to below response options |
PCAC 2.1 Pre Existing Conditions |
|
Update 04/2014:
Added the following statement: "For those conditions where there is a time interval indicated, only respond affirmatively if the diagnosis is made prior to the CPA event for which you are completing the event form."
Updated 'Acute Stroke' to specify that this response is meant to capture new onset strokes.
Updated Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality – Cyanotic and Non Cardiac to note that the response can be answered for adult patients if present.
Clarified timing of diagnosis on the response options of: Major Trauma & Myocardial ischemia.
Update 12/2014: Added following sentence to the definition for Septicemia: "Documentation of "presumed sepsis," without confirmatory positive blood cultures, would NOT constitute septicemia."
Update 02/2023:
Added note to specify the data that should be provided in the "Pre-Existing Conditions" field.
Added "pediatric", "newborn/neonate" notes to "Cardiac Malformation/Abnormality - Cyanotic" and "Congenital Malformation/Abnormality" response options.
Added "non-cardiac" note to "Congenital Malformation/Abnormality" response option.
Updated "Septicemia" response option to "Sepsis".
Reordered response options in alphabetical order. |
| PCAC 2.1 Pre-existing conditions |
Active or suspected bacterial or viral infection at admission or during hospitalization |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Removed element. |
| PCAC 2.1 Pre-existing conditions |
Emerging Infectious Disease |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Removed element. |
| PCAC 2.1 Pre-existing conditions |
Additional Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) donned by the responders |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Removed element. |
| PCAC 2.1 Pre-existing conditions |
History of vaping or e-cigarette use in the past 12 months |
Update 04/2020: Added new element.
Update 07/2020: Removed element. |
PCAC 3.1 Cardiac Arrest Event |
|
Update 4/2013: Added data element of Sustained Return of Spontanous Circulation (ROSC) achieved?
Update 4/2013: Added data element of For our-of-hospital events, ROSC attained?
Update 02/2023:
Added response option "DOB Unknown/Not Documented" to data element Date/Time of Birth.
Updated notes for abstraction for data element Date/Time of Birth.
Moved the note If the time is not documented select "Time Not Documented" to below response options for data element Date/Time of Birth.
Updated response options for data element Event Witnessed?
Moved the note If the time is not documented select "Time Not Documented" to below response options for data element Date/Time compression started.
Moved the note If the time is not documented select "Time Not Documented" to below response options for data element Date/Time sustained ROSC began (lasting > 20 min) OR resuscitation efforts were terminated (End of event).
|
PCAC 4.1 Arrival Information |
|
Update 4/2013: Added data element of Follows commands at time of initial assessment?
Update 12/2014:
Changed data element Initial Neurological Assessment? to Neurological Assessment performed within 1-hr of ROSC
Updated data element Initial Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) to Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) within 1-hr of ROSC? and moved element beneath Follows commands at time of initial assessment?
Moved Are pupils fixed and dilated element above Left pupil reaction
Removed the following data elements: Gag (under Neurological Assessment Findings:), Confounded (sedation/paralytic) exam, Sedation (within 1-hr of exam), Paralytic (within 1-hr of exam), and Other confounded exam
Update 02/2023:
Added descriptions to response options for data element Are pupils fixed and dilated
Added data element Status of patient (if not sedated/paralyzed)?
Added note to not complete "Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) within 1-hr of ROSC?" section if the patient is paralyzed.
Updated response options for data element Motor.
|
PCAC 4.2 Targeted Temperature Management |
|
Update 4/2013: Removed data elements of Was there ever a documented temperature of ≥ 37.5 degrees Celsius & If yes, when was a temperature of ≥ 37.5 degrees Celsius documented?
Update 4/2013: Added new data elements For All Patients of Was there ever a documented temperature of ≥ 38 degrees Celsius & If yes, when was a temperature of ≥ 38 degrees Celsius documented? & in patients with a fever, Was patient following commands at time of fever?
Update 12/2014:
Updated section name from PCAC 4.2 Cooling to PCAC 4.2 Targeted Temperature Management
Added data elements: Did you utilize targeted temperature management (TTM), and If yes, what was the targeted temperature (choose one)?, If targeted temperature was ≤36.0 degrees Celsius: Was goal temperature met?, If yes, Date/Time goal temperature met, Was there a documented temperature of ≤ 31.0 degrees Celsius 6 hours after the initiation of the temperature controlled period?
Updated the data element Cooling method (select all that apply) to Temperature control method (select all that apply); added new response options "Antipyretics" and "None"
Removed the following data elements: Was Active Cooling Initiated, and Treatment with induced hypothermia for a repeat event?, Was cooling initiated?, Was a temperature of ≤34.0 degrees Celsius met?, If yes, Date/Time a temperature of ≤34.0 degrees Celsius met, During the hypothermic period, was a temperature of above 34.5 degrees Celsius or a temperature below 32 degrees Celsius reached?
Replaced all references to "active cooling" with "targeted temperature management"
Replaced existing response options for data element Where was targeted temperature management initiated? with "Pre-hospital (by EMS)," "In-hospital (either at another hospital prior to transfer or in my hospital)," and "Unknown/Not documented"
Added 2 new reponse options for Clinical rationale documented by medical team why targeted temperature management was not initiated (check all that apply): "Facility does not routinely treat patients with targeted temperature management" and "Clinician preference"
Removed reponse options of "Day 4" and "Day 5 or after" for If yes, when was a temperature of ≥38 degrees Celsius documented? (Check all that apply)
Update 02/2023:
Updated data element Did you utilize targeted temperature management (TTM)? to Was targeted temperature management (TTM) utilized?, and updated the response options and Notes for Abstraction.
Added new data element Initial patient temp.
Updated response options and Notes for Abstraction for data element If yes, what was the targeted temperature (choose one)?.
Added new element Duration of continuous hypothermia.
Updated notes for data element Date/Time targeted temperature management initiated.
Updated response options for data element Clinical rationale documented by medical team why targeted temperature management was not initiated.
Updated response options and notes for data element If yes, when was a temperature of ≥38 degrees Celsius documented?.
Update 05/2023:
Updated Notes for Abstraction for element Was targeted temperature management (TTM) utilized?.
|
PCAC 5.1 Measurements and Medications |
|
Update 4/2013: Added data elements of Did patient receive any sedatives in the 0-6/6-24/24-48/48-72 hour time period post ROSC? & Did patient receive any paralytics in the /6-24/24-48/48-72 hour time period post ROSC?
Update 4/2013: Added data elements of: Were there at least two consecutive systolic blood pressure readings of <90mmHg separated by at least one hour in the first 0-6/6-24 hours post ROSC? & Select all vasopressors/inotropes patient was on during hours 0-6/6-24/24-48/48-72 post ROSC
Update 4/2013: Removed data elements of If Systolic BP <90mmHg or < 5th percentile <calculate in tool for pediatric patients> was patient on: Vasopressor/Inotrope or Vasodilator & Did patient receive and paralytics in th 0-72 hour time period post ROSC?
Update 12/2014:
Removed data elements: Sedation (within 1-hr), Paralytic (within 1-hr), Was there an SpO2 in the first 24 hours of <94% or >99%, If yes, FiO2 at time SpO2 assessed: (%), Calcium, Potassium, Date/Time of initial AST and ALT measurements (at your hospital), AST (U/L), ALT (U/L), Was there a PaO2 in the first 24 hours of >150mmHg, If yes, FiO2 at time PaO2 assessed(%)
Added data element: FiO2 at time SpO2 assessed: (%), Date/Time of initial Lactate
Update 02/2023:
Added new data element On invasive mechanical ventilator? |
| PCAC 5.1 Measurements and Medications |
Serial Measurements
Serial Blood Pressure Measurements |
Update 10/2013: Added a patient did not survive checkbox to each post ROSC time period
Update 02/2023:
Updated post ROSC time periods and notes for abstraction.
Added new element Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 0-6 hours post ROSC.
Added new element Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 6-12 hours post ROSC.
Added new element Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 12-24 hours post ROSC.
Added new element Was the patient on vasopressors/inotropes during the first 24-72 hours post ROSC. |
| PCAC 5.1 Measurements and Medications |
Initial Measurements |
Update 10/2018: Updated description for FiO2 at time SpO2 assessed: (%) |
| PCAC 5.2 Clinical Study Data |
|
Update 12/2014:
Updated response options for ECG interpretation; removed options "Sinus rhythm," "Heart block," and "Afib/flutter."
Removed Echo Studies Day 1-4 and RV Function sections
Updated response options for Head CT findings; removed options of "Evidence of hypoxic ischemia, "Subdural hematoma, "Ischemic stroke (either old or new)," and "Loss of Gray/White differentiation"
Added data elements: If EEG performed, was there evidence of any seizure activity, and If evidence of seizure activity, was their evidence of Status Epilepticus (sustained seizures)?
Removed data elements: Cerebral MRI findings (initial), Was it continuous or routine, Was there any evidence of Status Epilepticus, Electrographic seizures?
Removed the wording select all that apply from the data element Cath lab interventions
Update 02/2023:
Updated response options for data element Did patient go to the cath lab at any time during this admission?
Updated response options for data element Reason went to Cath lab.
Updated response options for data element Cath lab interventions.
Updated data element from ICD placed during this admission? to Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placed during this admission?
Updated response options for data element Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) placed during this admission?
Added section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only".
Added new element EEG (spot) performed within the first 24 hours post ROSC? to section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only".
Added new element If yes, Start Date/Time of EEG (spot) to section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only".
Added new element EEG (continuous) performed within the first 24 hours post ROSC? to section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only".
Added new element If yes, Start Date/Time of EEG (continuous) to section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only".
Added new element If yes, End Date/Time of EEG (continuous) to section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only".
Added new element Brain imaging (CT/MRI) performed within the first 5 days post ROSC? to section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only".
Added new element If yes, or at any point within 10 days, Date/Time of CT/MRI to section "For Comatose/Encephalopathic Patients Only". |
| PCAC Historic |
|
Update 02/2023: Added new section and moved retired PCAC elements to this section. |
| IHCA Site Characteristics |
|
Update 10/2018: Added new section |
NOT FOR USE WITHOUT PERMISSION - CONFIDENTIAL AND PROPRIETARY INFORMATION OF QUINTILES AND THE AMERICAN HEART
ASSOCIATION, INC.